Welcome to DU!
The truly grassroots left-of-center political community where regular people, not algorithms, drive the discussions and set the standards.
Join the community:
Create a free account
Support DU (and get rid of ads!):
Become a Star Member
Latest Breaking News
General Discussion
The DU Lounge
All Forums
Issue Forums
Culture Forums
Alliance Forums
Region Forums
Support Forums
Help & Search
Celerity
Celerity's Journal
Celerity's Journal
September 21, 2023

A new report shows that Amazon now takes 45 percent of all third-party sales on its website, part of the company’s goal to become a monopoly gatekeeper for economic transactions.
https://prospect.org/power/2023-09-21-amazons-185-billion-pay-to-play-system/

Amazon now takes 45 cents in fees out of every dollar of third-party sales at its marketplace, according to updated statistics in a new report from the Institute for Local Self-Reliance. The e-commerce giant’s extraction from third-party sales revenue was just 19 percent in 2014. It grew to 27 percent in 2017, 35 percent in 2020, and reached 45 percent this year, according to ILSR’s figures. This has imposed significant pressure on sellers’ ability to make a profit, and is contributing to inflation woes as fees get passed on to customers in the form of higher prices. Overall, Amazon is projected to make $185 billion in fees from third-party sellers in 2023: $125 billion from U.S. third-party sellers and another $60 billion from foreign-market businesses and vendor ads. In 2014, that number was $13 billion. Put another way, in nine years, Amazon has increased its fee revenue 14-fold.
The fees far exceed Amazon’s costs. For example, Amazon has already made $82 billion in fees from domestic and foreign third-party sellers in the first half of 2023, enough to cover all of its fulfillment facilities, which ship products sold by both third-party sellers and Amazon itself. “In other words, Amazon doesn’t have to build warehousing and shipping costs into the price of its own products, because it’s found a way to get smaller online sellers to pay those costs,” writes Stacy Mitchell, ILSR’s co-executive director and author of the report. In this sense, the third-party seller fees subsidize the below-cost sales that allow Amazon to drive competitors out of the market. ILSR’s updated numbers are roughly in line with other analyses like that of Marketplace Pulse, which estimated earlier this year that nearly 52 percent of third-party seller revenue is captured by Amazon.
Third-party seller exploitation is likely to be a major facet of the Federal Trade Commission’s antitrust case against Amazon, which is expected to be filed soon. The reason that third-party sellers don’t just leave the platform, given this abuse, is that Amazon has grabbed so much control of online commerce that these sellers can’t just bypass it. “Amazon’s dominance of online retail means that businesses that make or sell products have little choice but to rely on its site to reach customers,” ILSR writes. Most third-party businesses on Amazon don’t survive, in fact, at least not ones based in the U.S. Of the top 10,000 sellers on the site, more than half are based in China, according to data from Marketplace Pulse.

Amazon fees on third-party sellers fall into three main buckets: referral fees, advertising fees, and fulfillment fees. The referral fee is a straight off-the-top commission for the privilege of selling on Amazon, and that totals 15 percent for most products. Advertising and fulfillment have been the growth areas for Amazon. Advertising fees do not come from what most laymen would think of as traditional advertising. Much of it comes in the form of businesses paying to list products in Amazon’s search results under labels like “highly rated” (which often have nothing to do with the rating of the products). As with Google, those who get the visible space at the top of search listings are paying for it; those who do not are pushed to the bottom of search, typically unseen by customers. Because Amazon’s organic search “favors products with more sales,” ILSR writes, paying for search ads that boost sales increases a business’s listing in organic search as well. Referral and search ad fees combined have increased by almost 50 percent since 2017.
snip
Amazon's $185 Billion Pay-to-Play System

A new report shows that Amazon now takes 45 percent of all third-party sales on its website, part of the company’s goal to become a monopoly gatekeeper for economic transactions.
https://prospect.org/power/2023-09-21-amazons-185-billion-pay-to-play-system/

Amazon now takes 45 cents in fees out of every dollar of third-party sales at its marketplace, according to updated statistics in a new report from the Institute for Local Self-Reliance. The e-commerce giant’s extraction from third-party sales revenue was just 19 percent in 2014. It grew to 27 percent in 2017, 35 percent in 2020, and reached 45 percent this year, according to ILSR’s figures. This has imposed significant pressure on sellers’ ability to make a profit, and is contributing to inflation woes as fees get passed on to customers in the form of higher prices. Overall, Amazon is projected to make $185 billion in fees from third-party sellers in 2023: $125 billion from U.S. third-party sellers and another $60 billion from foreign-market businesses and vendor ads. In 2014, that number was $13 billion. Put another way, in nine years, Amazon has increased its fee revenue 14-fold.
The fees far exceed Amazon’s costs. For example, Amazon has already made $82 billion in fees from domestic and foreign third-party sellers in the first half of 2023, enough to cover all of its fulfillment facilities, which ship products sold by both third-party sellers and Amazon itself. “In other words, Amazon doesn’t have to build warehousing and shipping costs into the price of its own products, because it’s found a way to get smaller online sellers to pay those costs,” writes Stacy Mitchell, ILSR’s co-executive director and author of the report. In this sense, the third-party seller fees subsidize the below-cost sales that allow Amazon to drive competitors out of the market. ILSR’s updated numbers are roughly in line with other analyses like that of Marketplace Pulse, which estimated earlier this year that nearly 52 percent of third-party seller revenue is captured by Amazon.
Third-party seller exploitation is likely to be a major facet of the Federal Trade Commission’s antitrust case against Amazon, which is expected to be filed soon. The reason that third-party sellers don’t just leave the platform, given this abuse, is that Amazon has grabbed so much control of online commerce that these sellers can’t just bypass it. “Amazon’s dominance of online retail means that businesses that make or sell products have little choice but to rely on its site to reach customers,” ILSR writes. Most third-party businesses on Amazon don’t survive, in fact, at least not ones based in the U.S. Of the top 10,000 sellers on the site, more than half are based in China, according to data from Marketplace Pulse.

Amazon fees on third-party sellers fall into three main buckets: referral fees, advertising fees, and fulfillment fees. The referral fee is a straight off-the-top commission for the privilege of selling on Amazon, and that totals 15 percent for most products. Advertising and fulfillment have been the growth areas for Amazon. Advertising fees do not come from what most laymen would think of as traditional advertising. Much of it comes in the form of businesses paying to list products in Amazon’s search results under labels like “highly rated” (which often have nothing to do with the rating of the products). As with Google, those who get the visible space at the top of search listings are paying for it; those who do not are pushed to the bottom of search, typically unseen by customers. Because Amazon’s organic search “favors products with more sales,” ILSR writes, paying for search ads that boost sales increases a business’s listing in organic search as well. Referral and search ad fees combined have increased by almost 50 percent since 2017.
snip
September 21, 2023

Today on TAP: Commentators argue that the union is asking for too much. But a big win may help the UAW organize the non-union competition.
https://prospect.org/labor/2023-09-21-punditocracy-vs-the-uaw/

Yesterday, what we might politely term the non-labor wing of the Democratic punditocracy weighed in on the UAW strike against GM, Ford, and Stellantis. They didn’t like it. To be sure, both Washington Post columnist Catherine Rampell and investment banker and Obama 2009 auto bailout czar Steven Rattner, writing in The New York Times, acknowledged that the union’s wage demands were basically just, and that Big Three companies should have long since mitigated some of the concessions (like the creation of a lower-paid tier of workers) that the union agreed to make when the companies faced bankruptcy in 2009. They conceded that the gap between the companies’ CEO pay and median worker pay had risen to obscene levels, and, in sum, that the workers had every right to be very angry at their employers, who’d been making record profits in recent years.
And yet, both charged that the union was asking for way too much, such as the restoration of the yearly cost-of-living adjustments and defined-benefit pensions that the UAW, under Walter Reuther’s leadership, had won in 1950. The problem, they said, was that actions like these would render the Big Three woefully uncompetitive with the non-union auto plants in the South, the low-wage auto plants in Mexico, and Elon Musk’s non-union Tesla factory in California and battery factory in Nevada.
The psychopathically anti-union Wall Street Journal went further than that yesterday, with two articles comparing the productivity and cost of American workers unfavorably to the productivity and cost of workers (and robots) in East Asia, most particularly in China. As the Journal was the leading editorial voice demanding that the U.S. establish permanent normal trade relations with China back in the 1990s, the fact that the U.S.-China wage differential is an issue at all should really be laid at the Journal’s door. Causing this problem wasn’t bad enough, apparently; now they have the chutzpah to bemoan it.
But the complaint common to all these arguments is accurate as far as it goes. It’s indisputable that adopting even just some of the wage and benefit proposals the union is putting forth will widen the current gap between, say, what GM workers make, and the life that enables them to live, and what Tesla workers make, and the life that compels them to endure. The question is whether the contracts the UAW will win will lead to the rest of the industry leveling wages and working conditions up, or whether the labor standards in China, Alabama, and Elonland will level wages and working conditions down. The combination of a big UAW win and the new organizing rules promulgated by the National Labor Relations Board might just enable the union to organize some of those lower-wage plants, or at least compel them to raise wages and benefits to fend off the union’s campaigns.
snip
The Punditocracy vs. the UAW

Today on TAP: Commentators argue that the union is asking for too much. But a big win may help the UAW organize the non-union competition.
https://prospect.org/labor/2023-09-21-punditocracy-vs-the-uaw/

Yesterday, what we might politely term the non-labor wing of the Democratic punditocracy weighed in on the UAW strike against GM, Ford, and Stellantis. They didn’t like it. To be sure, both Washington Post columnist Catherine Rampell and investment banker and Obama 2009 auto bailout czar Steven Rattner, writing in The New York Times, acknowledged that the union’s wage demands were basically just, and that Big Three companies should have long since mitigated some of the concessions (like the creation of a lower-paid tier of workers) that the union agreed to make when the companies faced bankruptcy in 2009. They conceded that the gap between the companies’ CEO pay and median worker pay had risen to obscene levels, and, in sum, that the workers had every right to be very angry at their employers, who’d been making record profits in recent years.
And yet, both charged that the union was asking for way too much, such as the restoration of the yearly cost-of-living adjustments and defined-benefit pensions that the UAW, under Walter Reuther’s leadership, had won in 1950. The problem, they said, was that actions like these would render the Big Three woefully uncompetitive with the non-union auto plants in the South, the low-wage auto plants in Mexico, and Elon Musk’s non-union Tesla factory in California and battery factory in Nevada.
The psychopathically anti-union Wall Street Journal went further than that yesterday, with two articles comparing the productivity and cost of American workers unfavorably to the productivity and cost of workers (and robots) in East Asia, most particularly in China. As the Journal was the leading editorial voice demanding that the U.S. establish permanent normal trade relations with China back in the 1990s, the fact that the U.S.-China wage differential is an issue at all should really be laid at the Journal’s door. Causing this problem wasn’t bad enough, apparently; now they have the chutzpah to bemoan it.
But the complaint common to all these arguments is accurate as far as it goes. It’s indisputable that adopting even just some of the wage and benefit proposals the union is putting forth will widen the current gap between, say, what GM workers make, and the life that enables them to live, and what Tesla workers make, and the life that compels them to endure. The question is whether the contracts the UAW will win will lead to the rest of the industry leveling wages and working conditions up, or whether the labor standards in China, Alabama, and Elonland will level wages and working conditions down. The combination of a big UAW win and the new organizing rules promulgated by the National Labor Relations Board might just enable the union to organize some of those lower-wage plants, or at least compel them to raise wages and benefits to fend off the union’s campaigns.
snip
September 21, 2023

The White House says there should be no negotiating over an oncoming government shutdown.
https://prospect.org/politics/2023-09-21-biden-has-right-idea-freedom-caucus/

America is staring down the barrel of yet another Republican-imposed government shutdown—the 21st in history. As my colleague David Dayen writes, this wasn’t supposed to happen. The debt ceiling deal from a few months ago included an agreement on what the budget should look like next year. But the Freedom Caucus—a couple dozen of the most extremist right-wing House Republicans—has forced the GOP to renege on the deal. The reason, it seems, is that they are incoherently mad at President Biden and the Democratic Party. They can’t agree on what specifically they want, whether it’s defunding the prosecution of Donald Trump, or extracting even more cuts from federal agencies, or a personal baby seal club for every Republican voter, or what. A purely messaging budget resolution that would have funded the government for just one month in exchange for deep spending cuts just went down in flames. But one thing is clear: The Freedom Caucus is extremely mad.
Luckily, President Biden has the right idea: letting House Republicans twist in the wind. Now, I thought it was the wrong move to negotiate with Republicans over the debt ceiling, though Biden ended up getting a much more favorable deal than I had expected. But since that deal was done, how else to approach a party that can’t hold up its own end of a bargain? In the past, the Democrats have been less willing to stand up for themselves. Back in 2011, for instance, President Obama decided to try to negotiate a deficit reduction deal by offering up hundreds of billions of dollars in cuts to Social Security and Medicare in return for Republicans raising the debt ceiling. Those cuts were thankfully avoided only because the Freedom Caucus refused to countenance even a token tax increase on the rich.
Or consider a stipulation of the House GOP budget resolution that just went down in flames due to the caucus’s mad rage: the creation of a bipartisan commission to come up with suggestions to cut the budget deficit. The real purpose of a commission like this is to try to shove through large cuts to Social Security and Medicare to make budget headroom for tax cuts for the rich, which is so unpopular that it could never be passed through the ordinary legislative process. We know this thanks to the Bowles-Simpson deficit reduction commission, created by an executive order from none other than President Obama back in February 2010. The commission produced a report whose very first recommendation was, sure enough, a large tax cut for the rich (though it did not get support from all the commission members). These days, by contrast, the Biden administration calls such an idea a “death panel” for Social Security. The Democrats really have wised up on this question.
As an aside, it is quite remarkable how argument-proof this demand for starving grandma is to all available evidence, at least on the right. The endless growth in Medicare spending, which is by far the largest driver of projections showing massive deficit increases over the long term, has actually leveled off over the last decade or so—saving about $3.6 trillion since 2011 relative to the prior spending trajectory. As The New York Times reports, nobody is quite sure why it happened. But Republicans don’t seem to have even noticed. For them, starving grandma is an end in itself. Structurally speaking, the basic problem here is that the U.S. constitutional structure requires compromise during times of divided government, but a critical mass of Republicans are simply too crazy to negotiate. Whereas in a parliamentary system, the majority has the full run of government, and hence there is no need to get opposition buy-in for anything, in our archaic system, we do. So when one party goes nuts, the government tends to get shut down all the time.
snip
Biden Has the Right Idea About the Freedom Caucus

The White House says there should be no negotiating over an oncoming government shutdown.
https://prospect.org/politics/2023-09-21-biden-has-right-idea-freedom-caucus/

America is staring down the barrel of yet another Republican-imposed government shutdown—the 21st in history. As my colleague David Dayen writes, this wasn’t supposed to happen. The debt ceiling deal from a few months ago included an agreement on what the budget should look like next year. But the Freedom Caucus—a couple dozen of the most extremist right-wing House Republicans—has forced the GOP to renege on the deal. The reason, it seems, is that they are incoherently mad at President Biden and the Democratic Party. They can’t agree on what specifically they want, whether it’s defunding the prosecution of Donald Trump, or extracting even more cuts from federal agencies, or a personal baby seal club for every Republican voter, or what. A purely messaging budget resolution that would have funded the government for just one month in exchange for deep spending cuts just went down in flames. But one thing is clear: The Freedom Caucus is extremely mad.
Luckily, President Biden has the right idea: letting House Republicans twist in the wind. Now, I thought it was the wrong move to negotiate with Republicans over the debt ceiling, though Biden ended up getting a much more favorable deal than I had expected. But since that deal was done, how else to approach a party that can’t hold up its own end of a bargain? In the past, the Democrats have been less willing to stand up for themselves. Back in 2011, for instance, President Obama decided to try to negotiate a deficit reduction deal by offering up hundreds of billions of dollars in cuts to Social Security and Medicare in return for Republicans raising the debt ceiling. Those cuts were thankfully avoided only because the Freedom Caucus refused to countenance even a token tax increase on the rich.
Or consider a stipulation of the House GOP budget resolution that just went down in flames due to the caucus’s mad rage: the creation of a bipartisan commission to come up with suggestions to cut the budget deficit. The real purpose of a commission like this is to try to shove through large cuts to Social Security and Medicare to make budget headroom for tax cuts for the rich, which is so unpopular that it could never be passed through the ordinary legislative process. We know this thanks to the Bowles-Simpson deficit reduction commission, created by an executive order from none other than President Obama back in February 2010. The commission produced a report whose very first recommendation was, sure enough, a large tax cut for the rich (though it did not get support from all the commission members). These days, by contrast, the Biden administration calls such an idea a “death panel” for Social Security. The Democrats really have wised up on this question.
As an aside, it is quite remarkable how argument-proof this demand for starving grandma is to all available evidence, at least on the right. The endless growth in Medicare spending, which is by far the largest driver of projections showing massive deficit increases over the long term, has actually leveled off over the last decade or so—saving about $3.6 trillion since 2011 relative to the prior spending trajectory. As The New York Times reports, nobody is quite sure why it happened. But Republicans don’t seem to have even noticed. For them, starving grandma is an end in itself. Structurally speaking, the basic problem here is that the U.S. constitutional structure requires compromise during times of divided government, but a critical mass of Republicans are simply too crazy to negotiate. Whereas in a parliamentary system, the majority has the full run of government, and hence there is no need to get opposition buy-in for anything, in our archaic system, we do. So when one party goes nuts, the government tends to get shut down all the time.
snip
September 21, 2023
https://www.dezeen.com/2023/09/18/spridd-t-shaped-house-stockholm-residential-architecture/
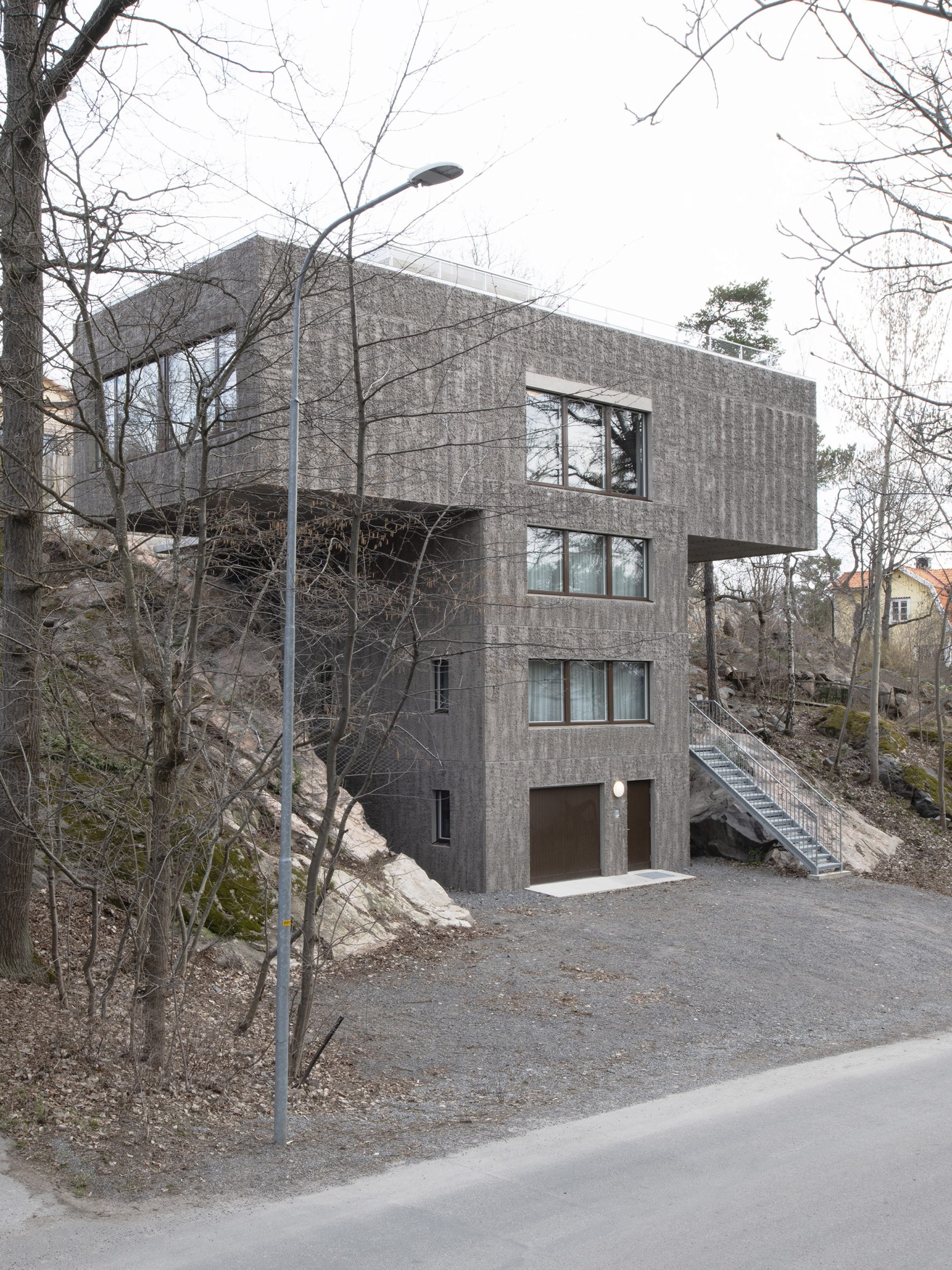
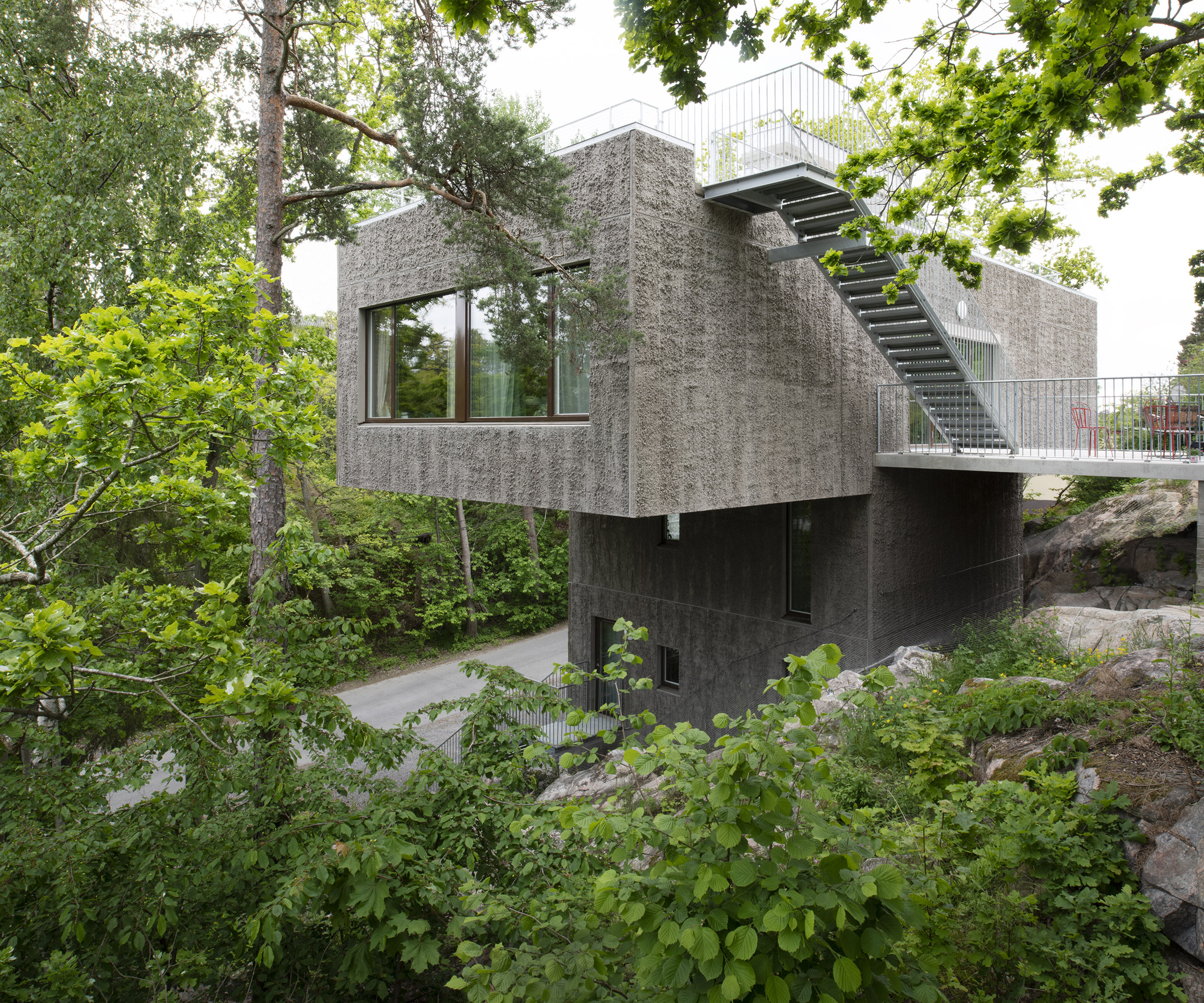



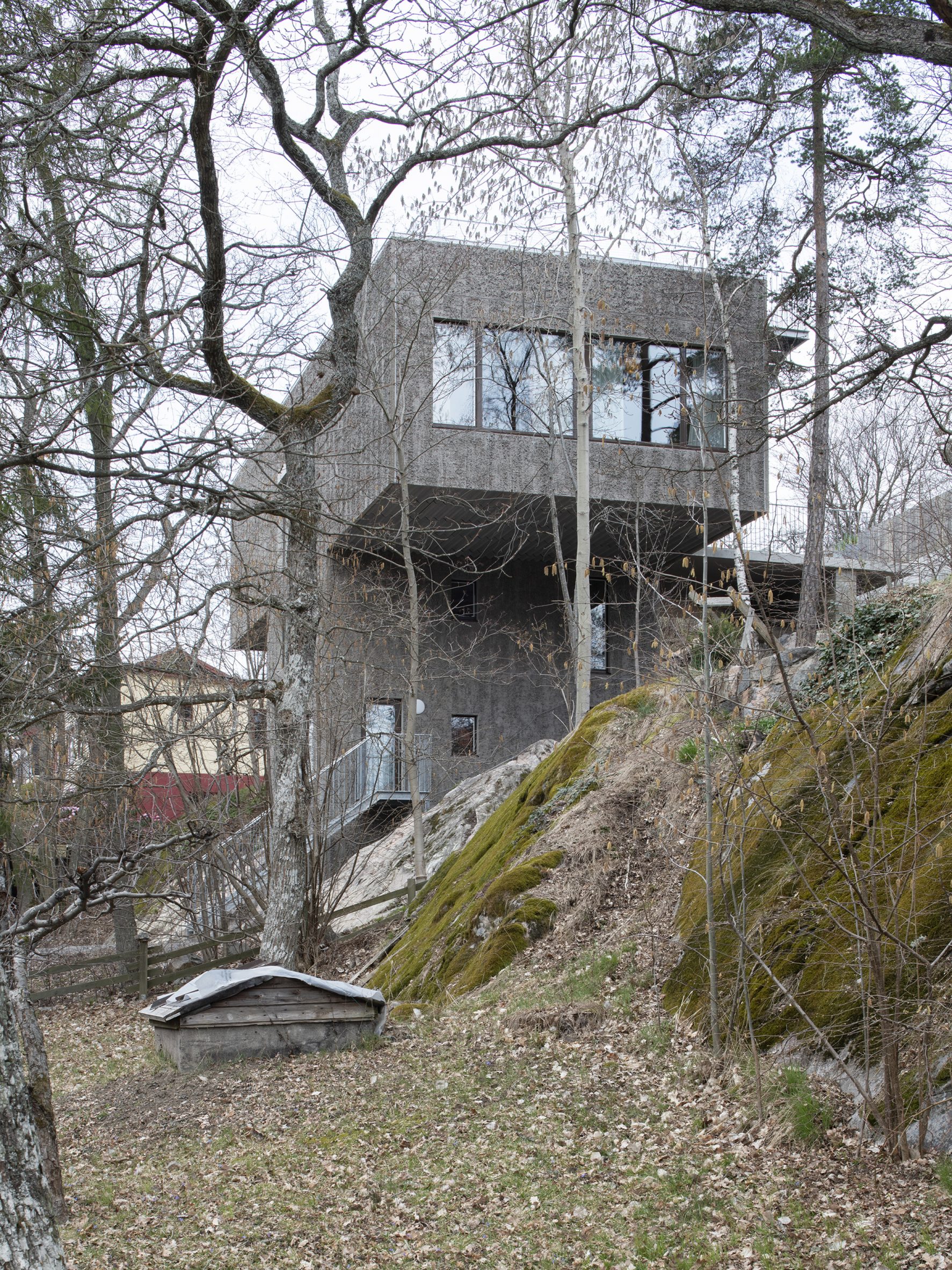
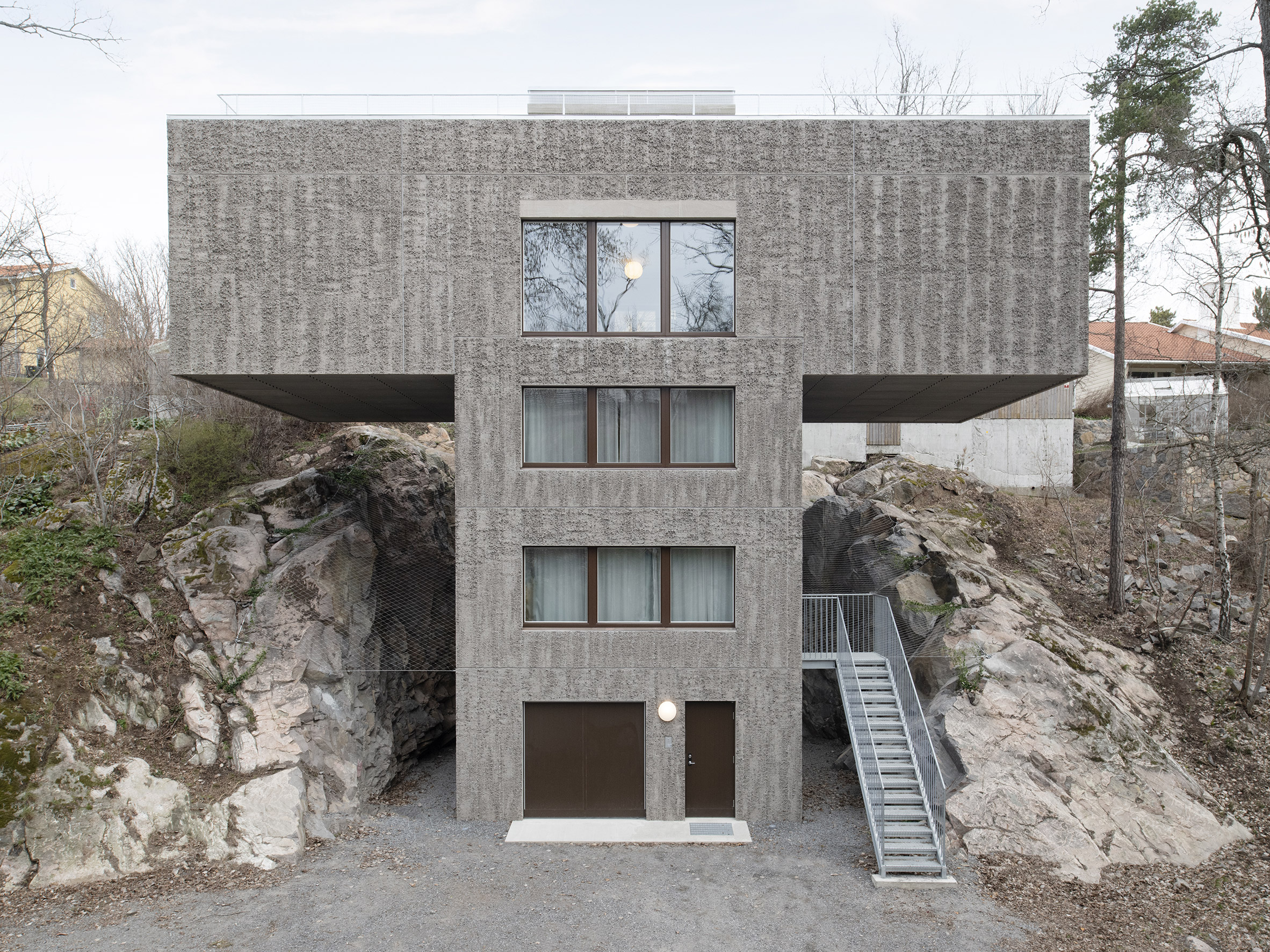
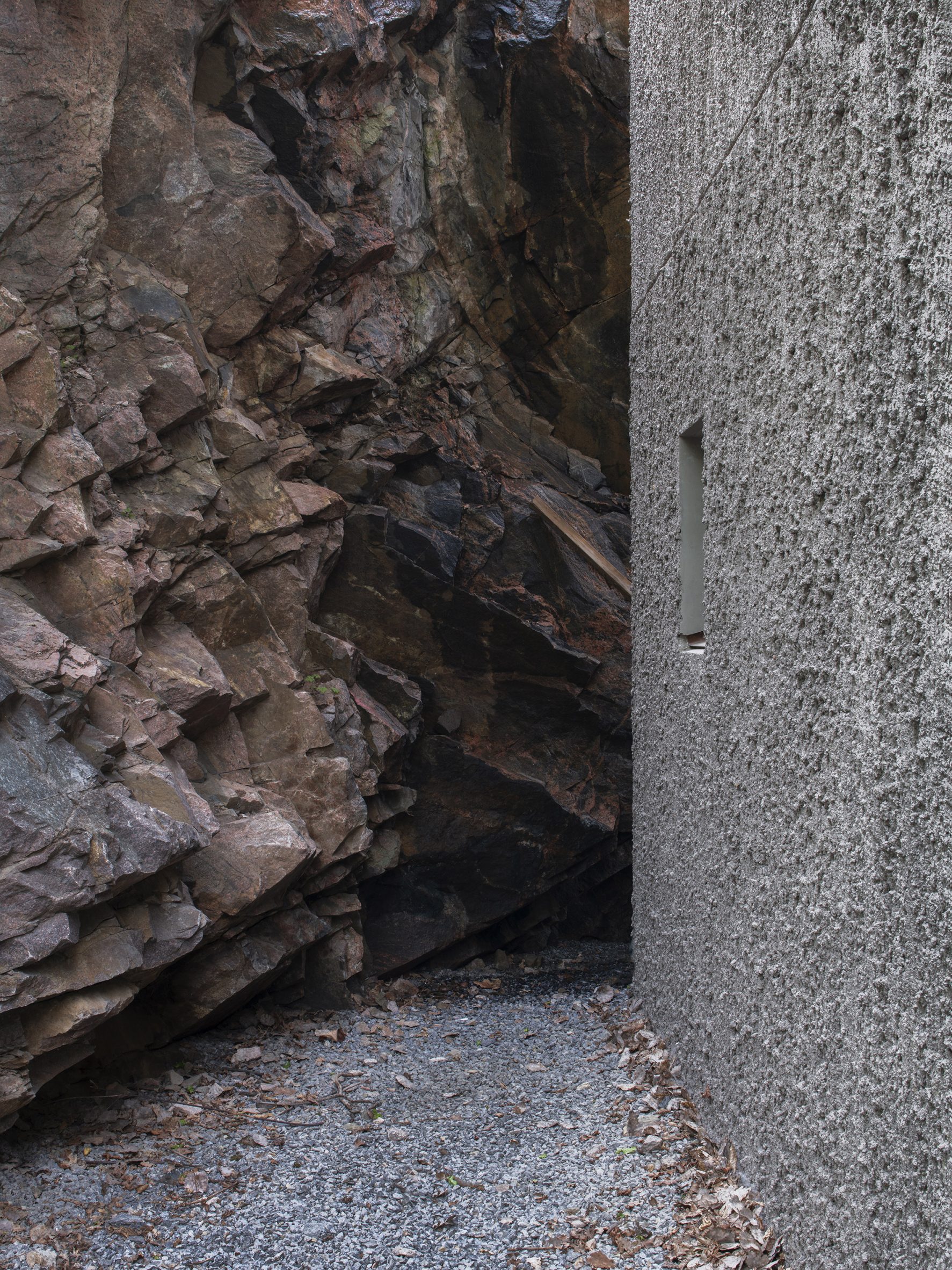
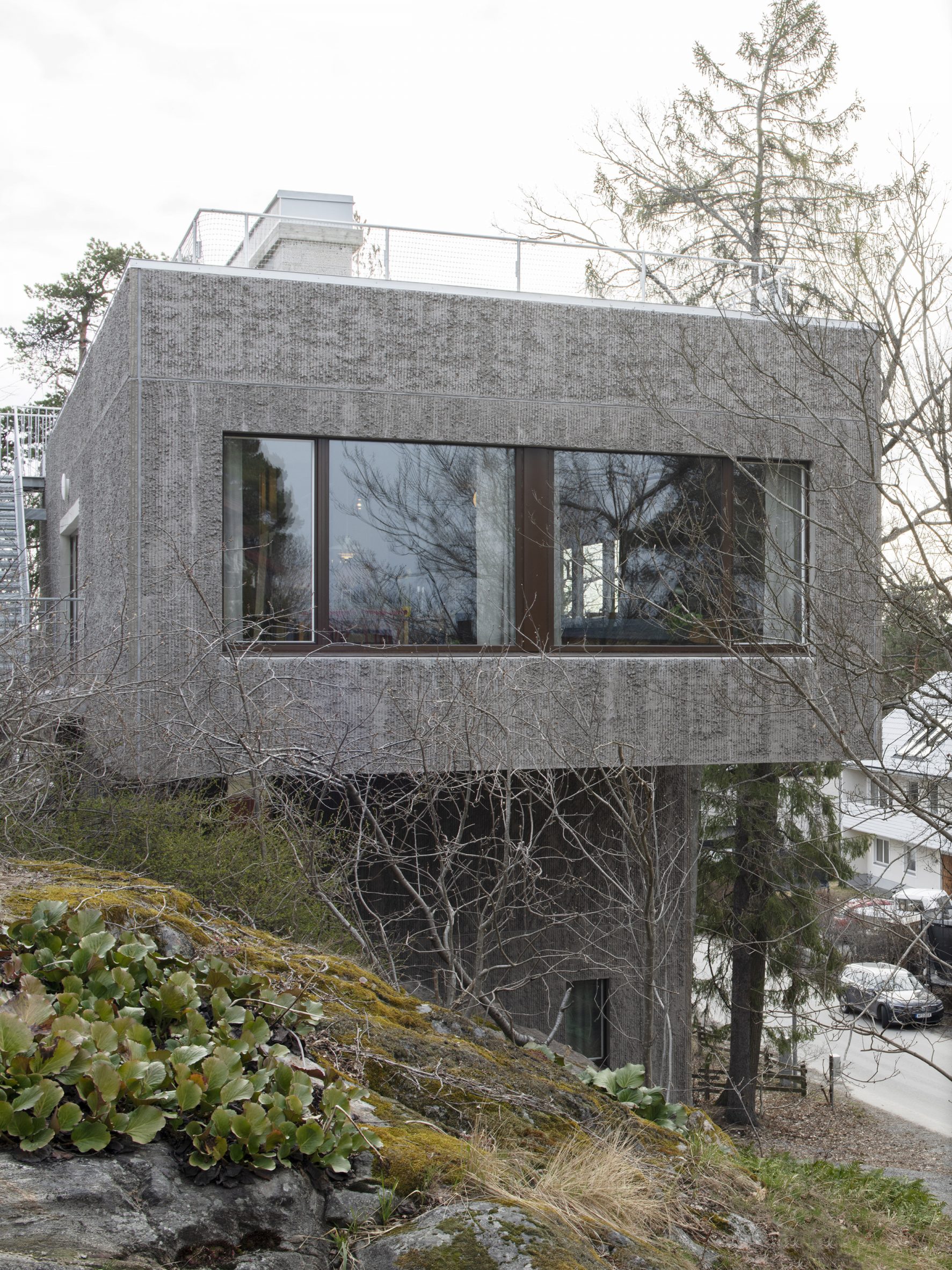
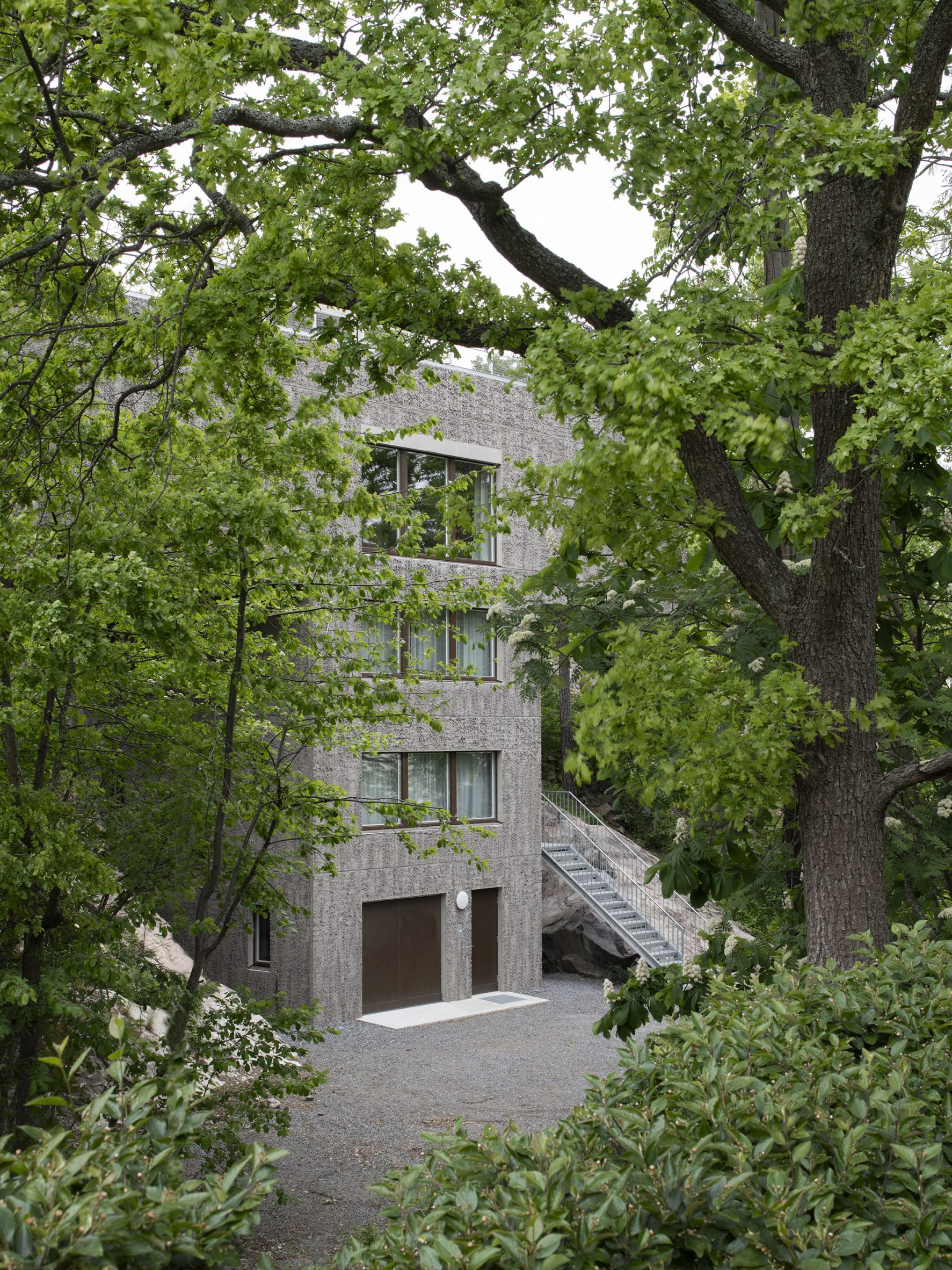
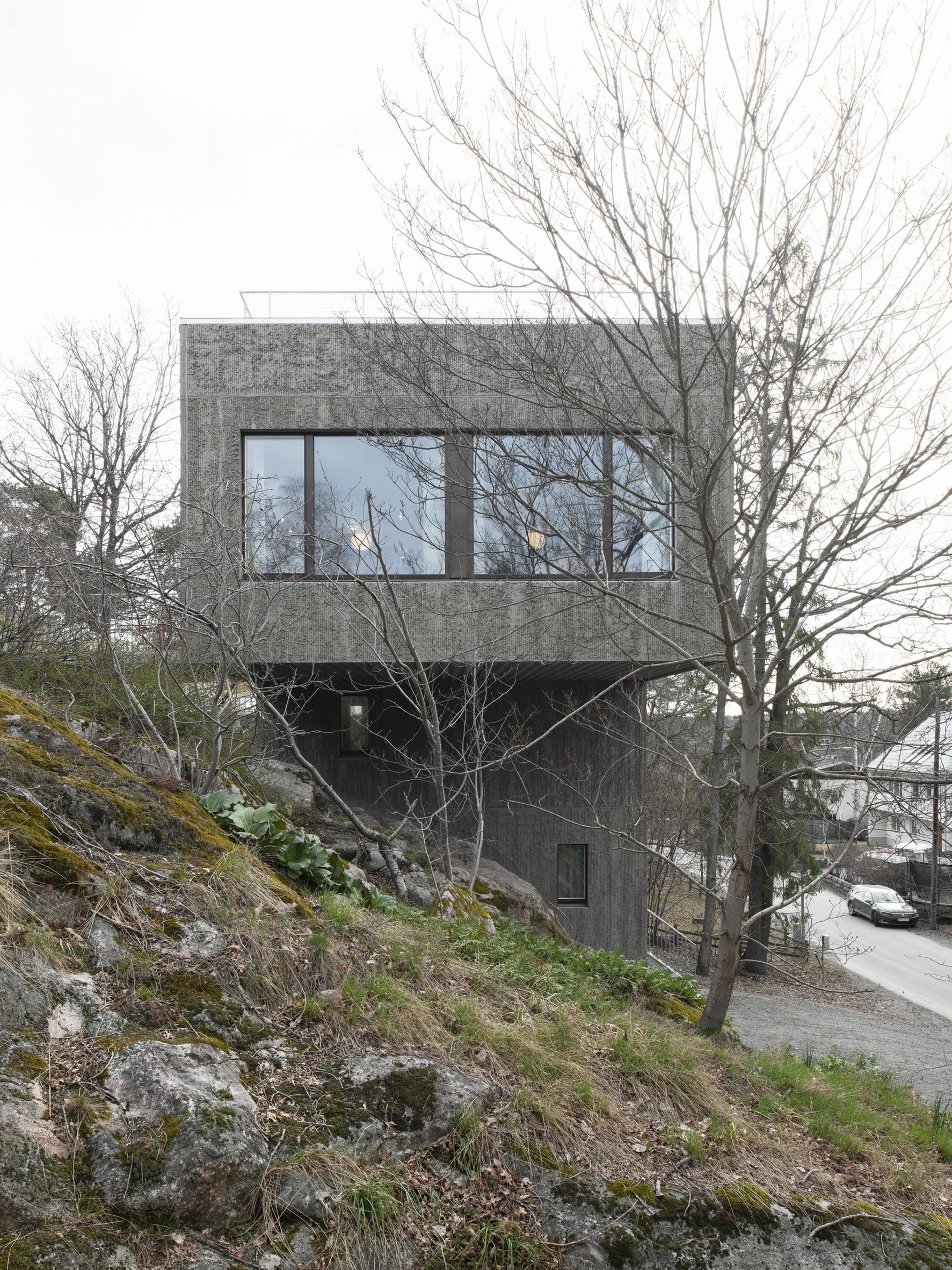
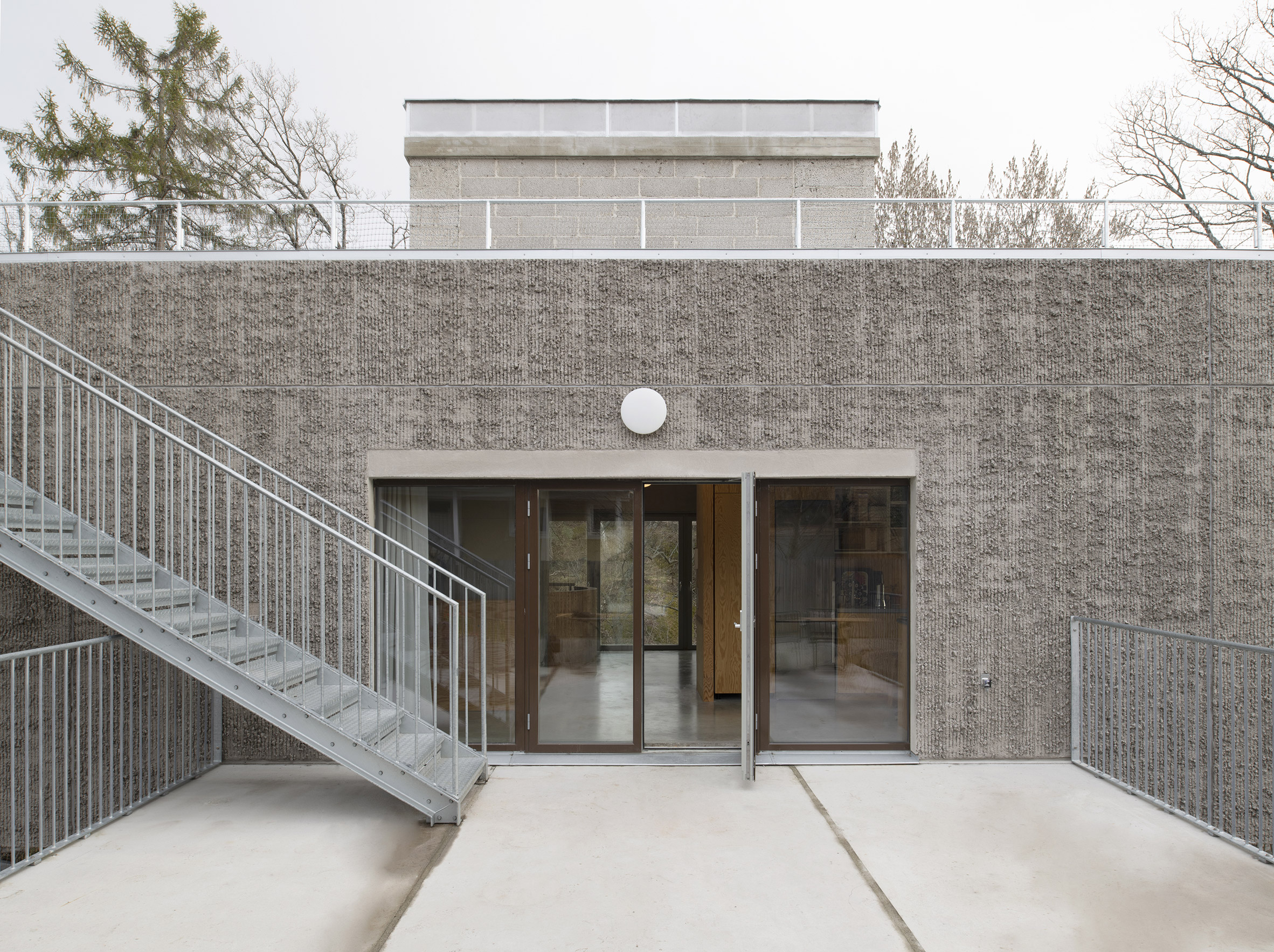
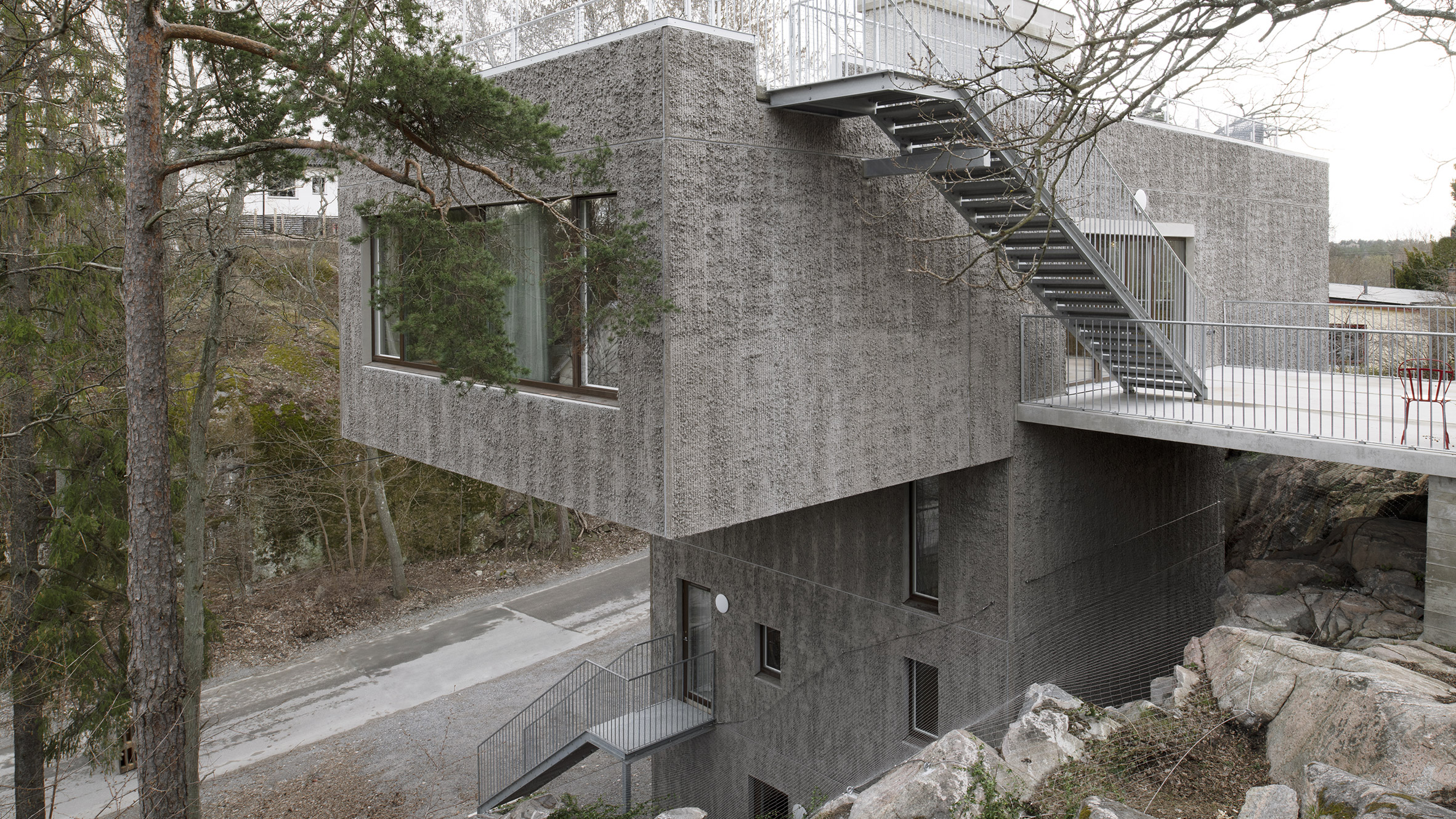
Raked concrete covers this T-shaped house, which architecture studio Spridd has slotted into a sloped site surrounded by trees on the island of Nacka in Stockholm. Appropriately called T House, the home was created by Spridd for a family, along with a separate guest apartment for an elderly relative.



To minimise excavation of the steeply sloping, south-facing plot, the studio designed a narrow central body for the house that slots between rocks. It expands outwards at its top storey, forming two cantilevered volumes that accommodate a generous open-plan living space. "The T-shape enables a minimal excavation as it only requires a small foundation at the bottom," Spridd told Dezeen. "The shape also provides an advantageous symmetry in the structure which stands independent of itself without attachment to the bedrock."
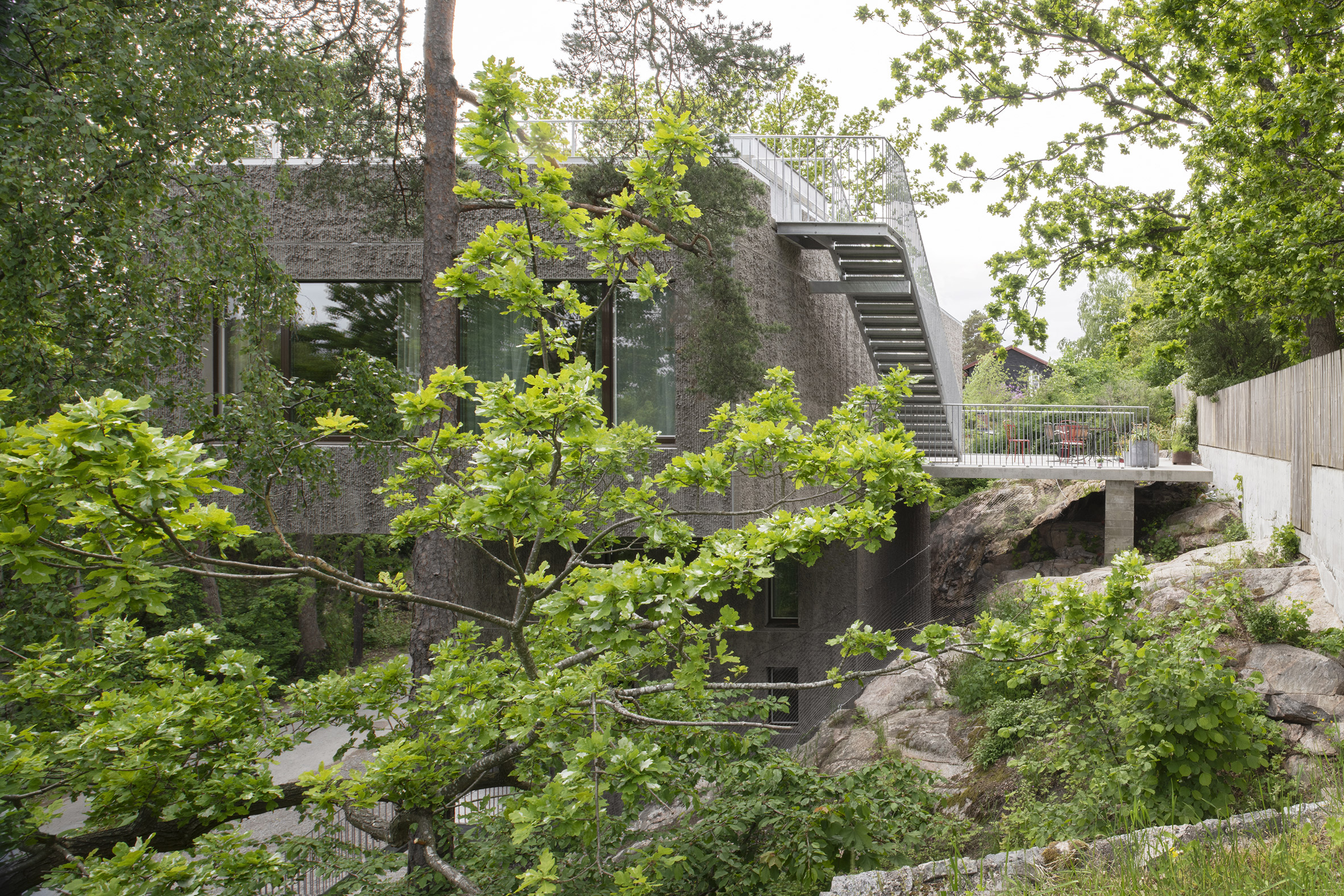


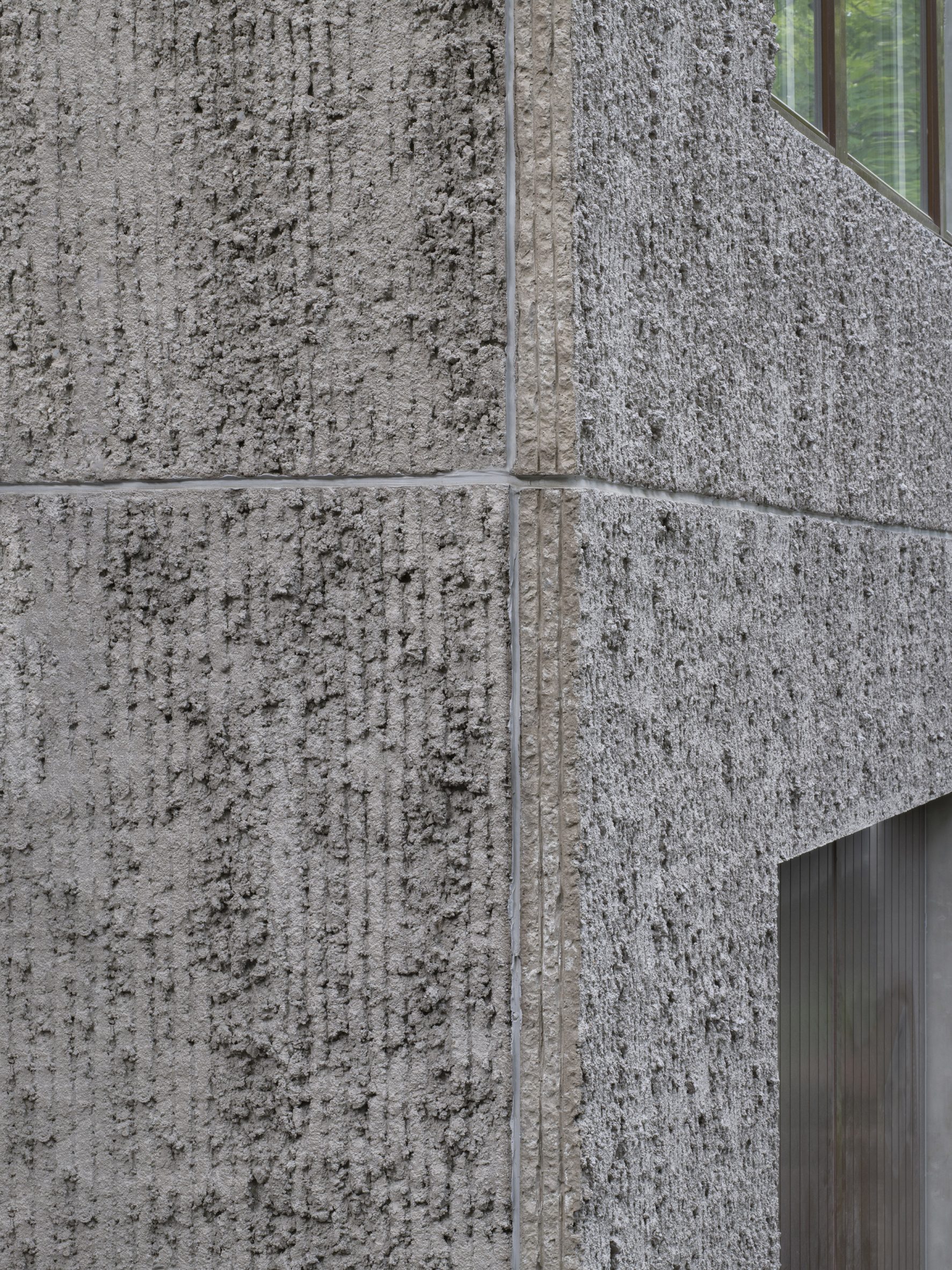
T House is constructed from prefabricated sandwich panels covered with concrete. Inside, the panels have a smooth finish while a raked treatment was manually applied externally. The raked-concrete facades ensure the house is in dialogue with the textures of the rocky cliffside site and the bark of the surrounding trees. Externally, brown-framed ribbon windows on the south, east and west facades give the home a modernist feel.
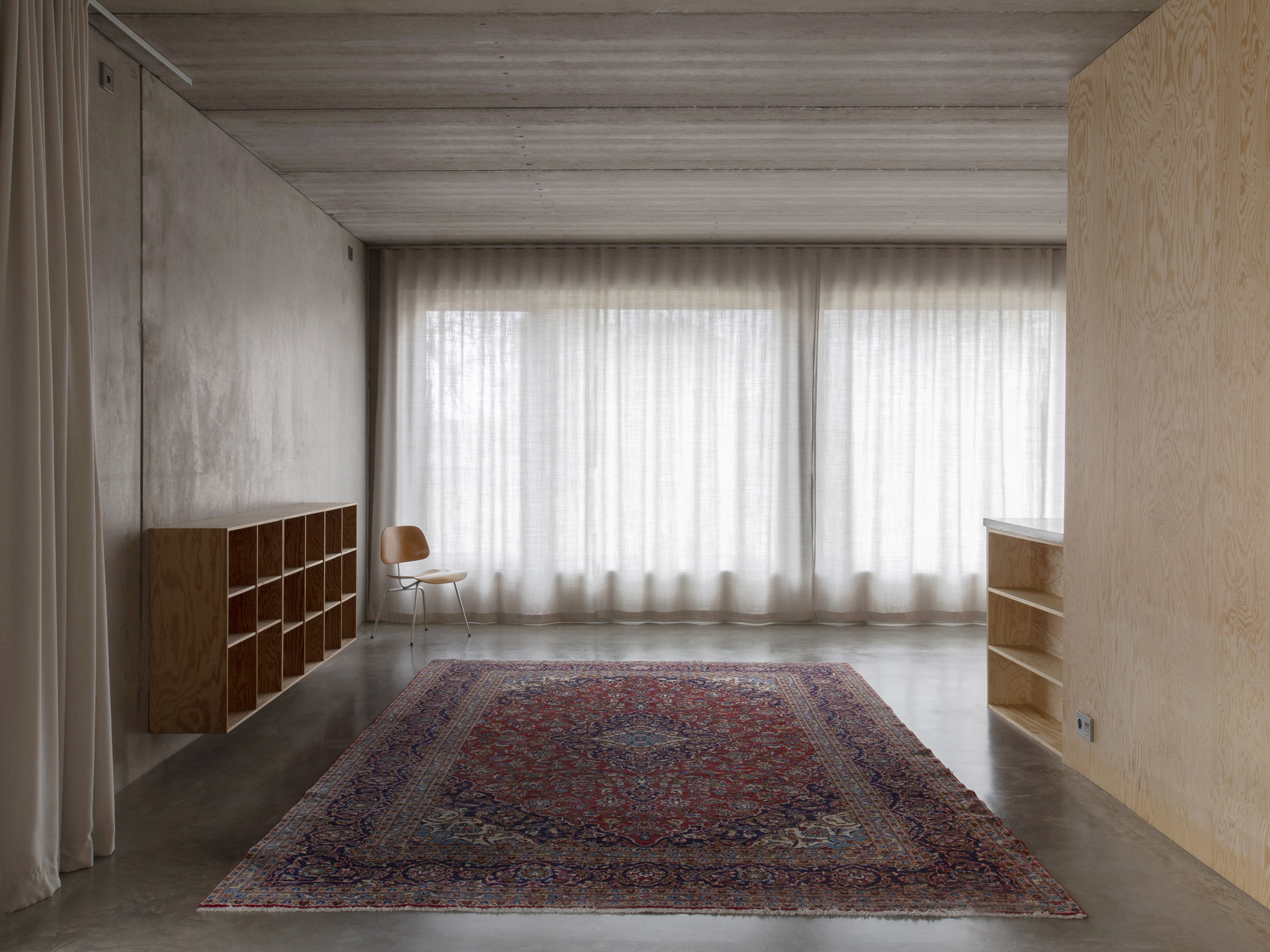



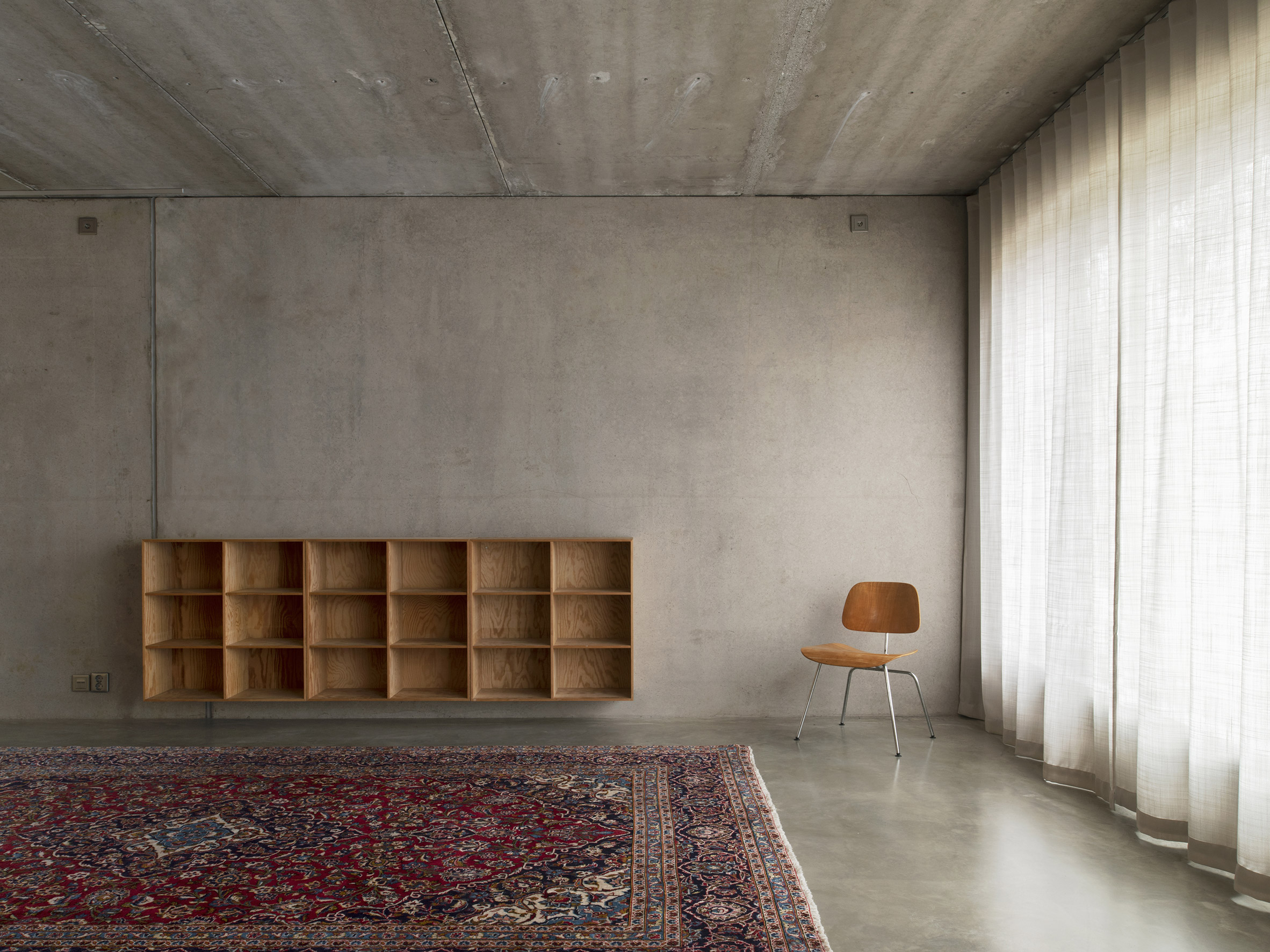
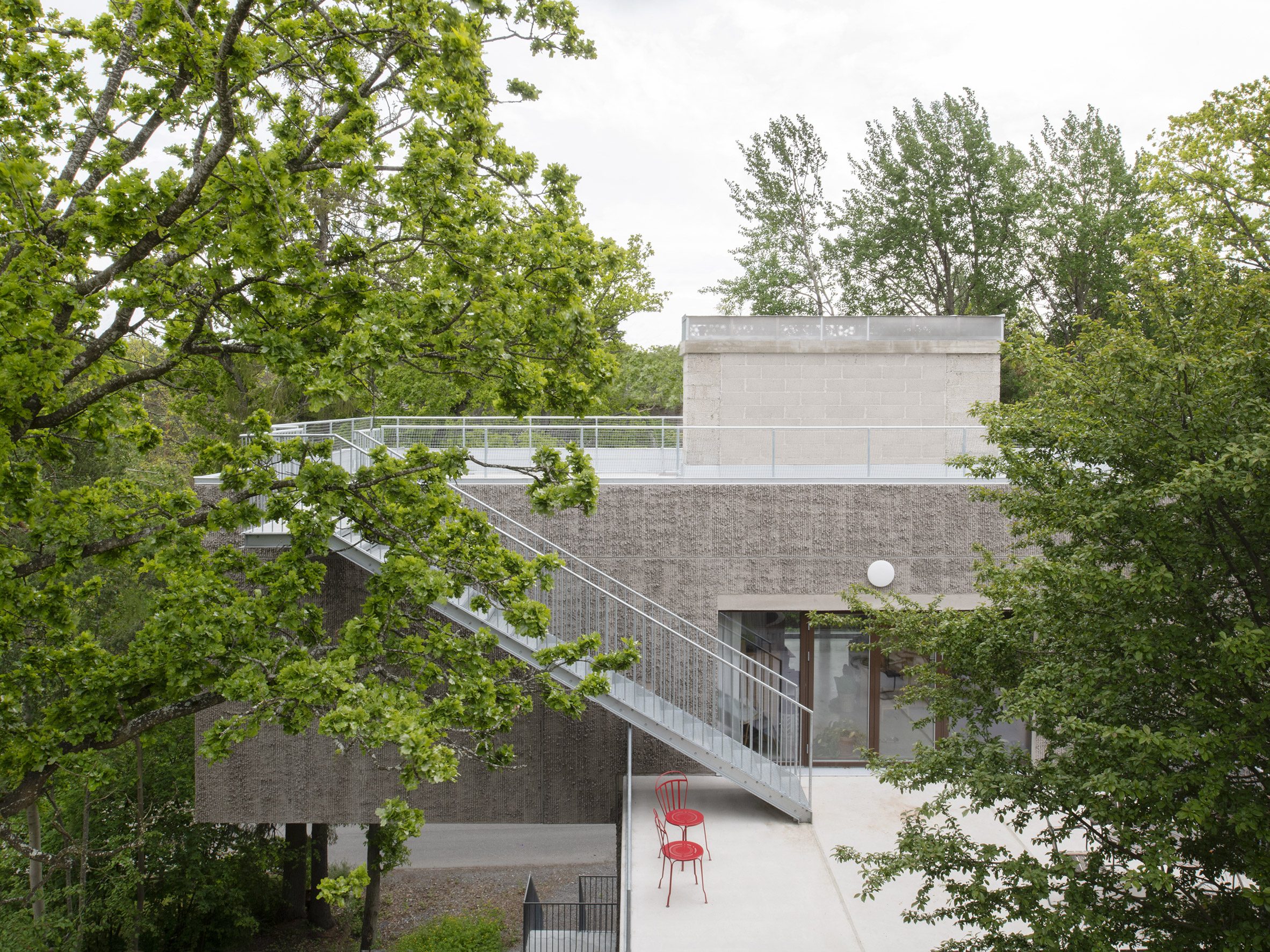
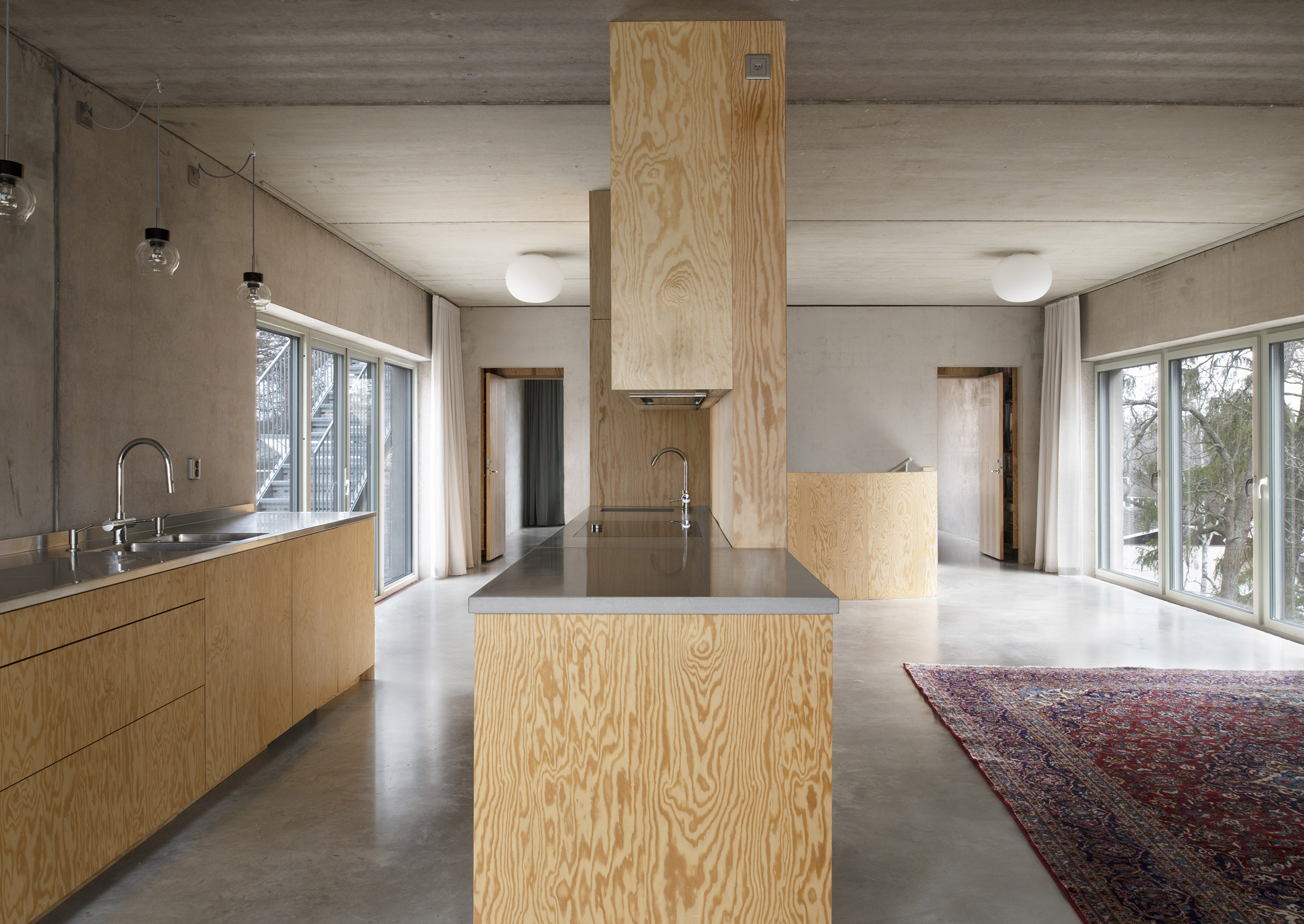
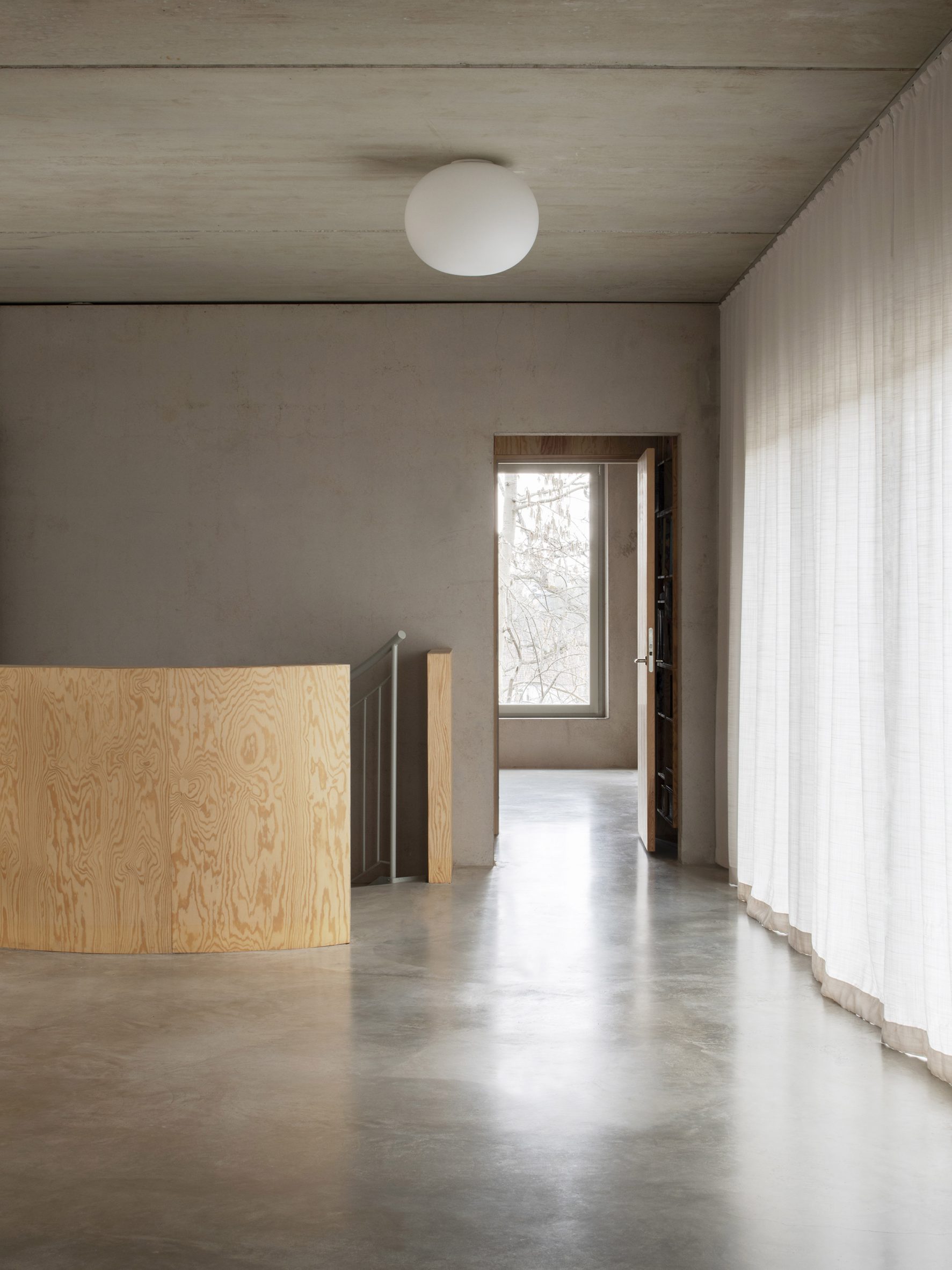
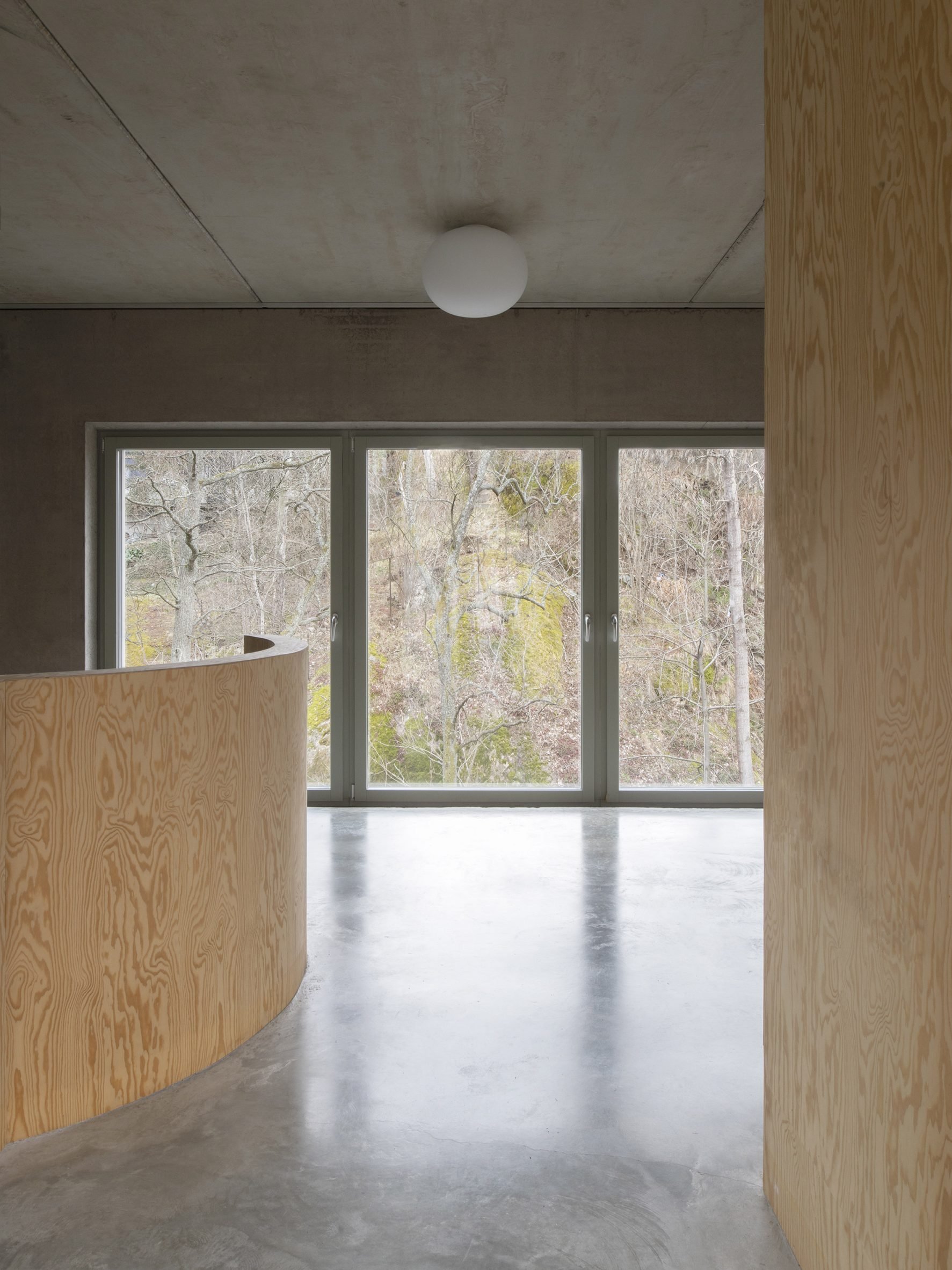
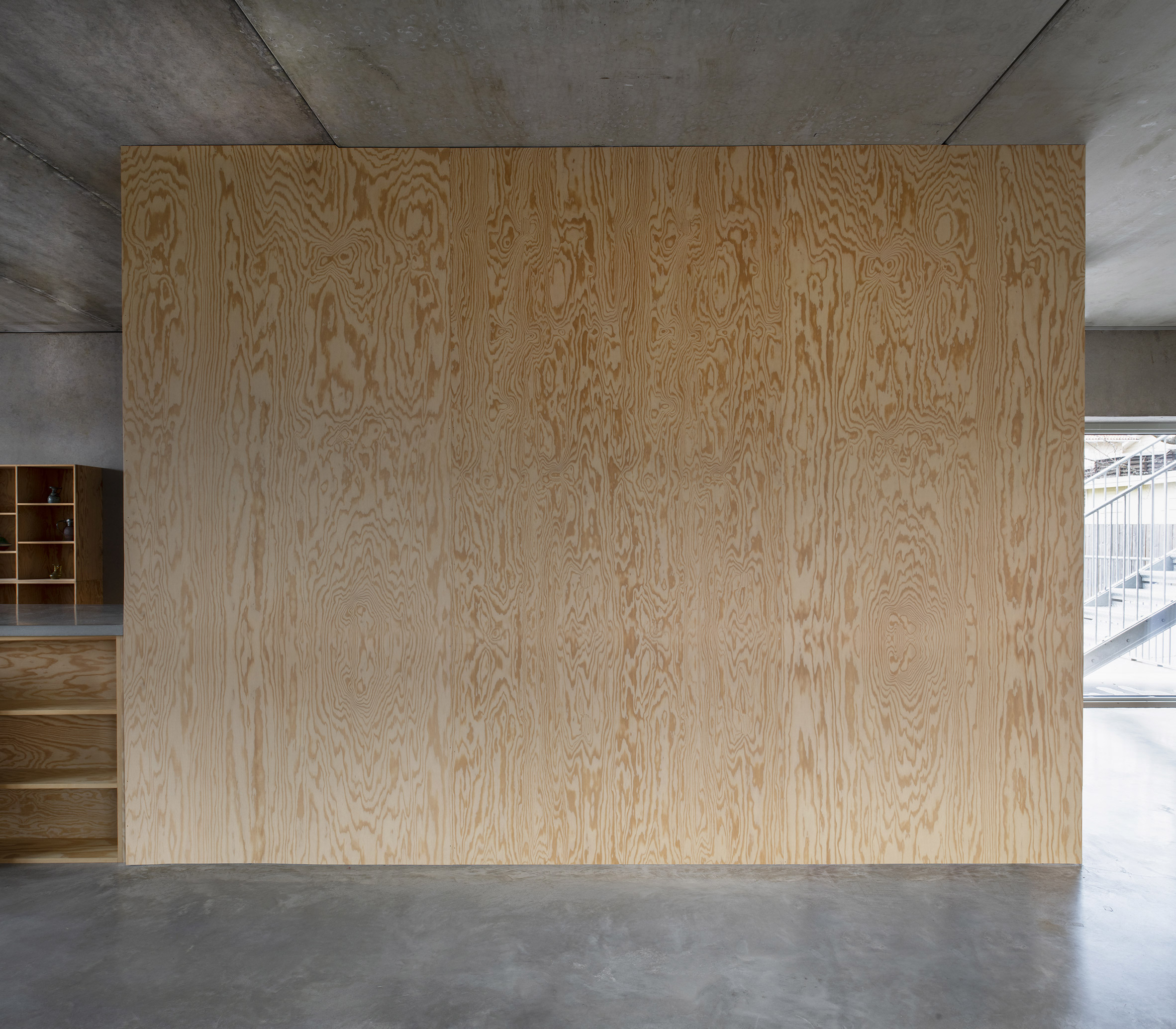
Inside T House, a curved staircase leads from the level access ground floor to the guest apartment on the first floor and a main suite on the second floor. On the third storey, smooth concrete walls, floors and ceilings are teamed with warm plywood joinery in the kitchen, the stair bannister and a dividing wall between the kitchen and living area. "The interior has a warm character with the exposed wooden surfaces in contrast with the hard exterior," said Spridd. Large doors in the kitchen open to an outdoor terrace, where metal stairs lead to the roof. Both spaces give views over the rocky hillside and hardy shrubs and trees.
snip









Spridd slots T-shaped house into rocky hillside in Stockholm
Spridd is a Swedish architectural office in Stockholm that was founded in 2005 by Klas Ruin and Ola Broms Wessel.https://www.dezeen.com/2023/09/18/spridd-t-shaped-house-stockholm-residential-architecture/



Raked concrete covers this T-shaped house, which architecture studio Spridd has slotted into a sloped site surrounded by trees on the island of Nacka in Stockholm. Appropriately called T House, the home was created by Spridd for a family, along with a separate guest apartment for an elderly relative.



To minimise excavation of the steeply sloping, south-facing plot, the studio designed a narrow central body for the house that slots between rocks. It expands outwards at its top storey, forming two cantilevered volumes that accommodate a generous open-plan living space. "The T-shape enables a minimal excavation as it only requires a small foundation at the bottom," Spridd told Dezeen. "The shape also provides an advantageous symmetry in the structure which stands independent of itself without attachment to the bedrock."


T House is constructed from prefabricated sandwich panels covered with concrete. Inside, the panels have a smooth finish while a raked treatment was manually applied externally. The raked-concrete facades ensure the house is in dialogue with the textures of the rocky cliffside site and the bark of the surrounding trees. Externally, brown-framed ribbon windows on the south, east and west facades give the home a modernist feel.



Inside T House, a curved staircase leads from the level access ground floor to the guest apartment on the first floor and a main suite on the second floor. On the third storey, smooth concrete walls, floors and ceilings are teamed with warm plywood joinery in the kitchen, the stair bannister and a dividing wall between the kitchen and living area. "The interior has a warm character with the exposed wooden surfaces in contrast with the hard exterior," said Spridd. Large doors in the kitchen open to an outdoor terrace, where metal stairs lead to the roof. Both spaces give views over the rocky hillside and hardy shrubs and trees.
snip









September 21, 2023
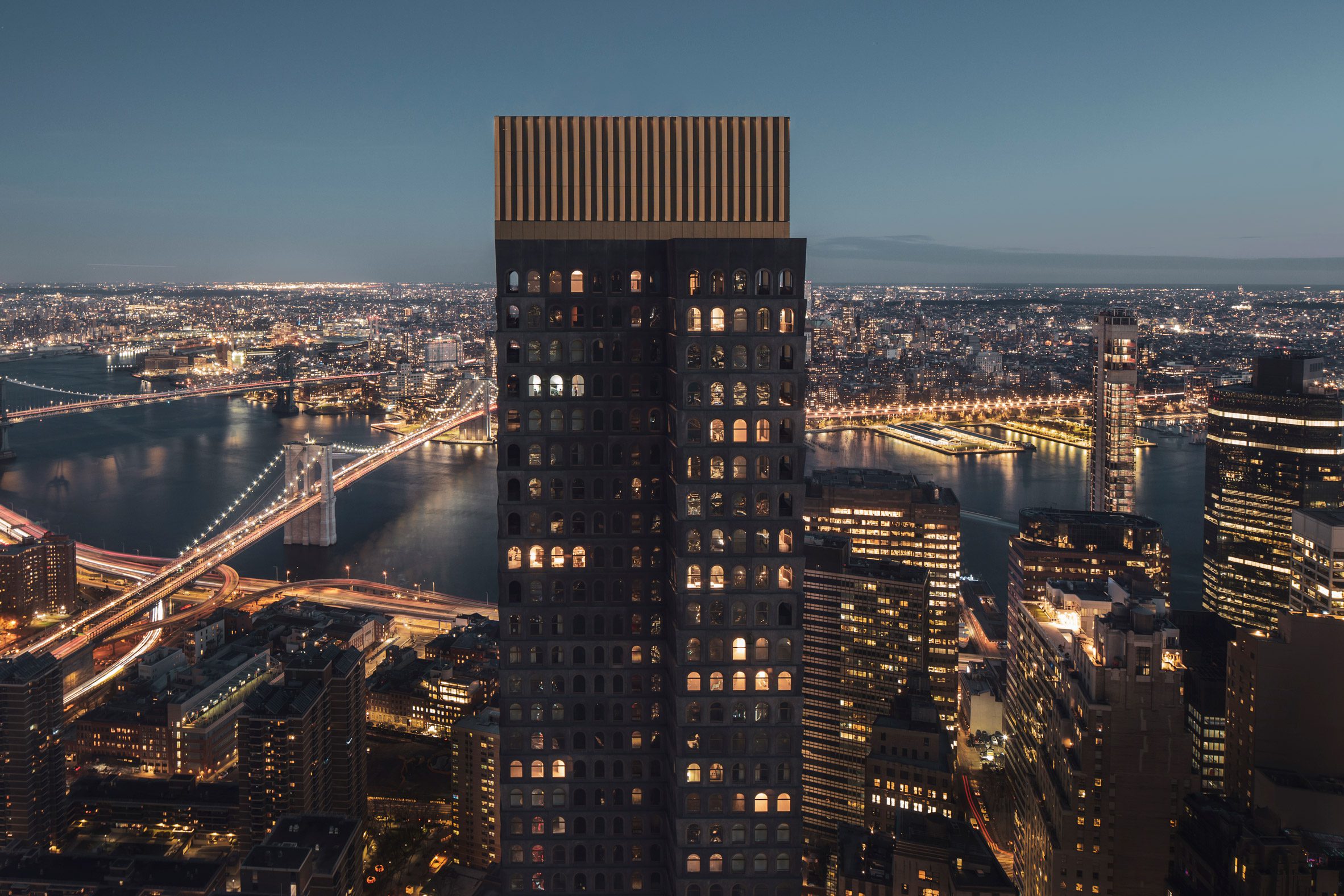
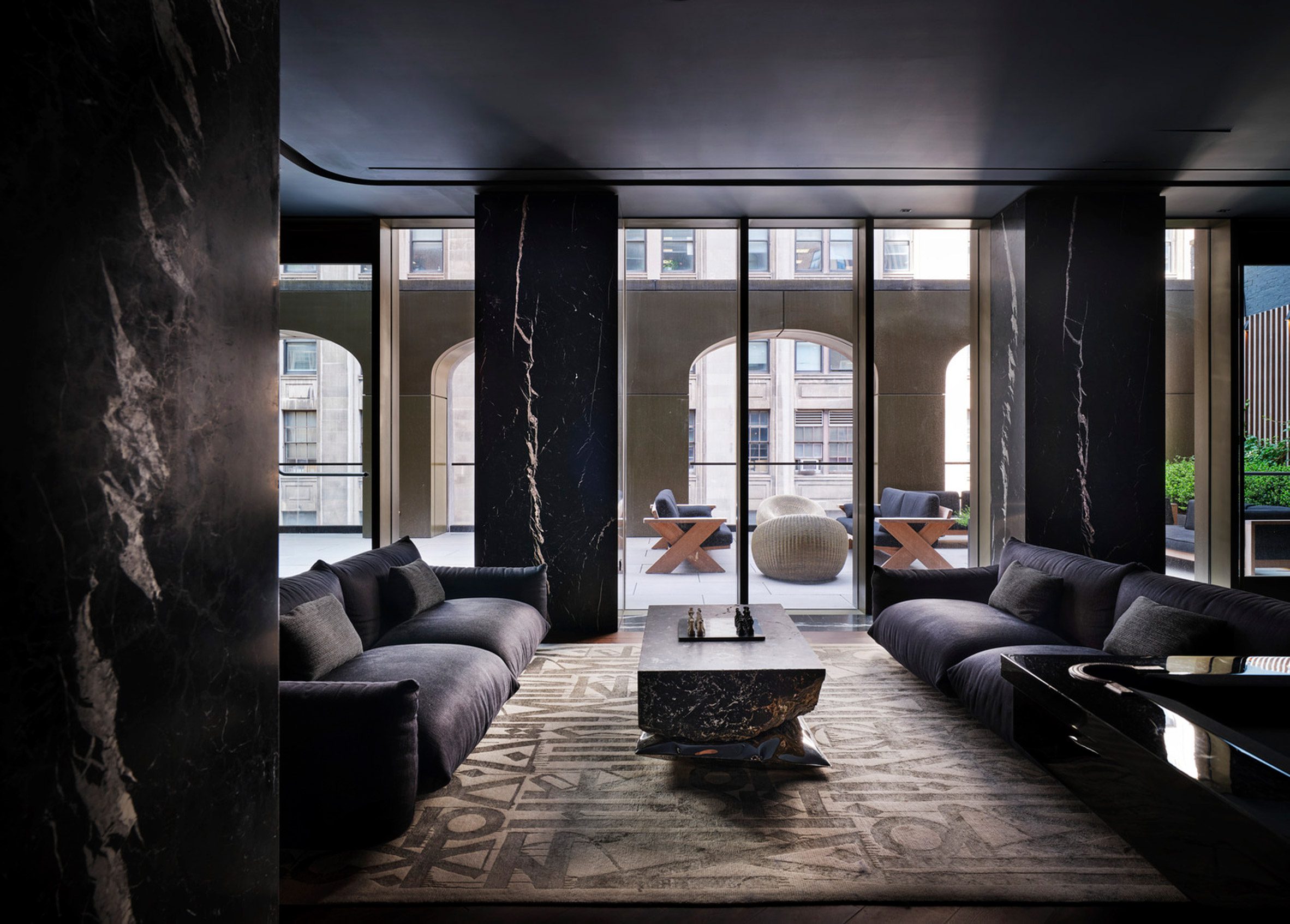
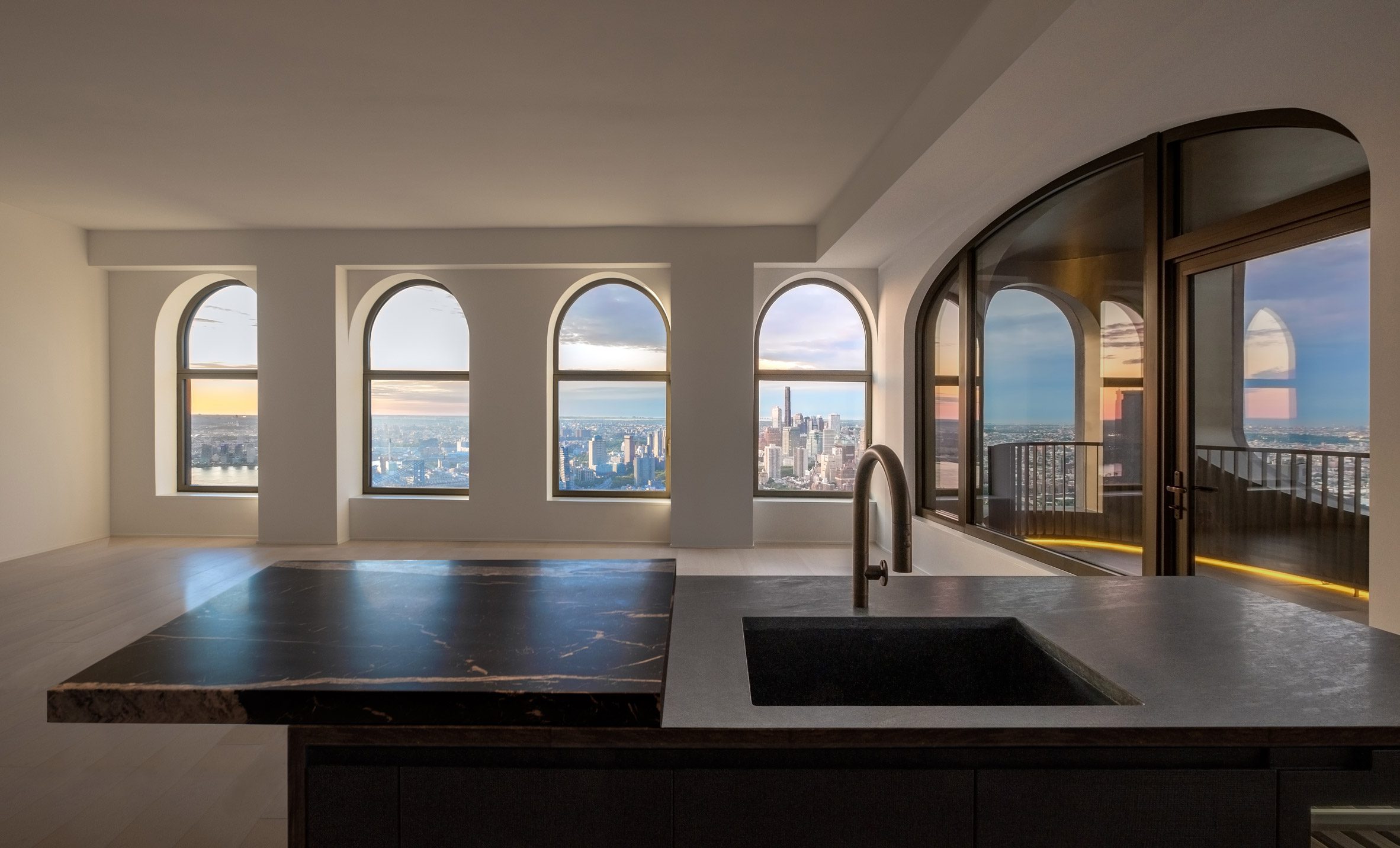



The latest edition of our Dezeen Debate newsletter features David Adjaye's reveal of the 130 William skyscraper in Lower Manhattan. Subscribe to Dezeen Debate now. Ghanaian-British architect Adjaye has completed the 130 William skyscraper in Lower Manhattan, which is the first skyscraper finished by the architect and his studio Adjaye Associates. The tower is 800 feet tall and has an exterior that is covered in hand-troweled concrete panels. Readers were fascinated by the tower. One thought it was "wonderful" that the skyscraper is not "just another blue glass box", whilst another disagreed, describing the building as "another pointless skyscraper for the super-rich to live in".
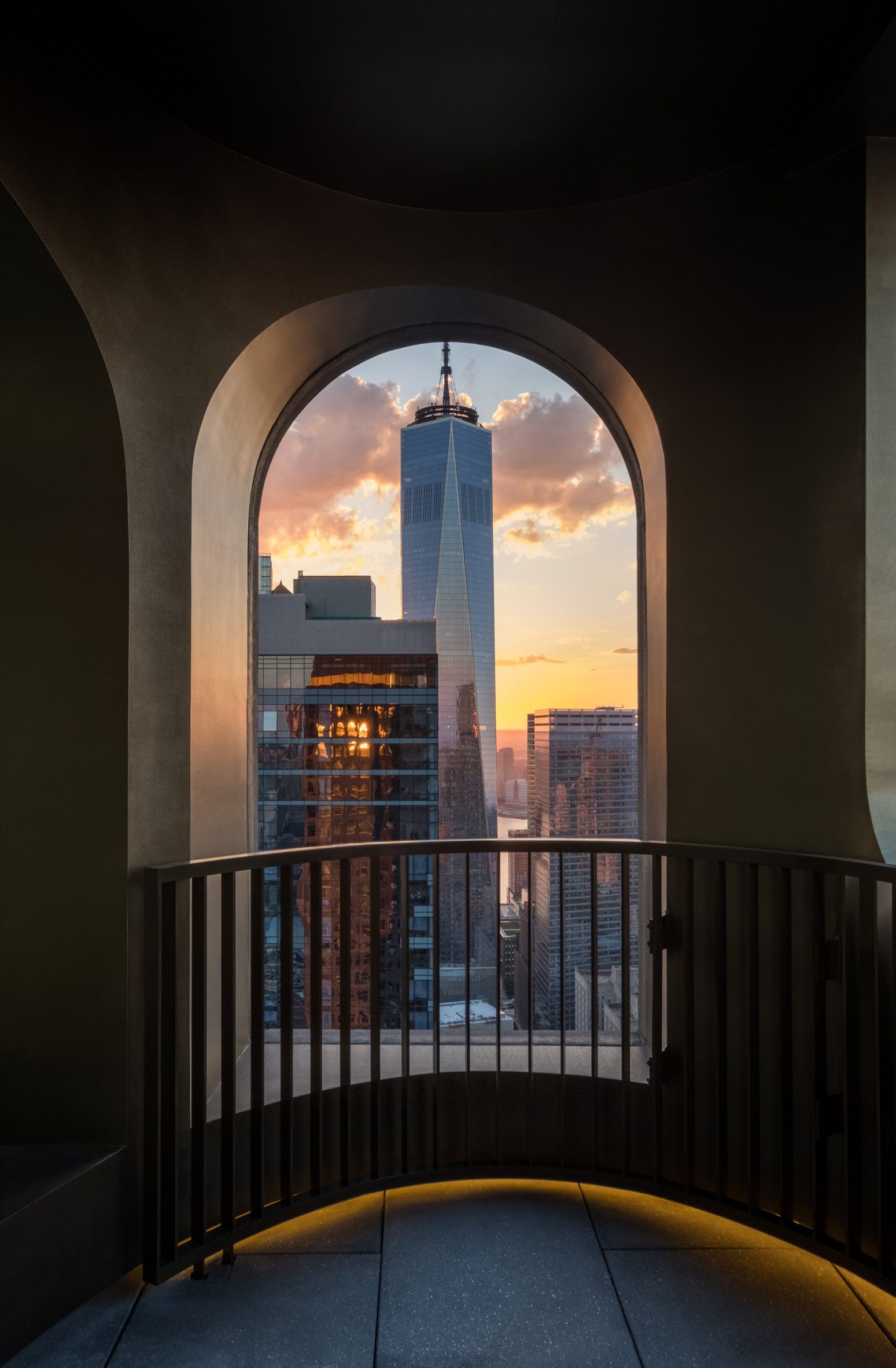
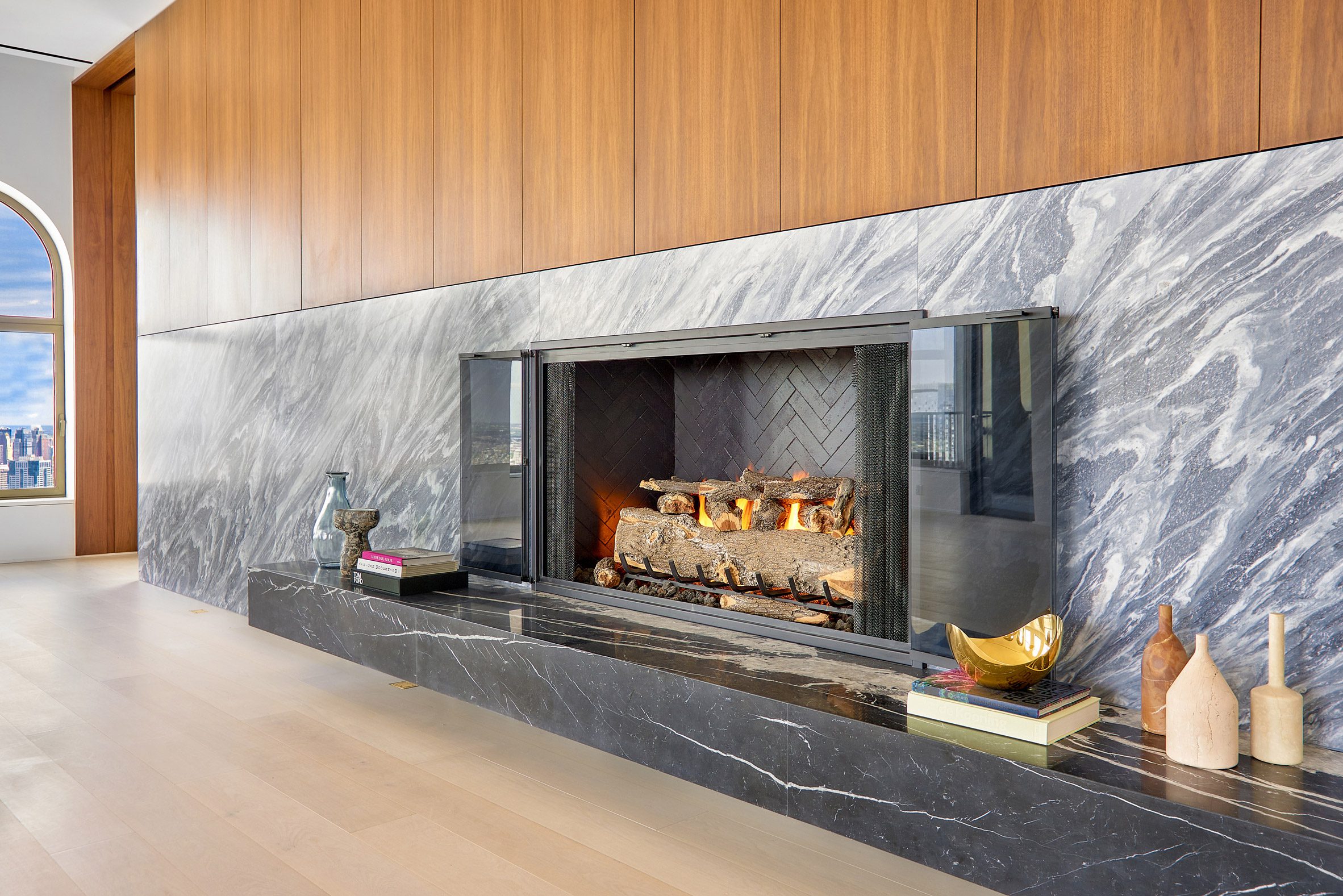
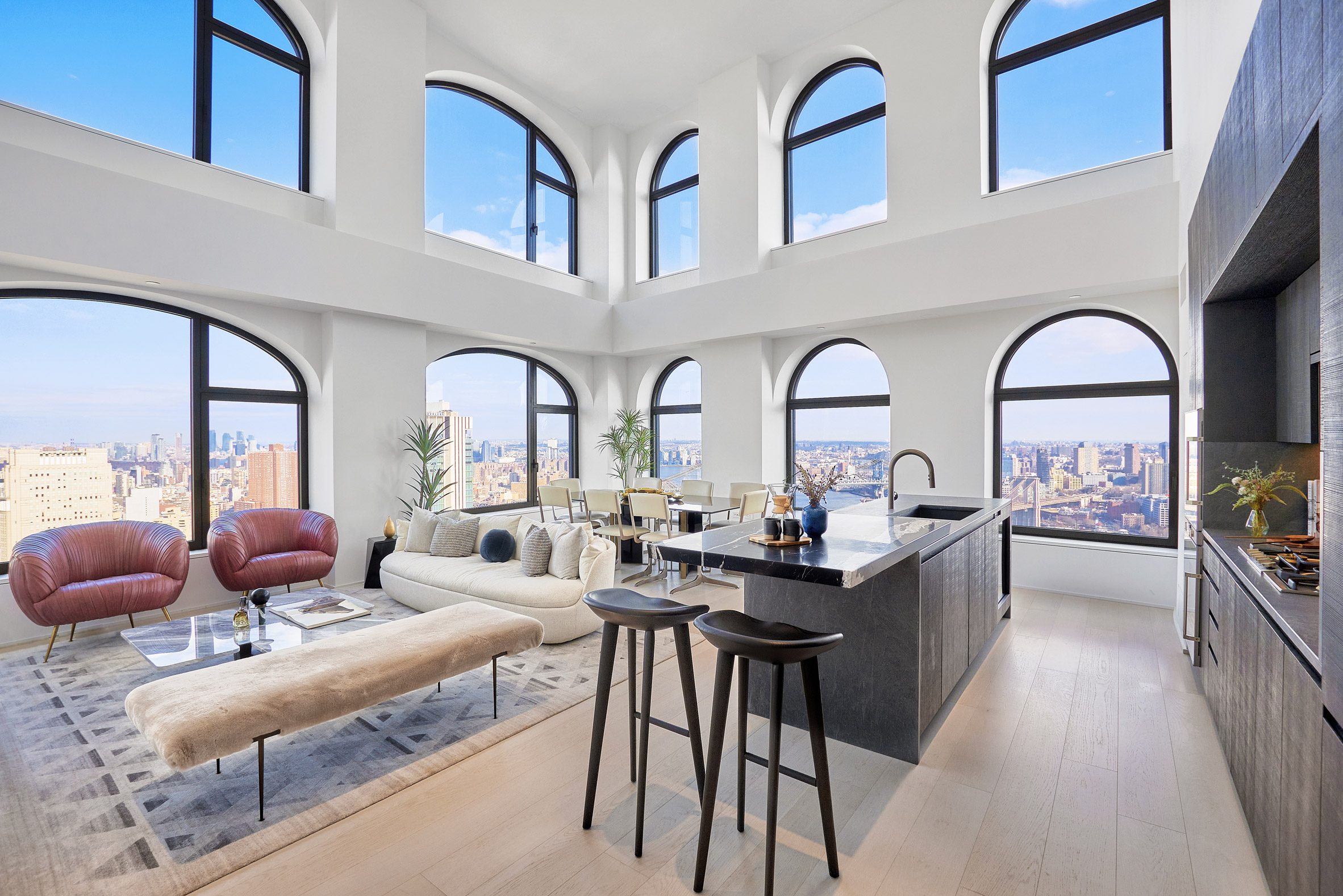
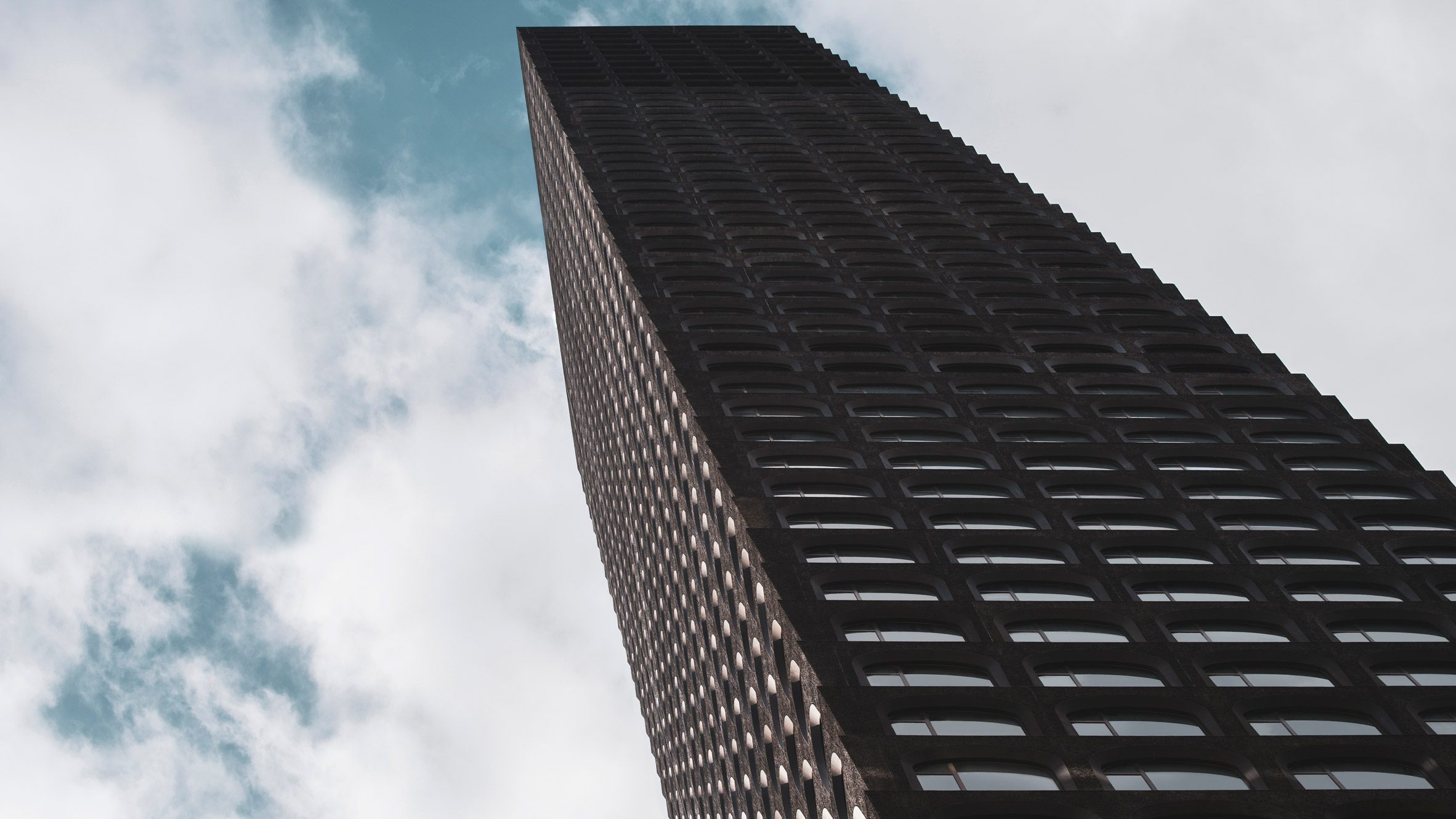
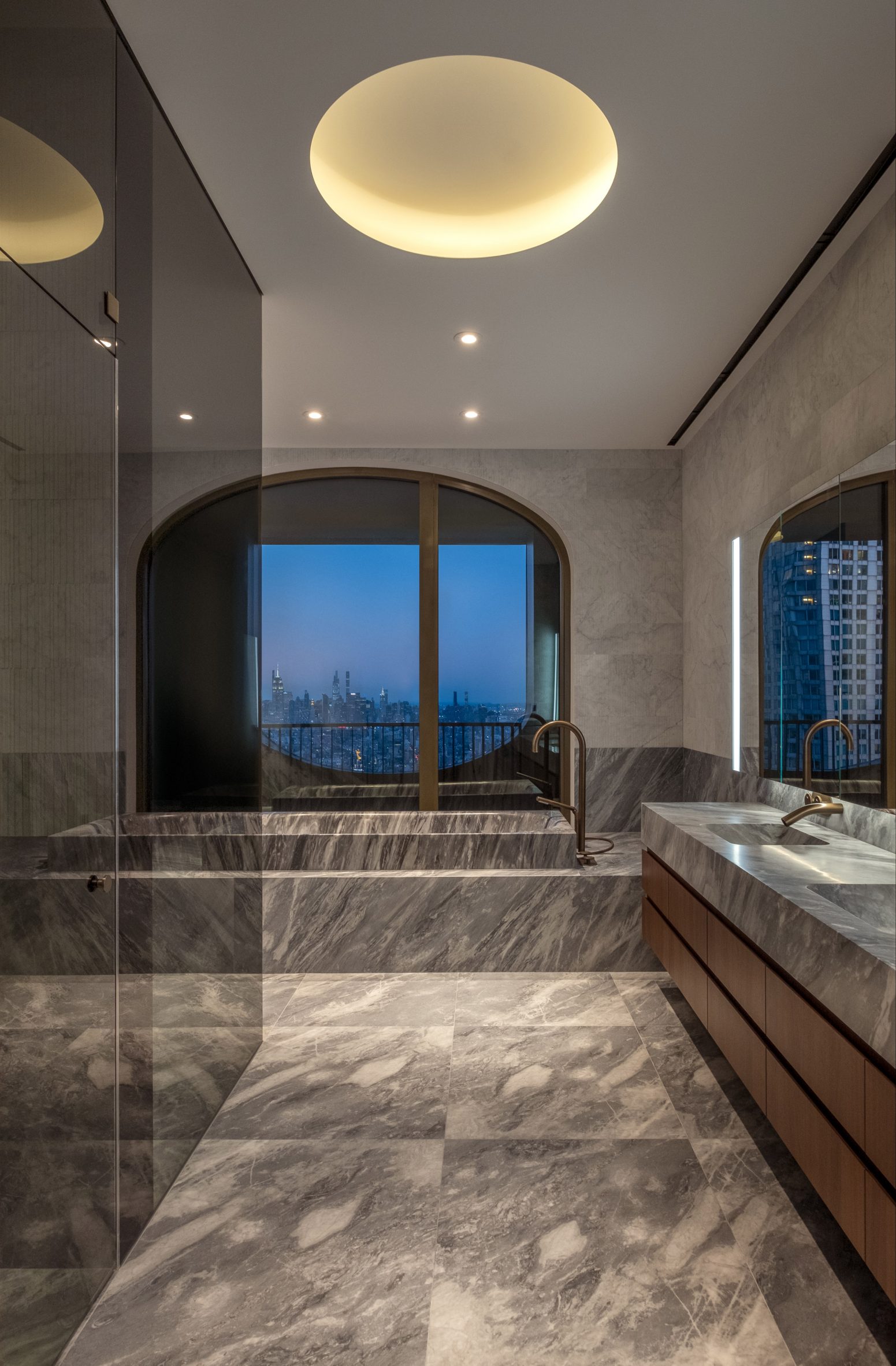
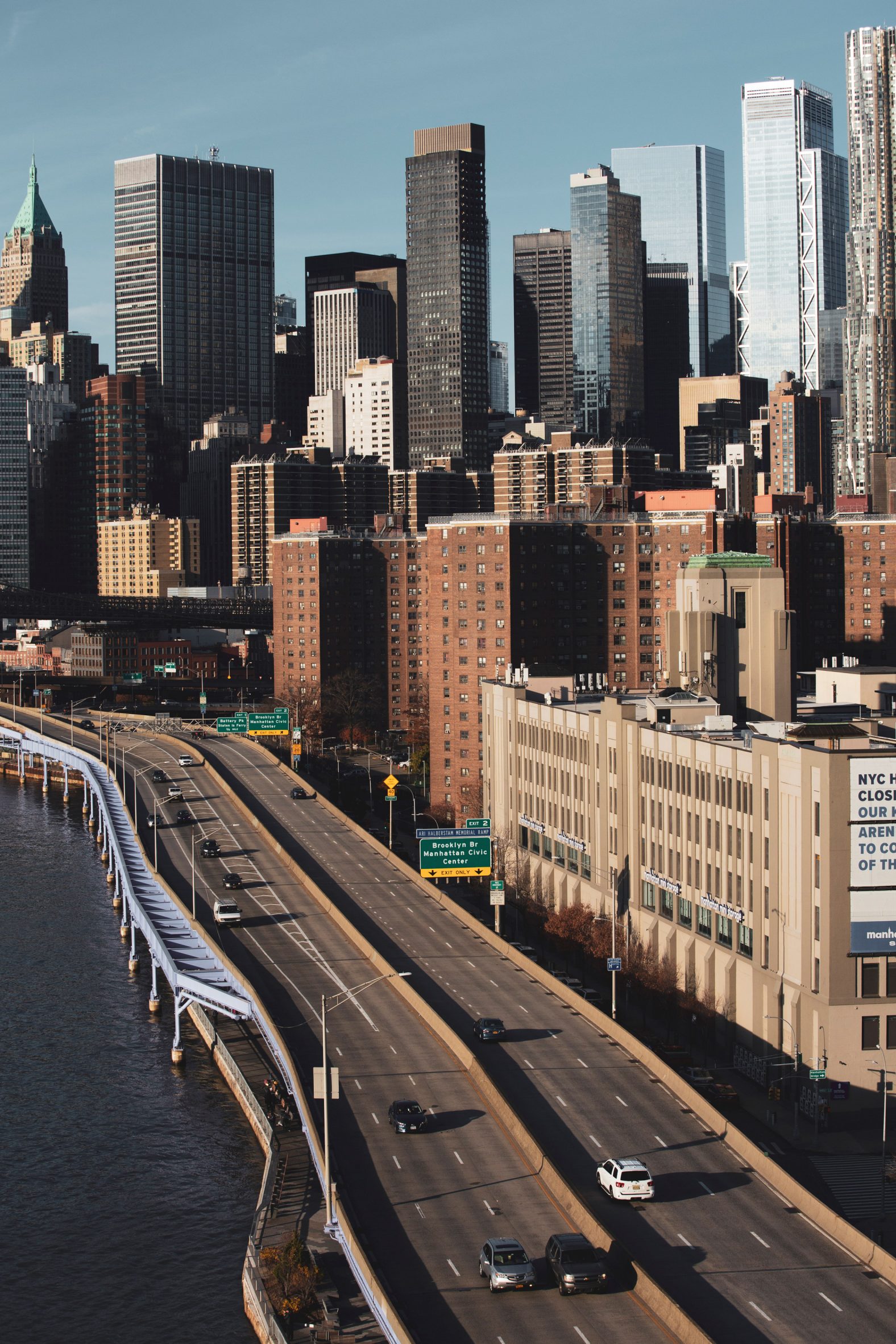
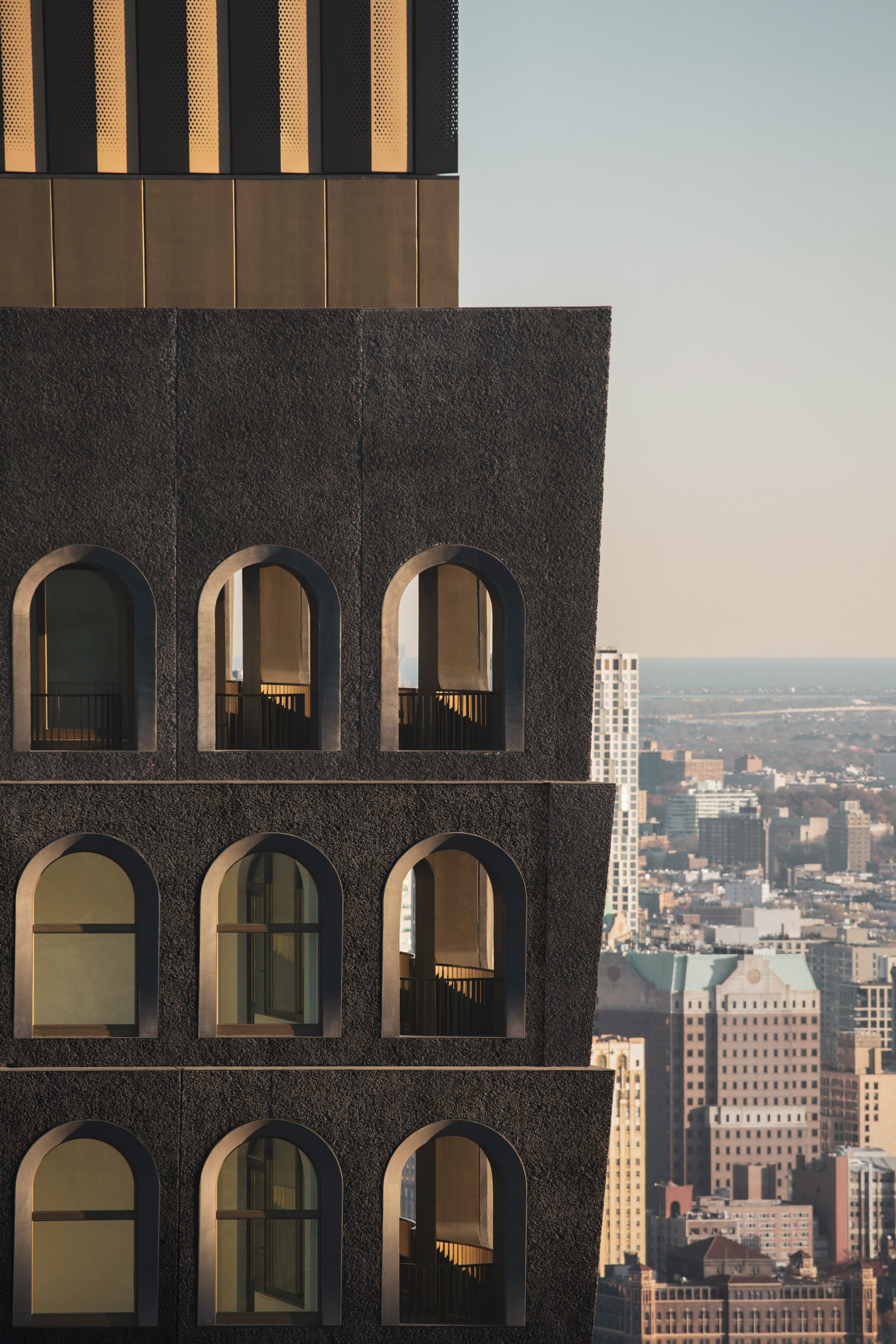
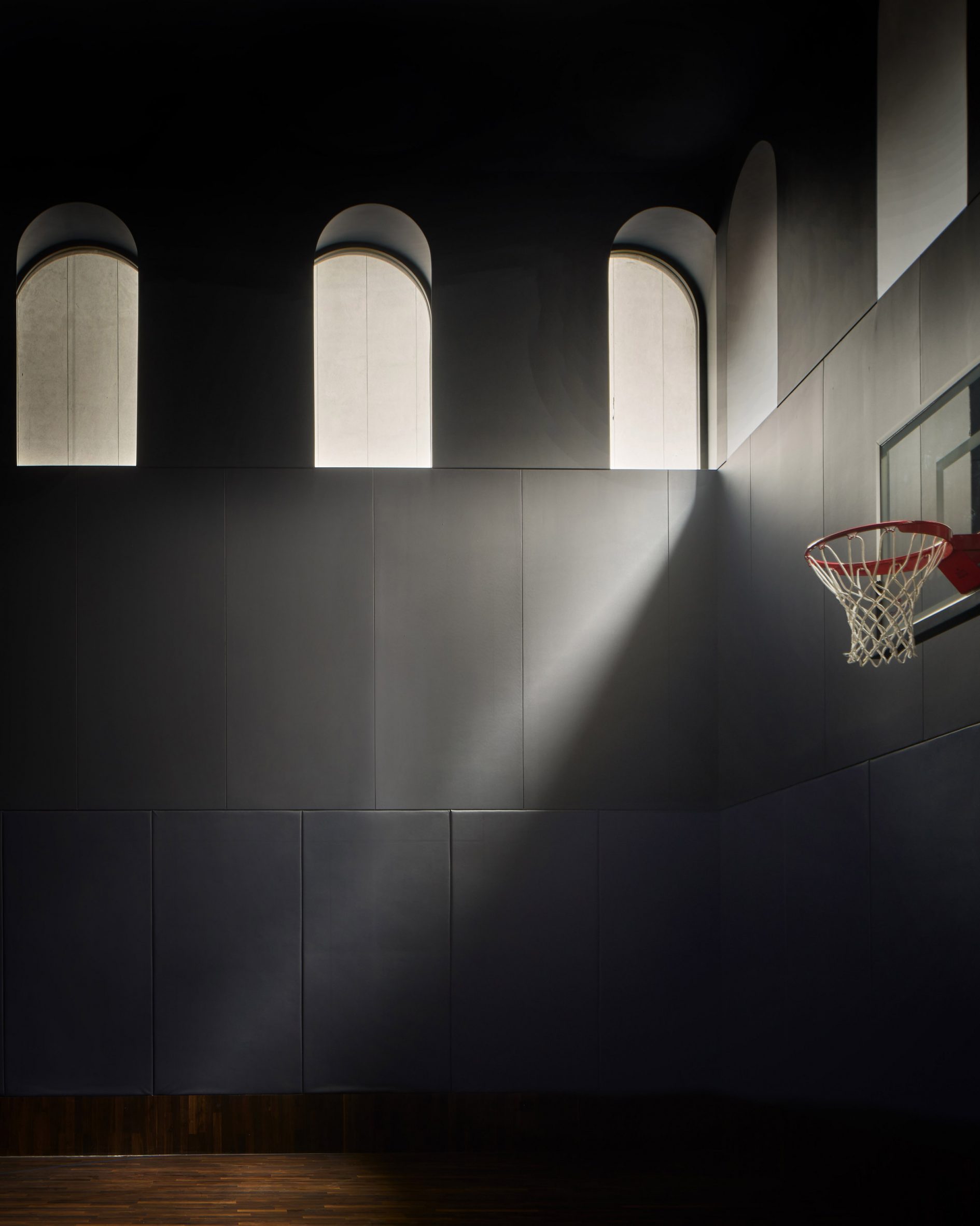
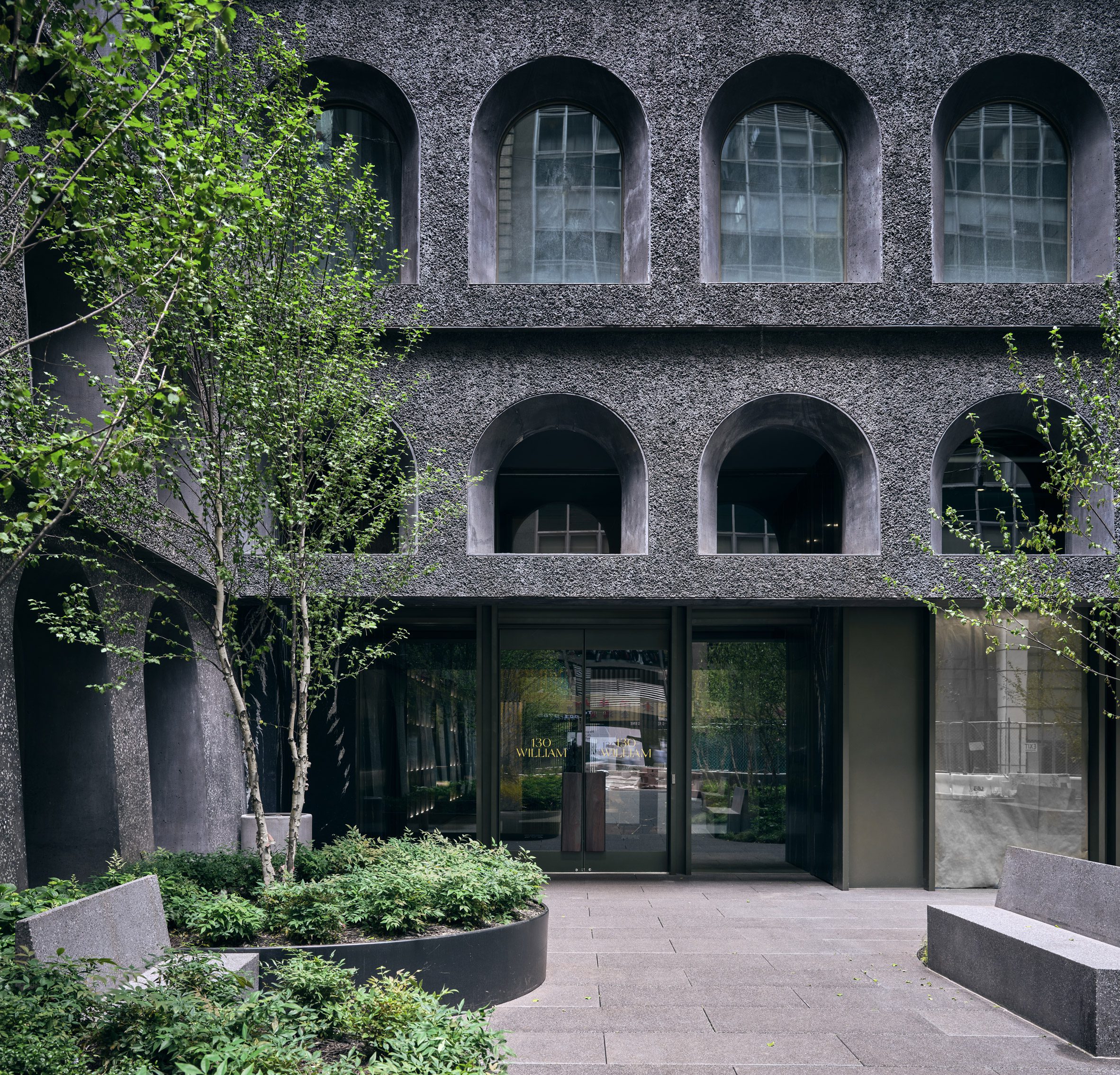
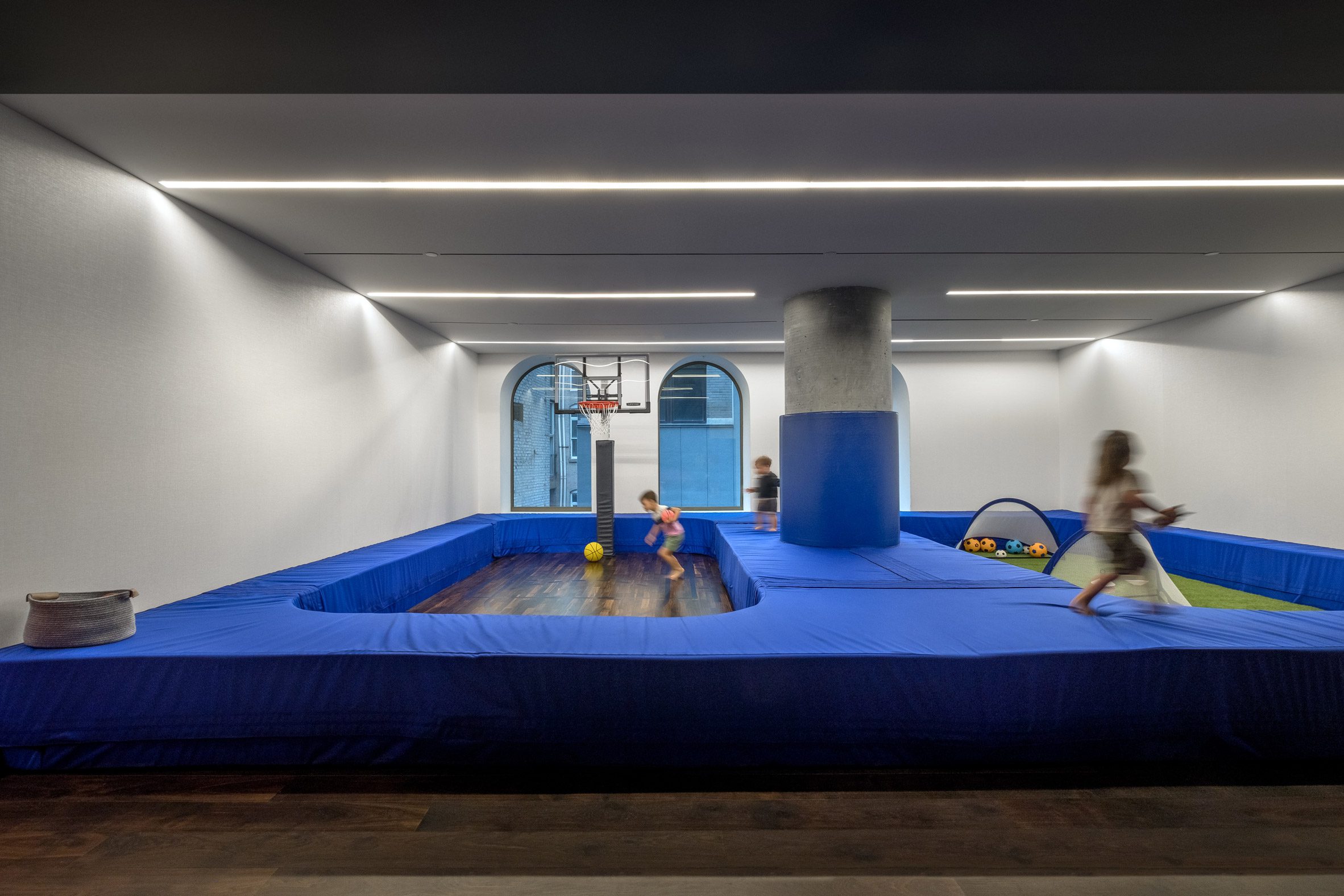
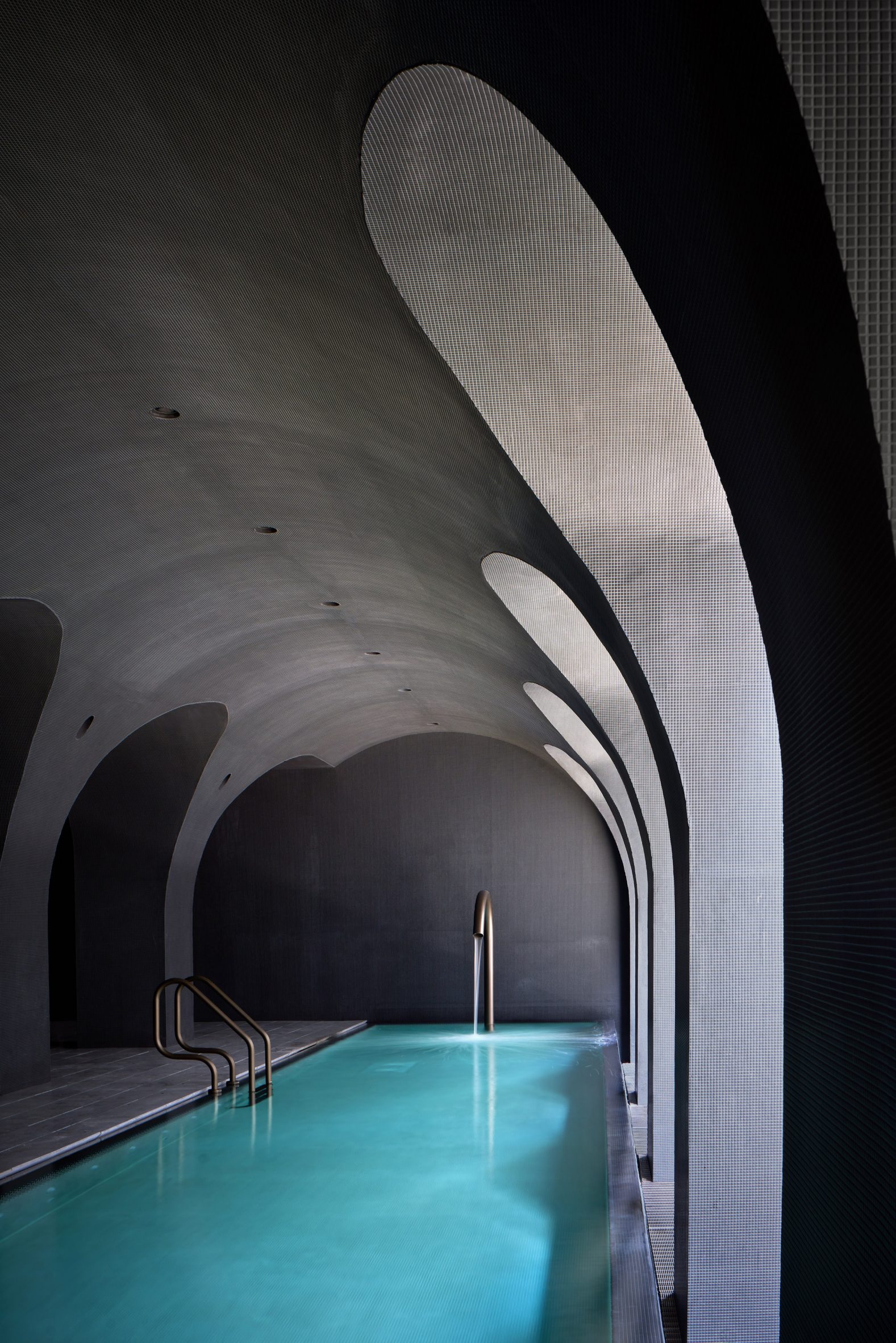











Dezeen Debate features David Adjaye's "wonderful" first skyscraper in New York
https://www.dezeen.com/2023/06/29/dezeen-debate-david-adjaye-first-skyscraper-new-york/


The latest edition of our Dezeen Debate newsletter features David Adjaye's reveal of the 130 William skyscraper in Lower Manhattan. Subscribe to Dezeen Debate now. Ghanaian-British architect Adjaye has completed the 130 William skyscraper in Lower Manhattan, which is the first skyscraper finished by the architect and his studio Adjaye Associates. The tower is 800 feet tall and has an exterior that is covered in hand-troweled concrete panels. Readers were fascinated by the tower. One thought it was "wonderful" that the skyscraper is not "just another blue glass box", whilst another disagreed, describing the building as "another pointless skyscraper for the super-rich to live in".











September 21, 2023
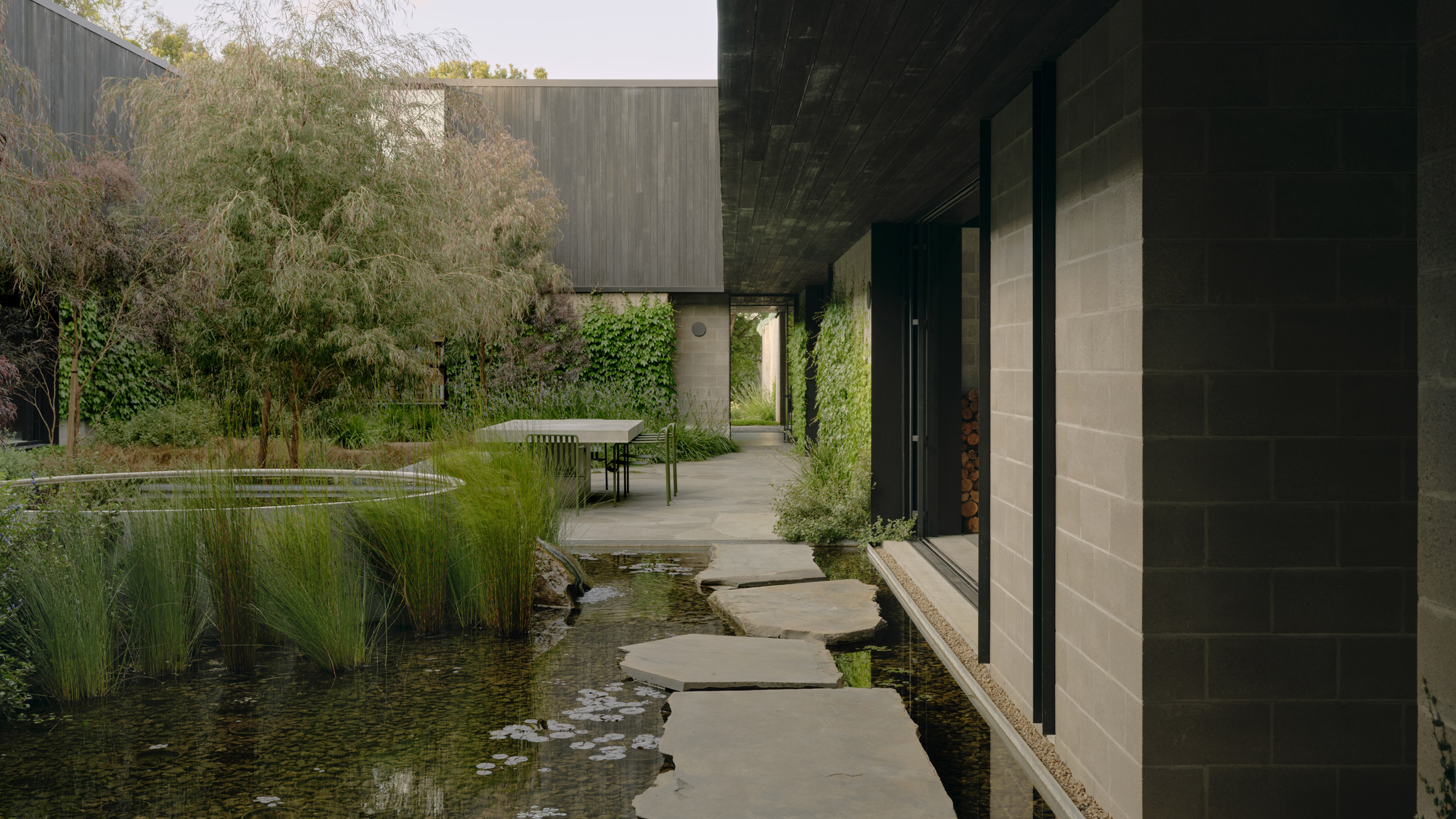
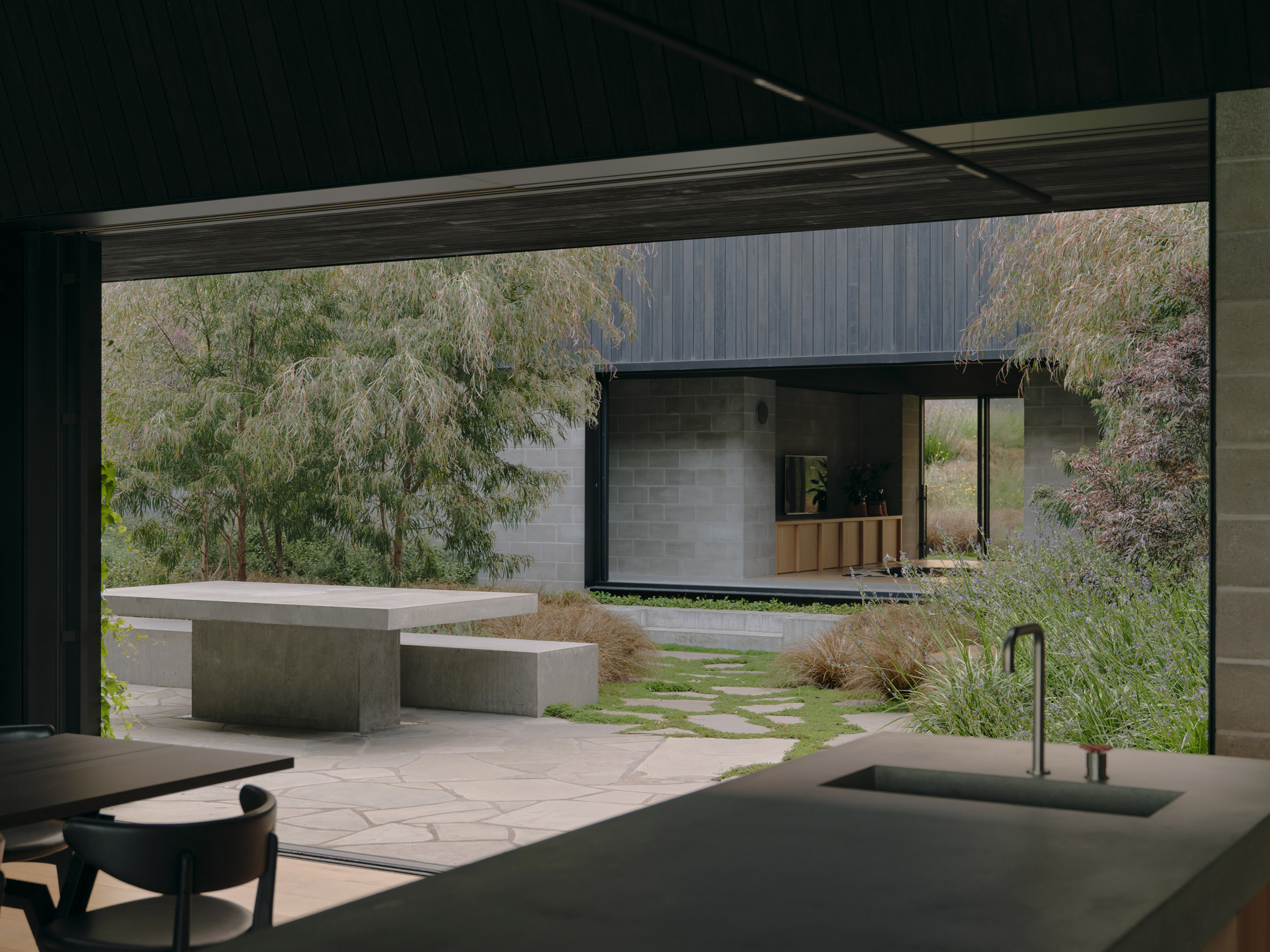
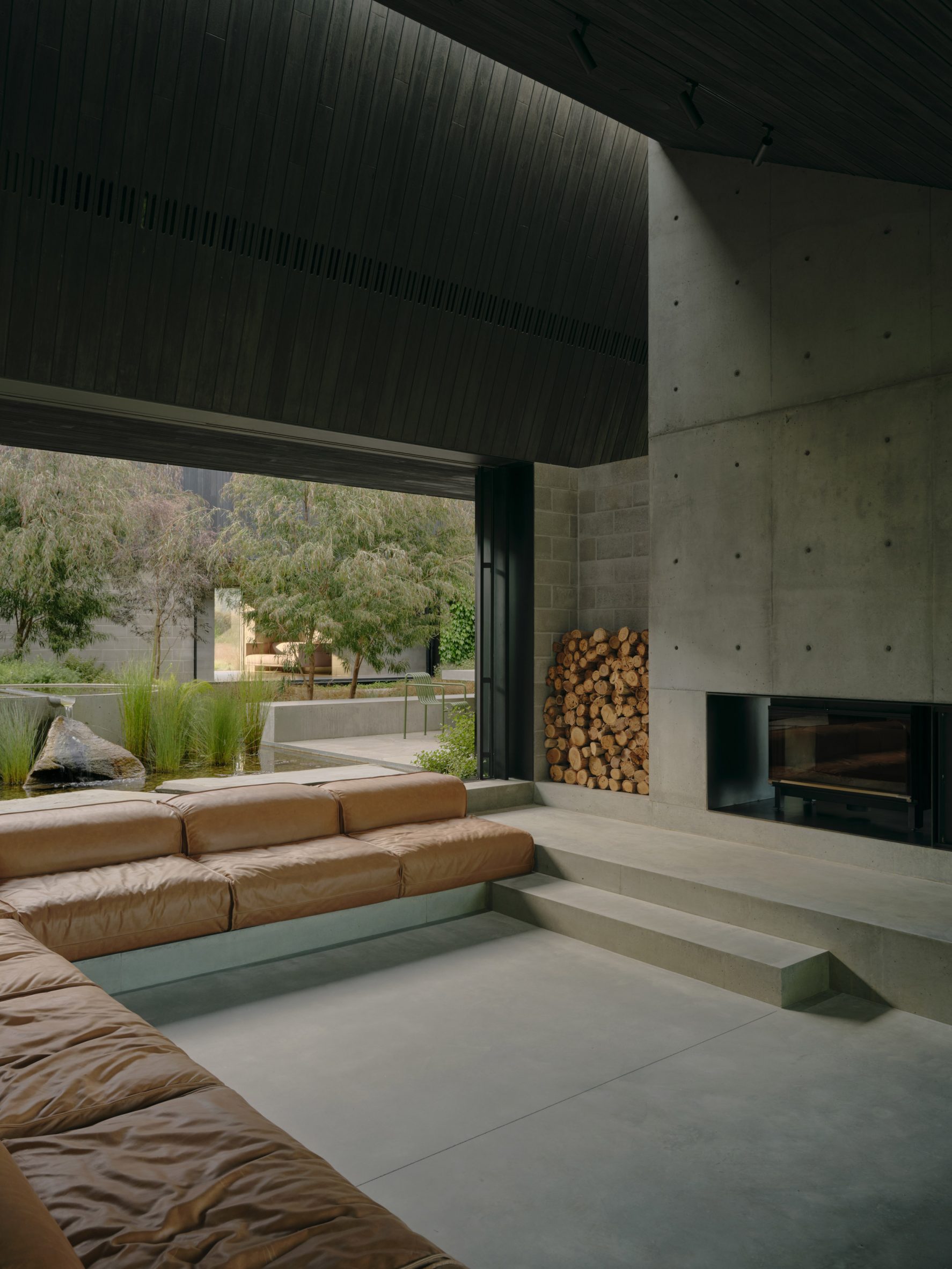



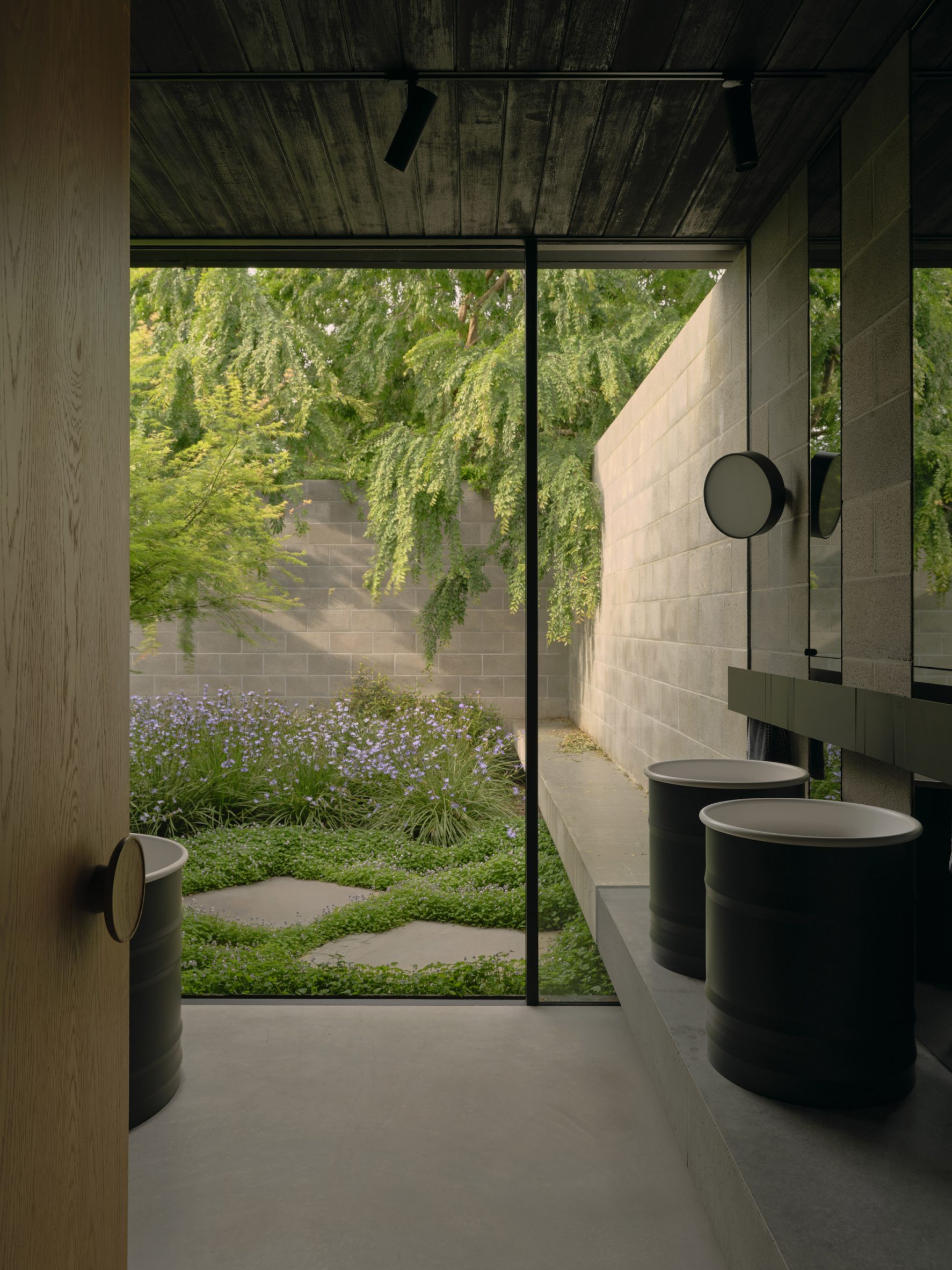
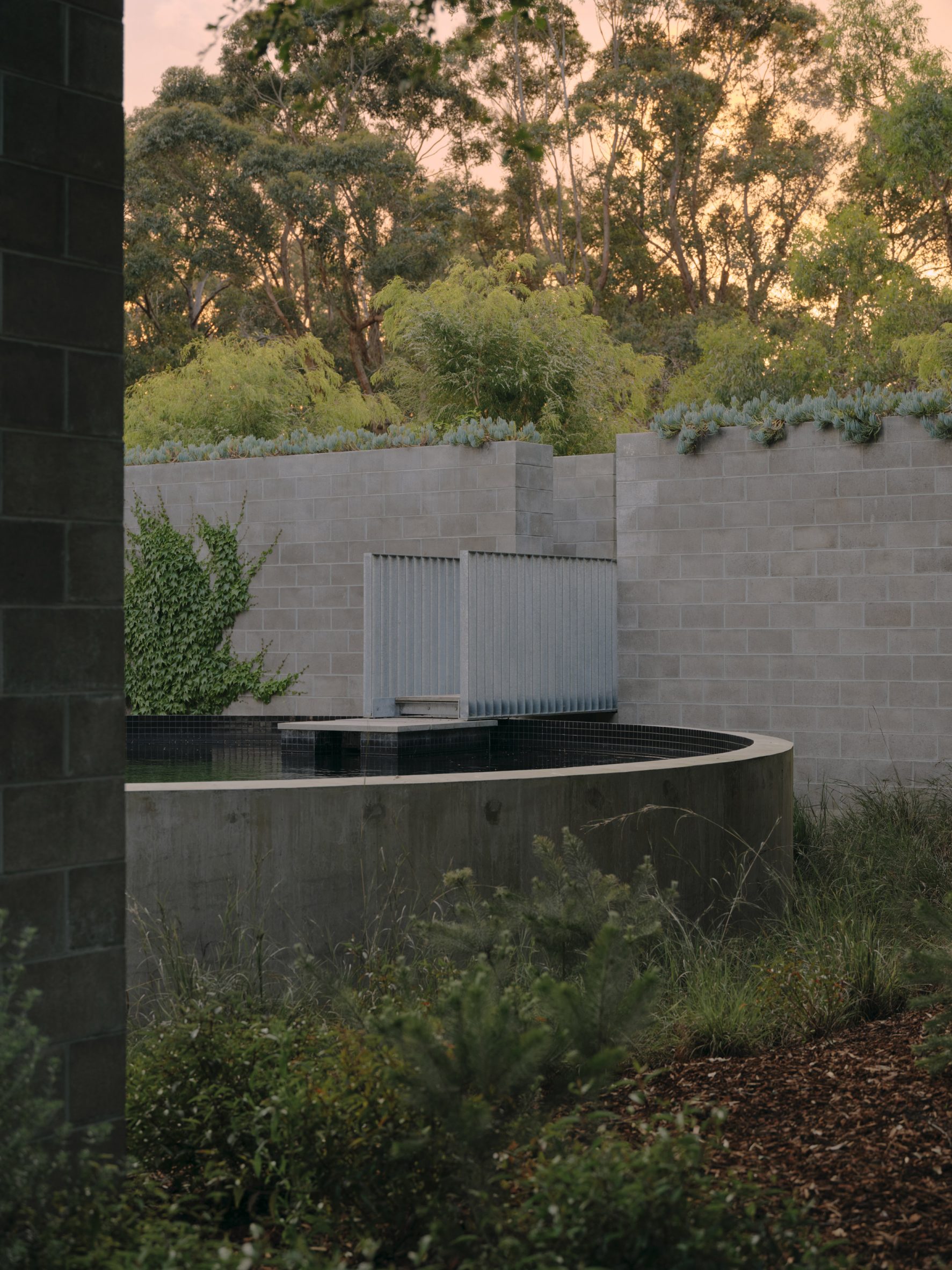
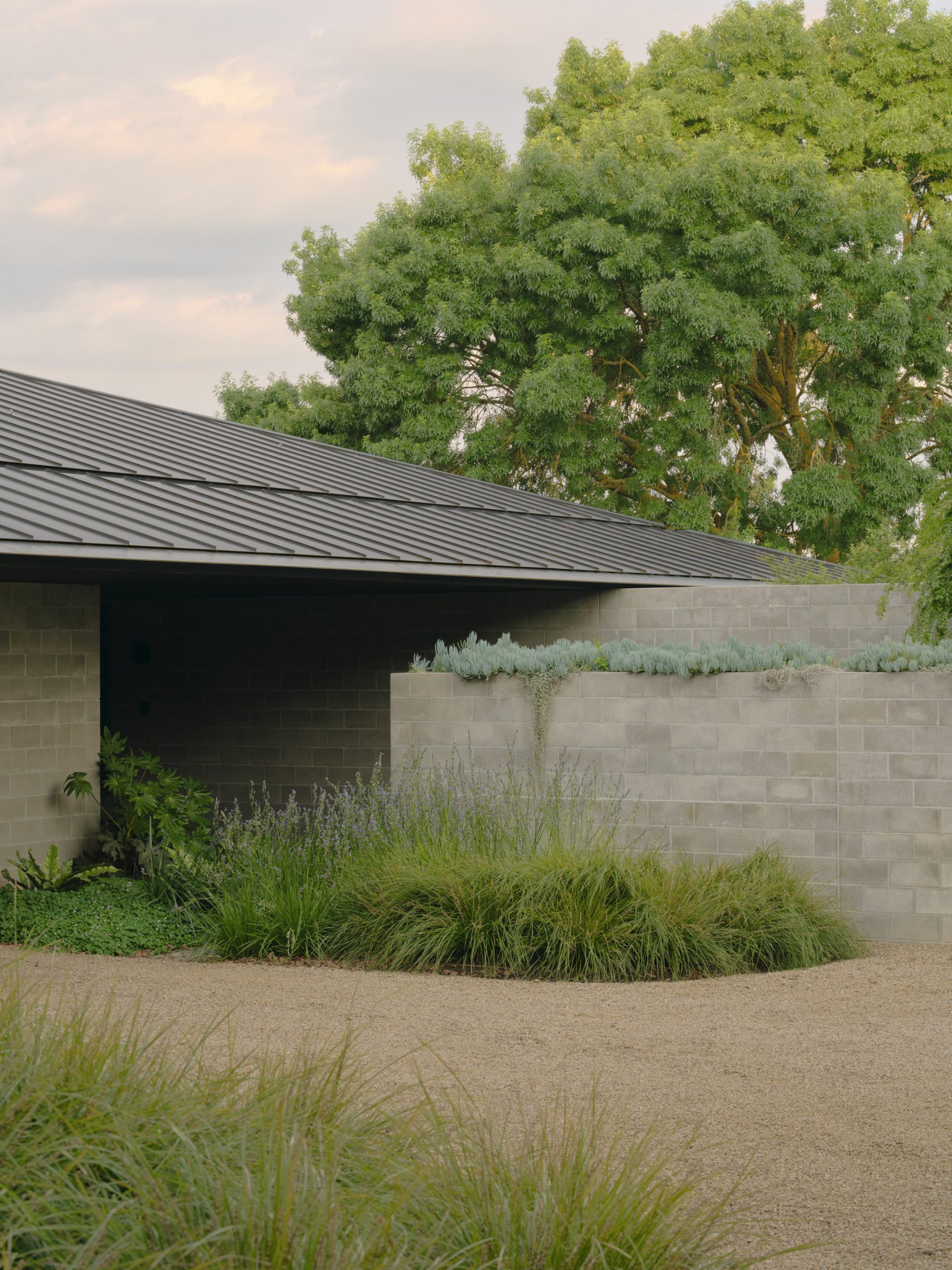
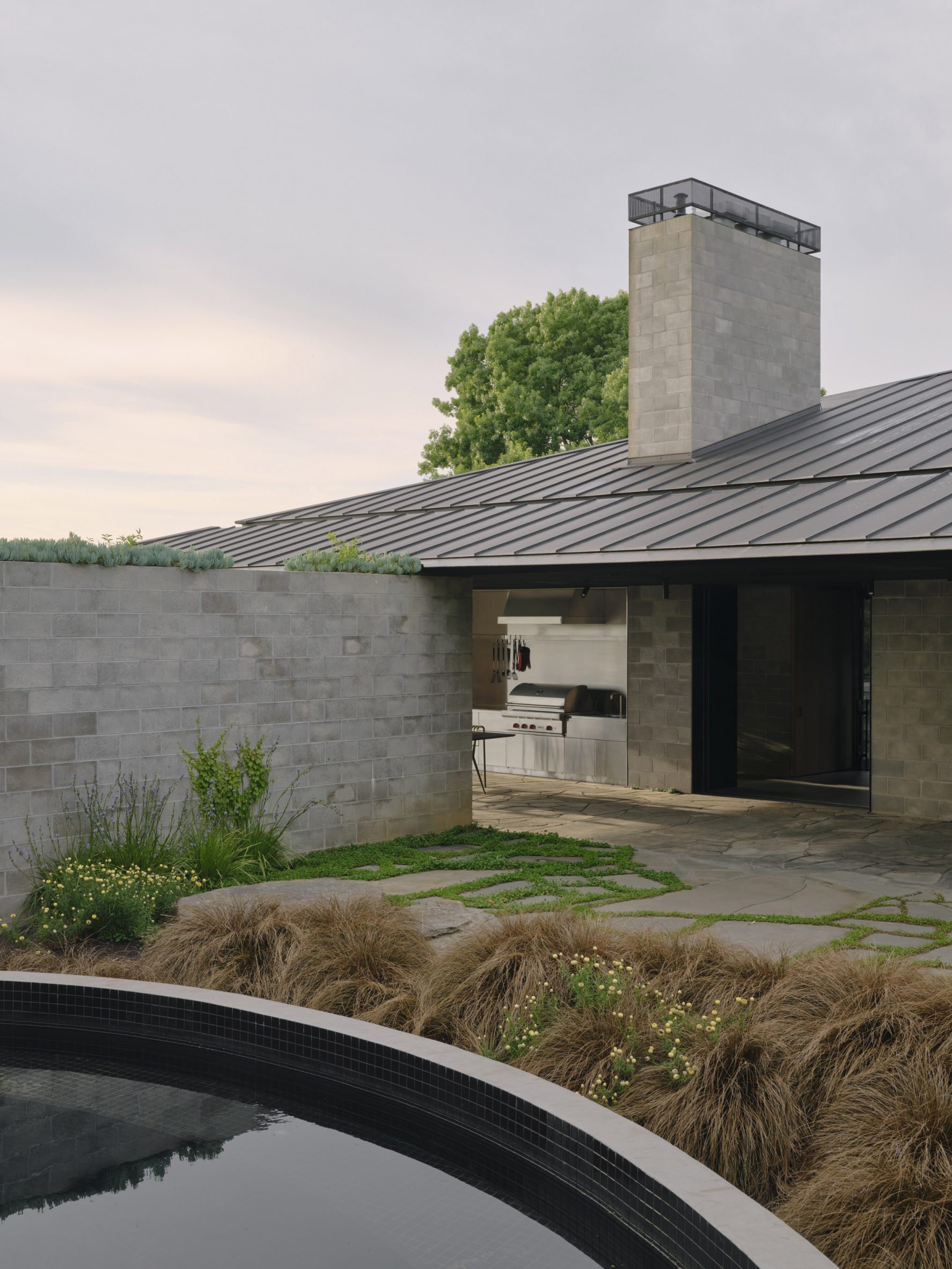
A low-slung roof with deep eaves shelters Merricks Farmhouse, a concrete-block home in Australia designed by South African studio Michael Lumby Architecture with Brisbane practice Nielsen Jenkins. Overlooking vineyards and the sea on the Mornington Peninsula in southeast Melbourne, the dwelling references local farmhouses and is designed by Michael Lumby Architecture and Nielsen Jenkins as a "refuge" in its exposed coastal setting.
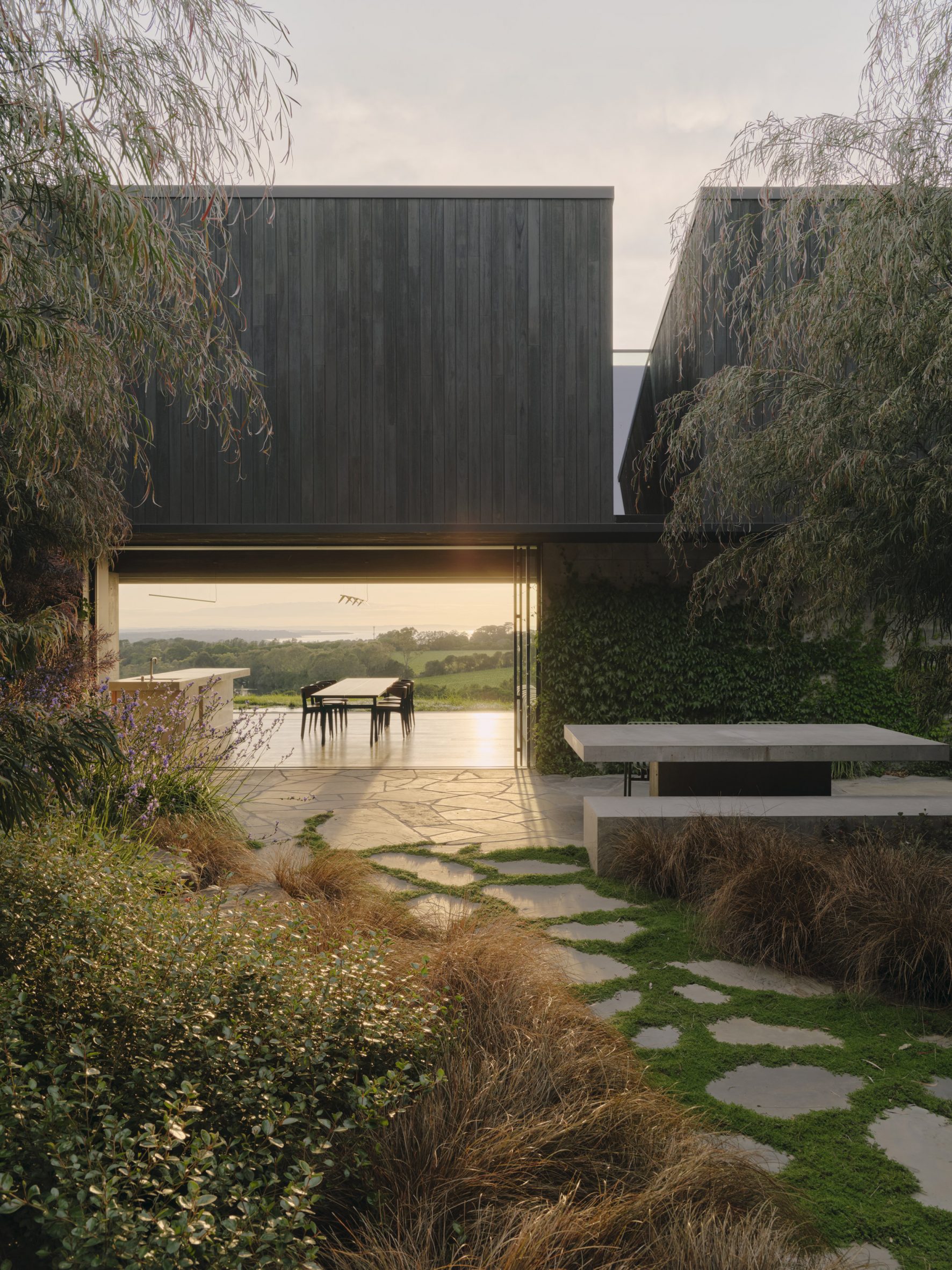
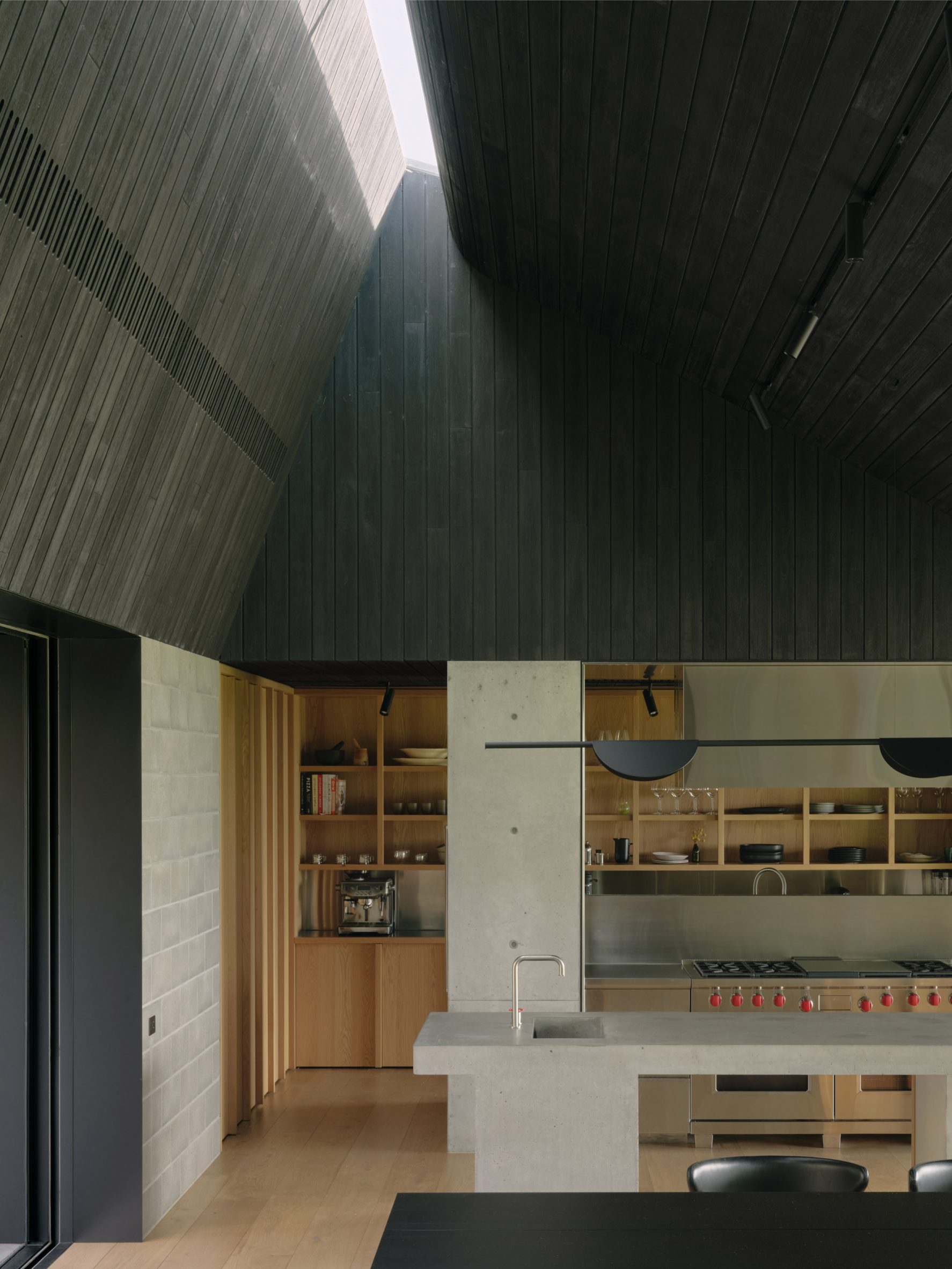
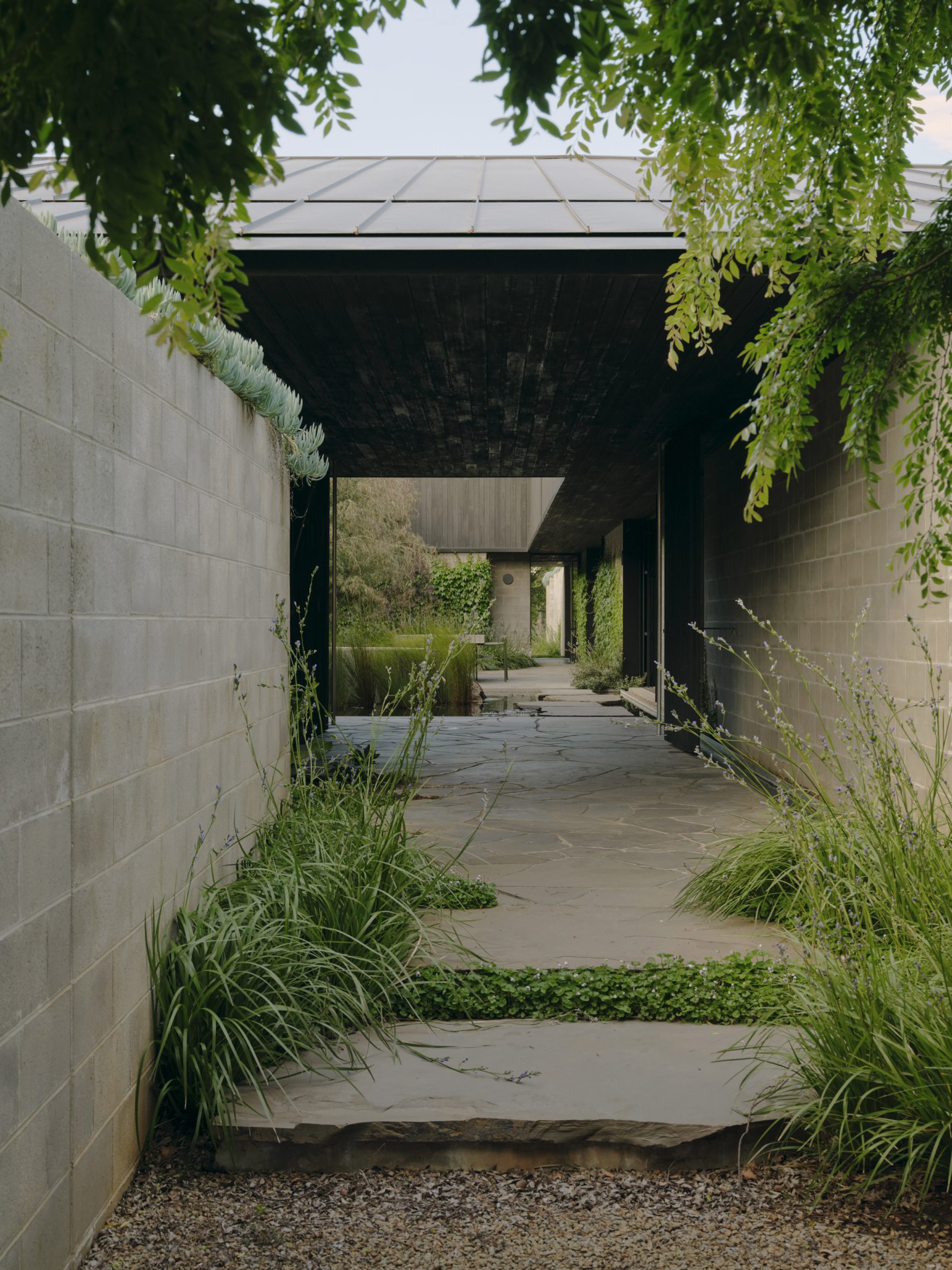
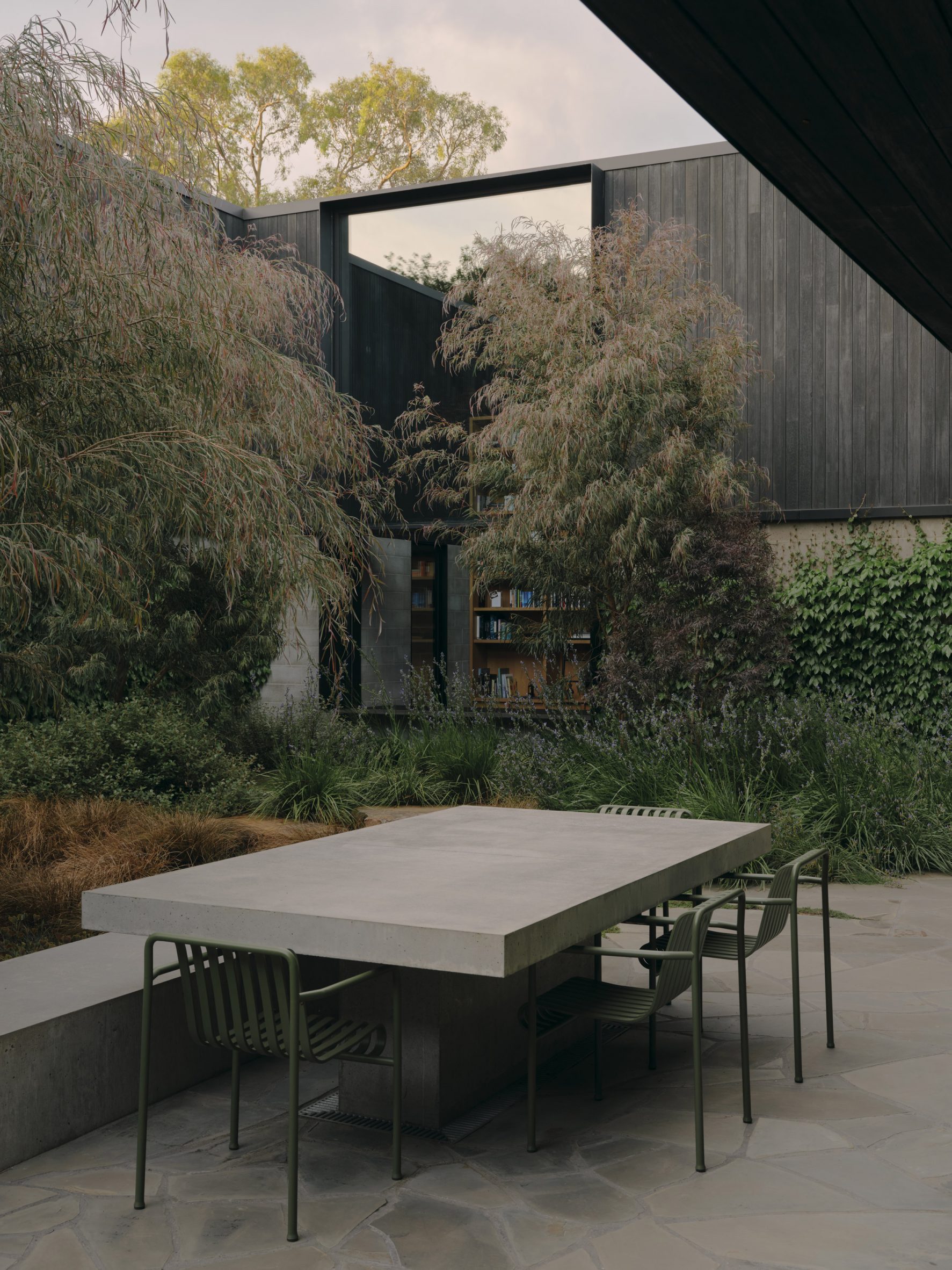




"As an outsider, I found myself being intrigued by the typical Australian farmhouse and perhaps in a naive way began to romanticise it with its low-slung roof, wrap-around porch and deep eaves," explained architect Michael Lumby. "With its siting on a prominent hilltop with no other buildings around, we were interested in how we could abstract this characteristic, distilling the notion of the Australian farmhouse into one idea – a line of shadow in the landscape," he added.
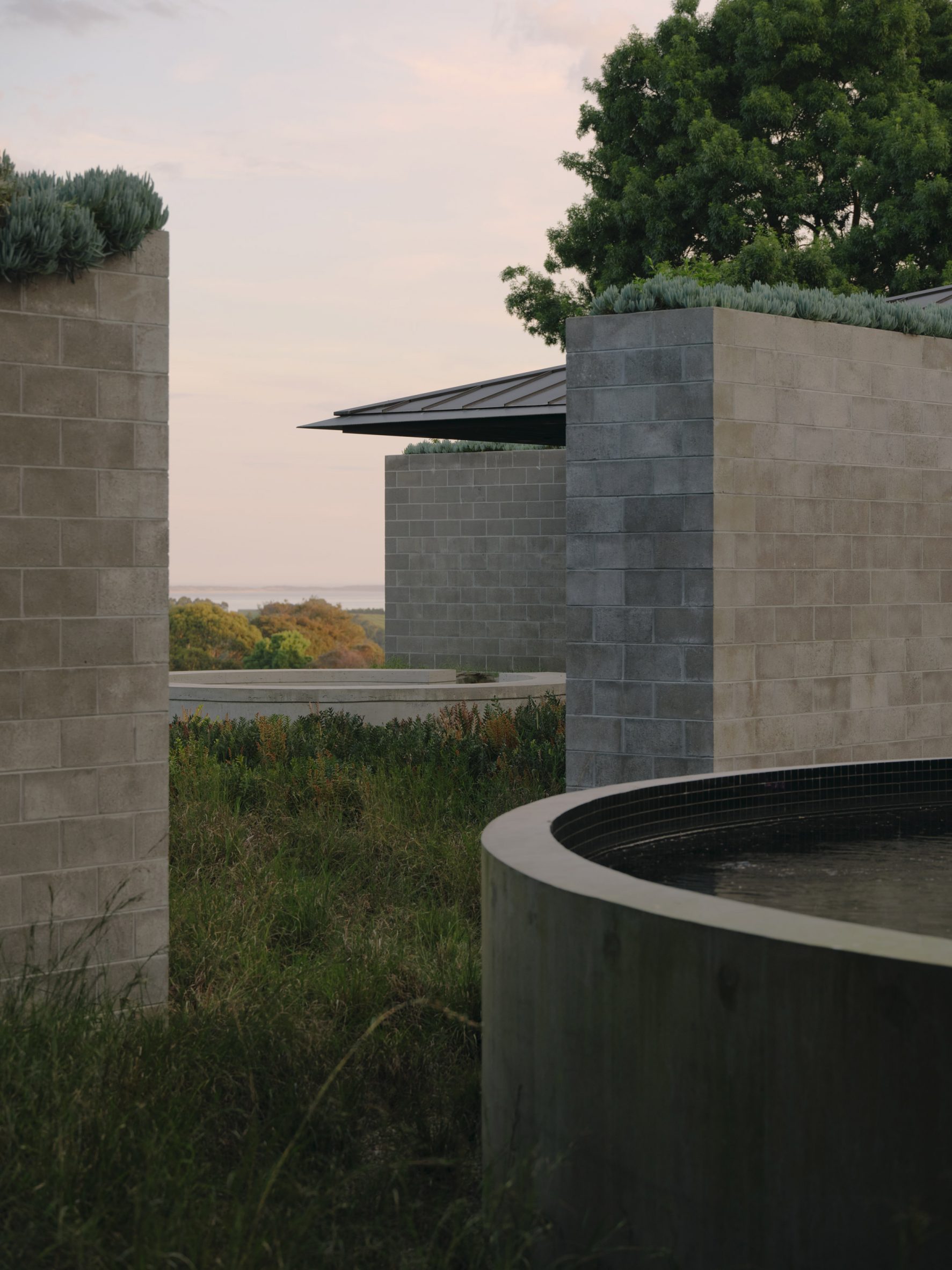
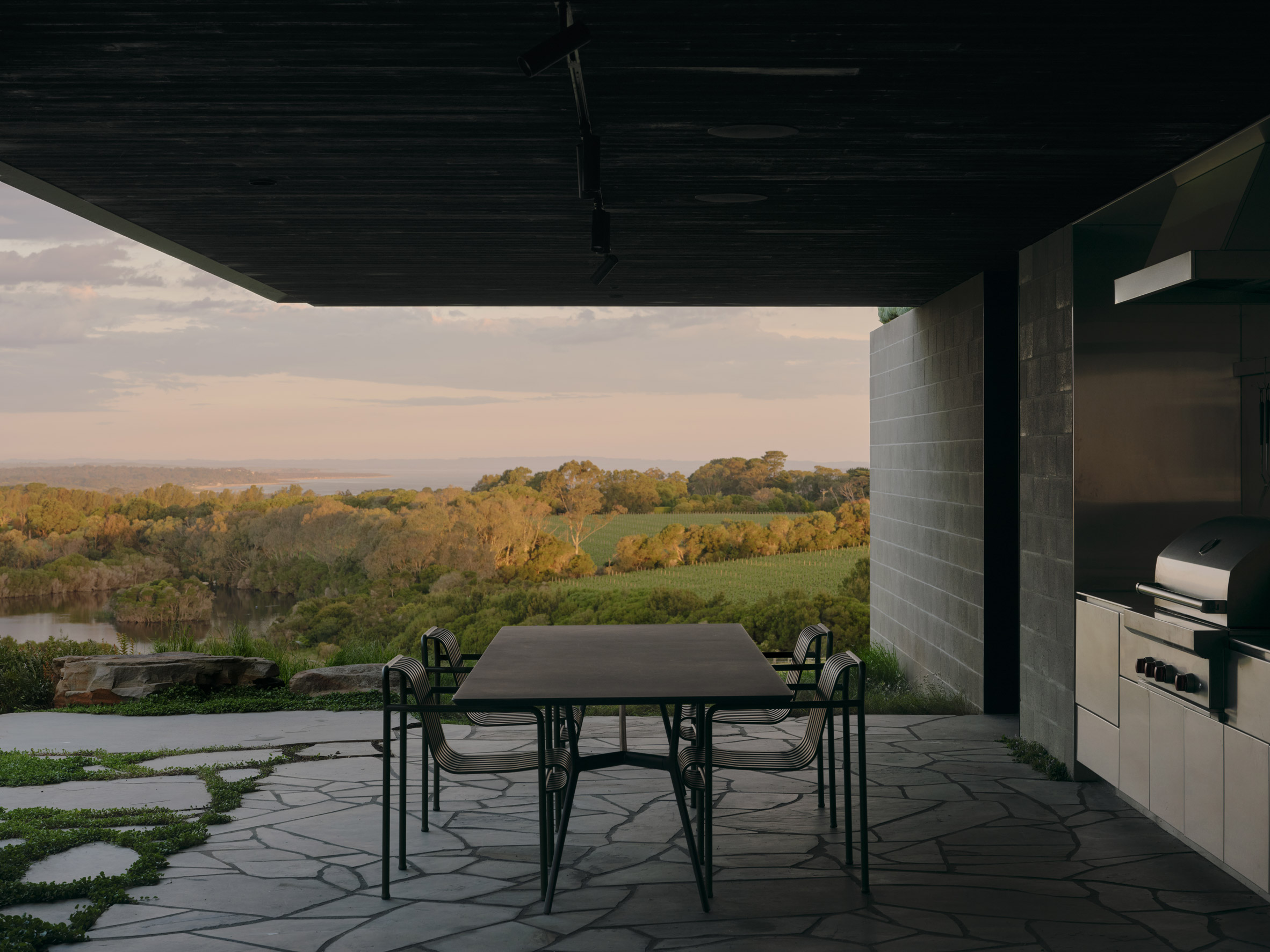
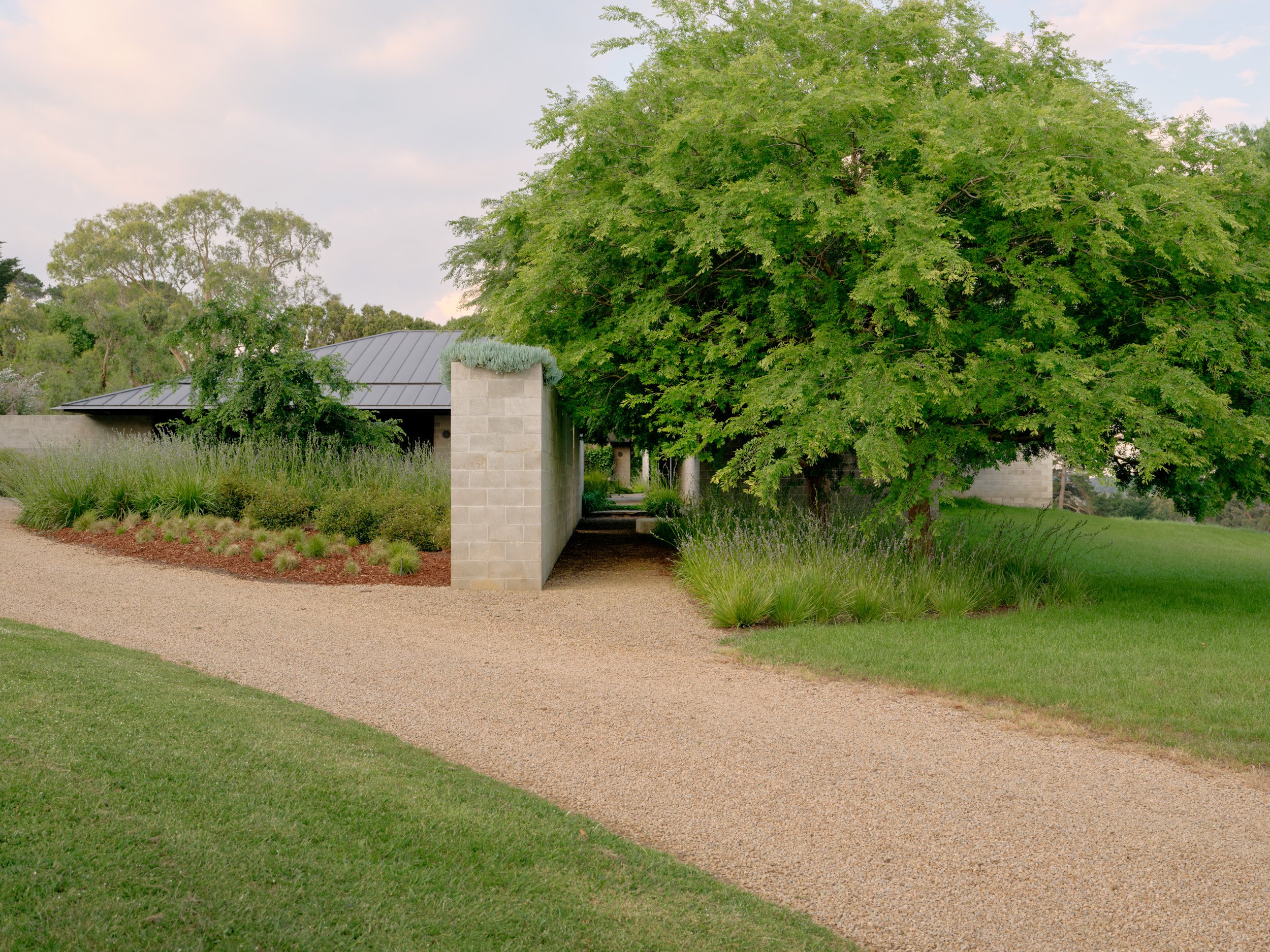
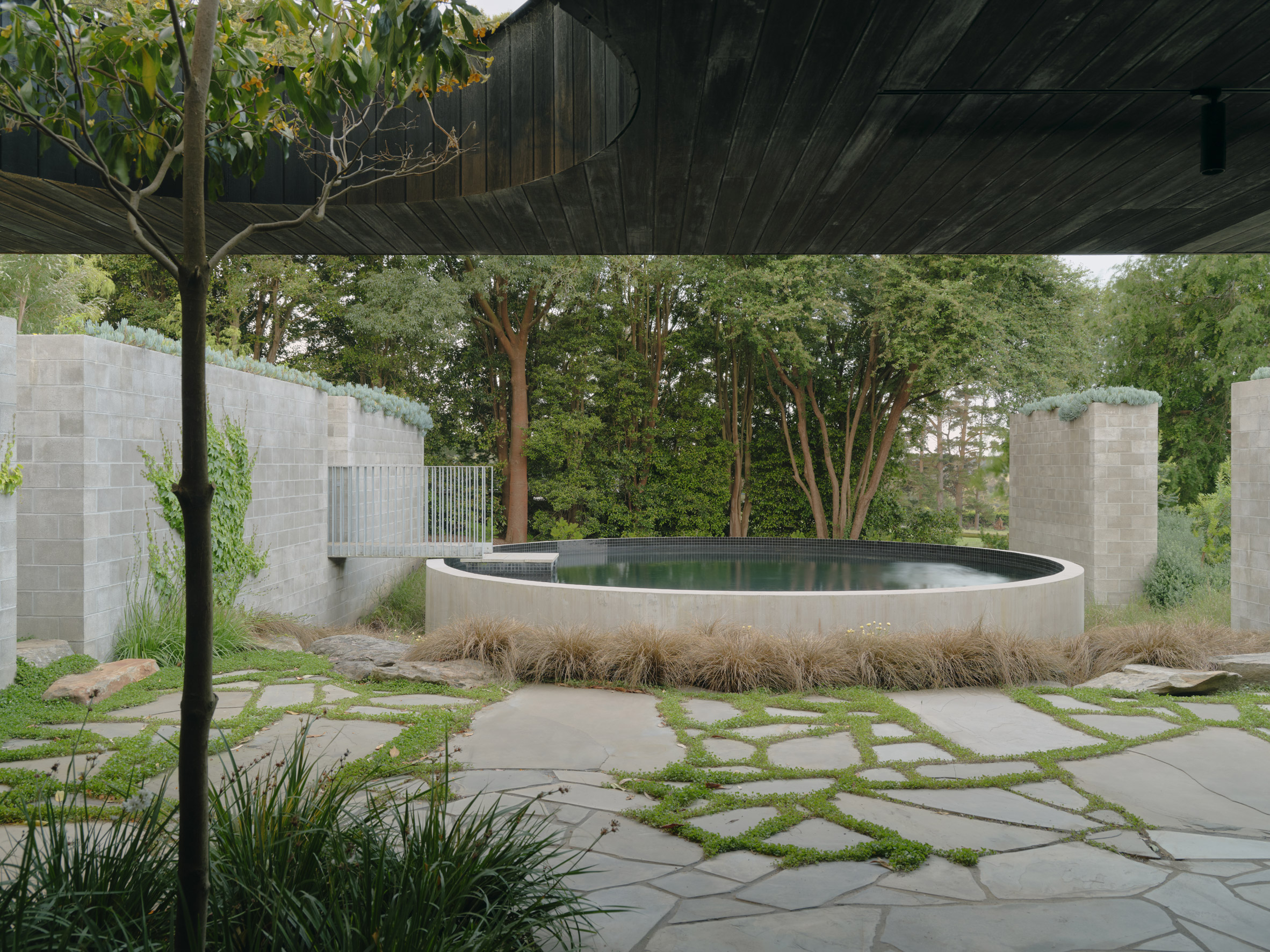




Merricks Farmhouse comprises a large open-plan living room and six bedrooms, which centre around a courtyard. The home is formed of exposed concrete blockwork, chosen by the studios to help reduce cost and retain focus on the landscape. "We used standard concrete construction blockwork to reduce cost and negate the need for extra finishing trades – materials generally were chosen to reduce maintenance and recede from the view both internally and externally," said Nielsen Jenkins co-founder Lachlan Nielsen. "As in a typical Australian farmhouse, the roof is visible and appears to float over the shadows below, but the walls it sits on will recede further and further as the landscape takes over."
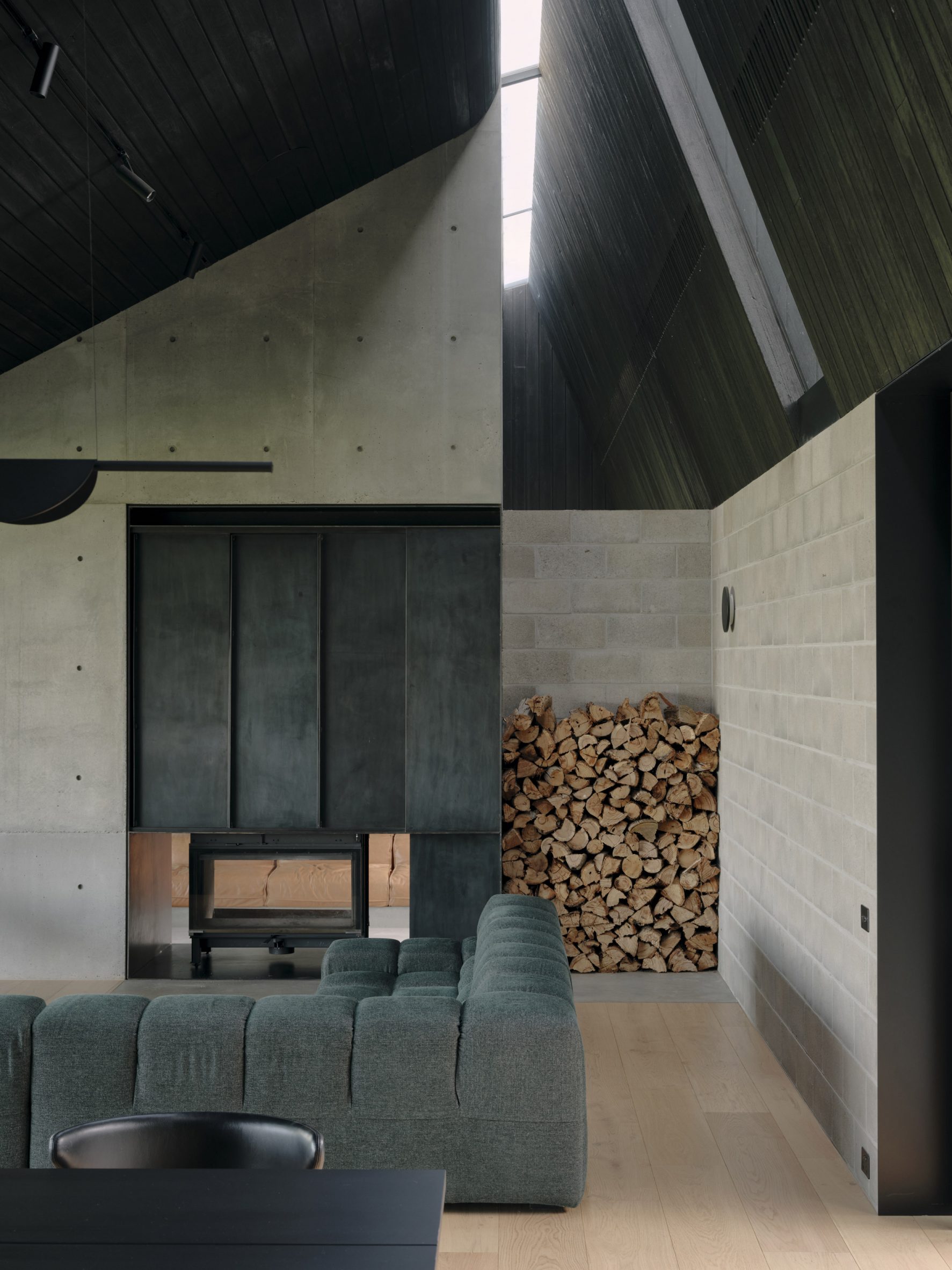
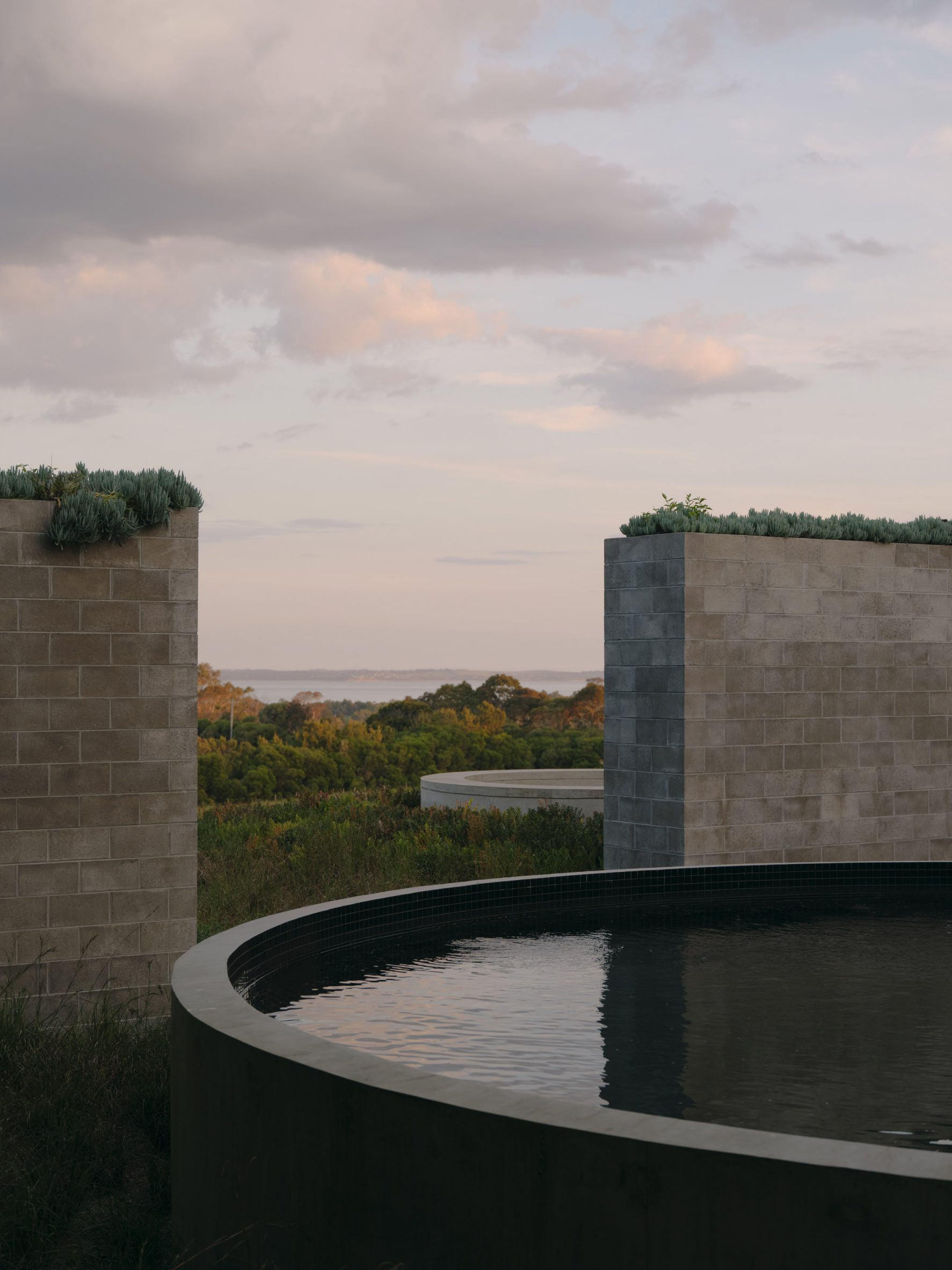
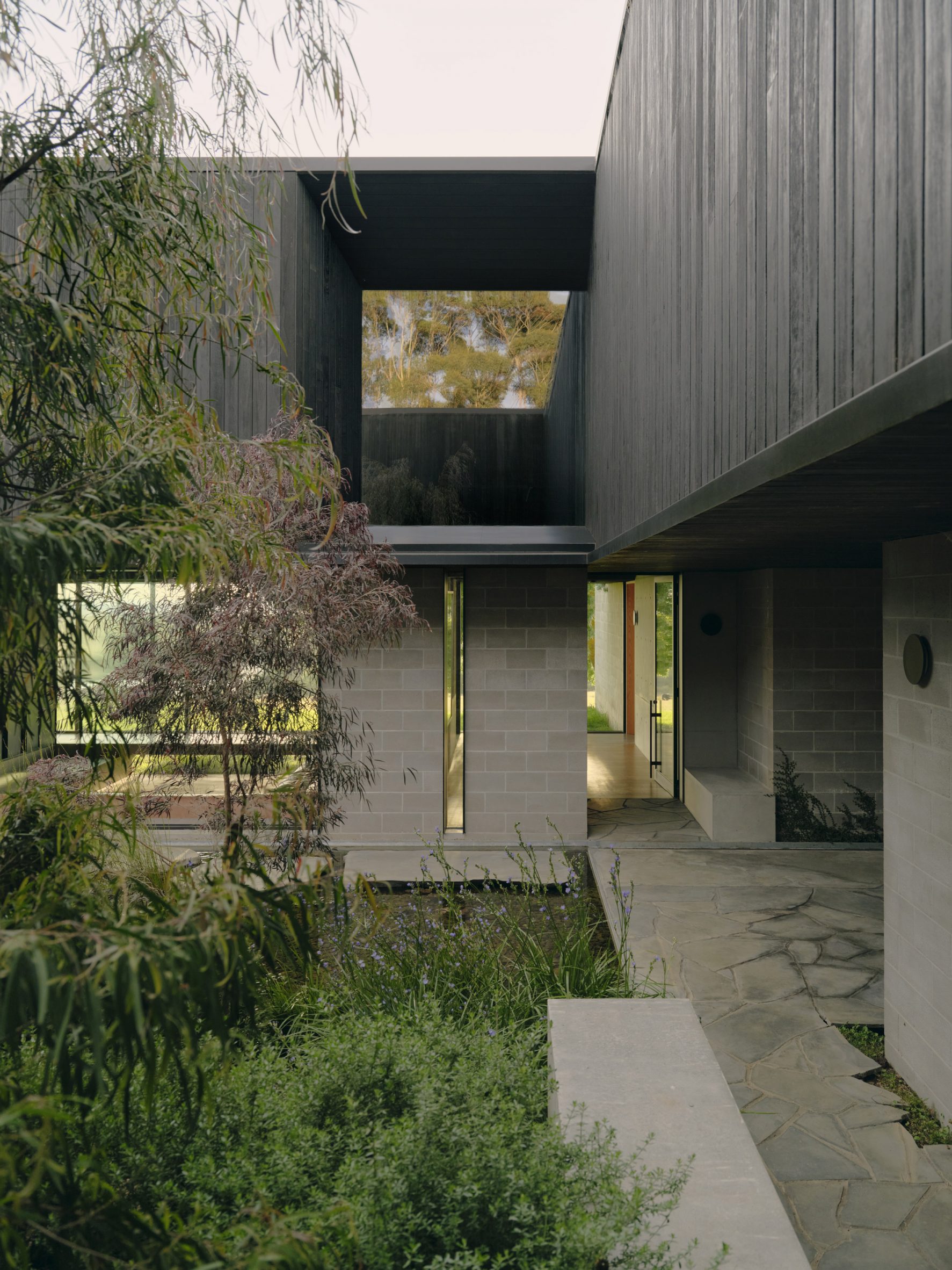
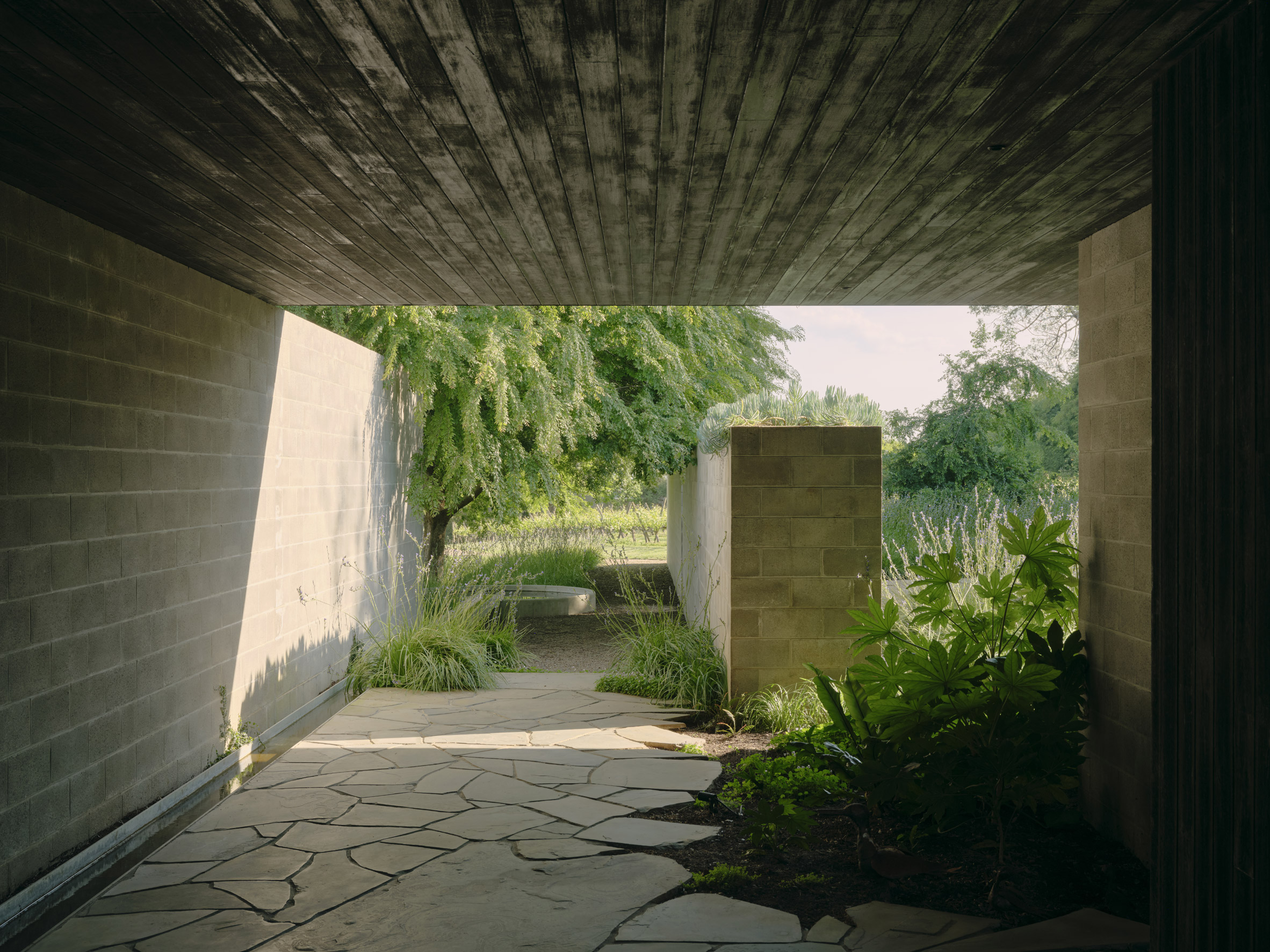




Tucked behind a walled entry court, a gravel path leads to the lush green courtyard at the centre of Merricks Farmhouse, which the team conceived as the most important "room". Rather than wrapping this courtyard with a single volume, the architects split the home into a series of blocks separated by small gardens, allowing glimpses through to the surroundings while maintaining a sense of privacy.
snip







Low-slung roof shelters blockwork home on Mornington Peninsula, Melbourne, Australia
https://www.dezeen.com/2023/09/13/merricks-farmhouse-michael-lumby-nielsen-jenkins/


A low-slung roof with deep eaves shelters Merricks Farmhouse, a concrete-block home in Australia designed by South African studio Michael Lumby Architecture with Brisbane practice Nielsen Jenkins. Overlooking vineyards and the sea on the Mornington Peninsula in southeast Melbourne, the dwelling references local farmhouses and is designed by Michael Lumby Architecture and Nielsen Jenkins as a "refuge" in its exposed coastal setting.




"As an outsider, I found myself being intrigued by the typical Australian farmhouse and perhaps in a naive way began to romanticise it with its low-slung roof, wrap-around porch and deep eaves," explained architect Michael Lumby. "With its siting on a prominent hilltop with no other buildings around, we were interested in how we could abstract this characteristic, distilling the notion of the Australian farmhouse into one idea – a line of shadow in the landscape," he added.




Merricks Farmhouse comprises a large open-plan living room and six bedrooms, which centre around a courtyard. The home is formed of exposed concrete blockwork, chosen by the studios to help reduce cost and retain focus on the landscape. "We used standard concrete construction blockwork to reduce cost and negate the need for extra finishing trades – materials generally were chosen to reduce maintenance and recede from the view both internally and externally," said Nielsen Jenkins co-founder Lachlan Nielsen. "As in a typical Australian farmhouse, the roof is visible and appears to float over the shadows below, but the walls it sits on will recede further and further as the landscape takes over."




Tucked behind a walled entry court, a gravel path leads to the lush green courtyard at the centre of Merricks Farmhouse, which the team conceived as the most important "room". Rather than wrapping this courtyard with a single volume, the architects split the home into a series of blocks separated by small gardens, allowing glimpses through to the surroundings while maintaining a sense of privacy.
snip







September 21, 2023
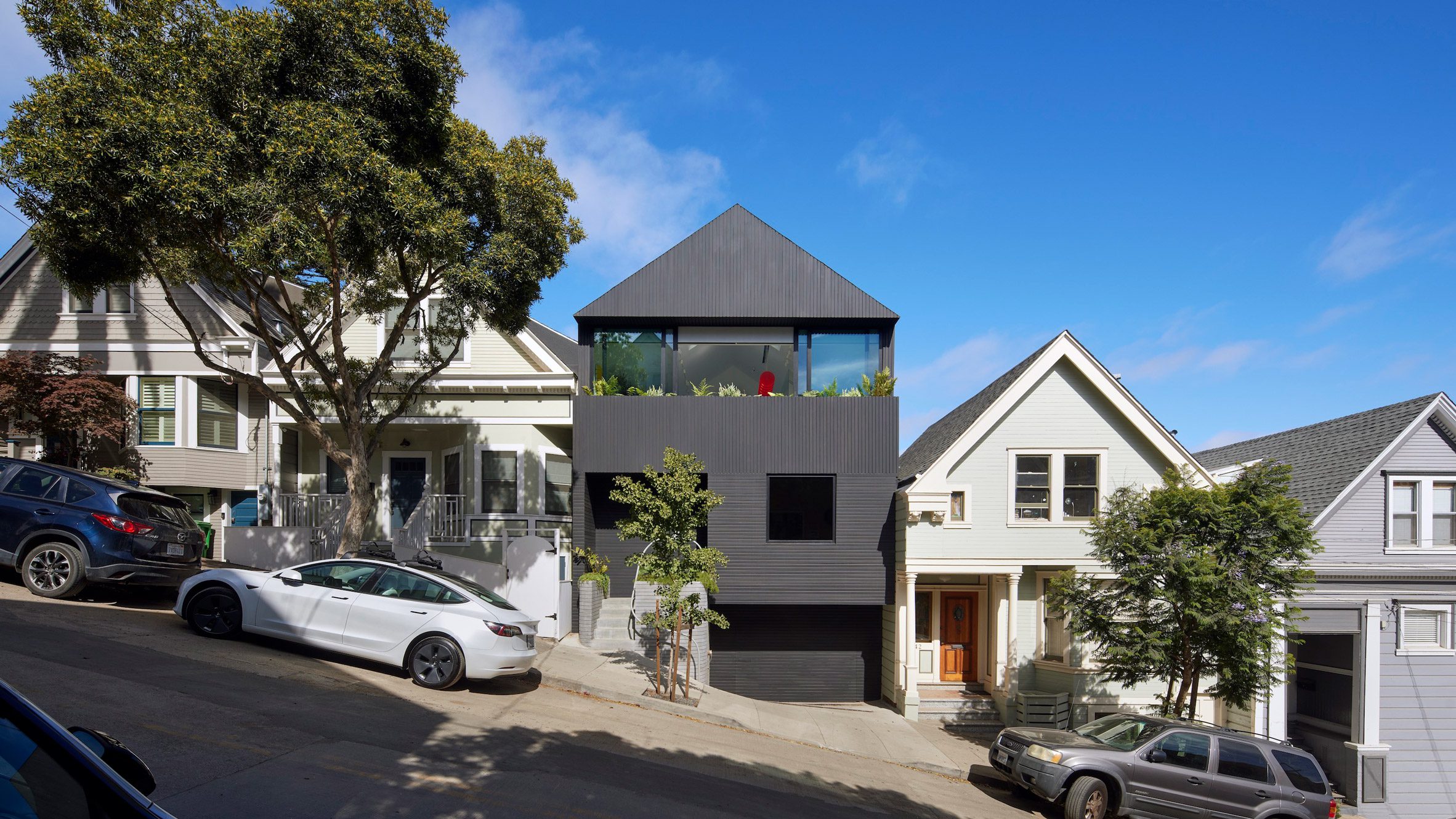
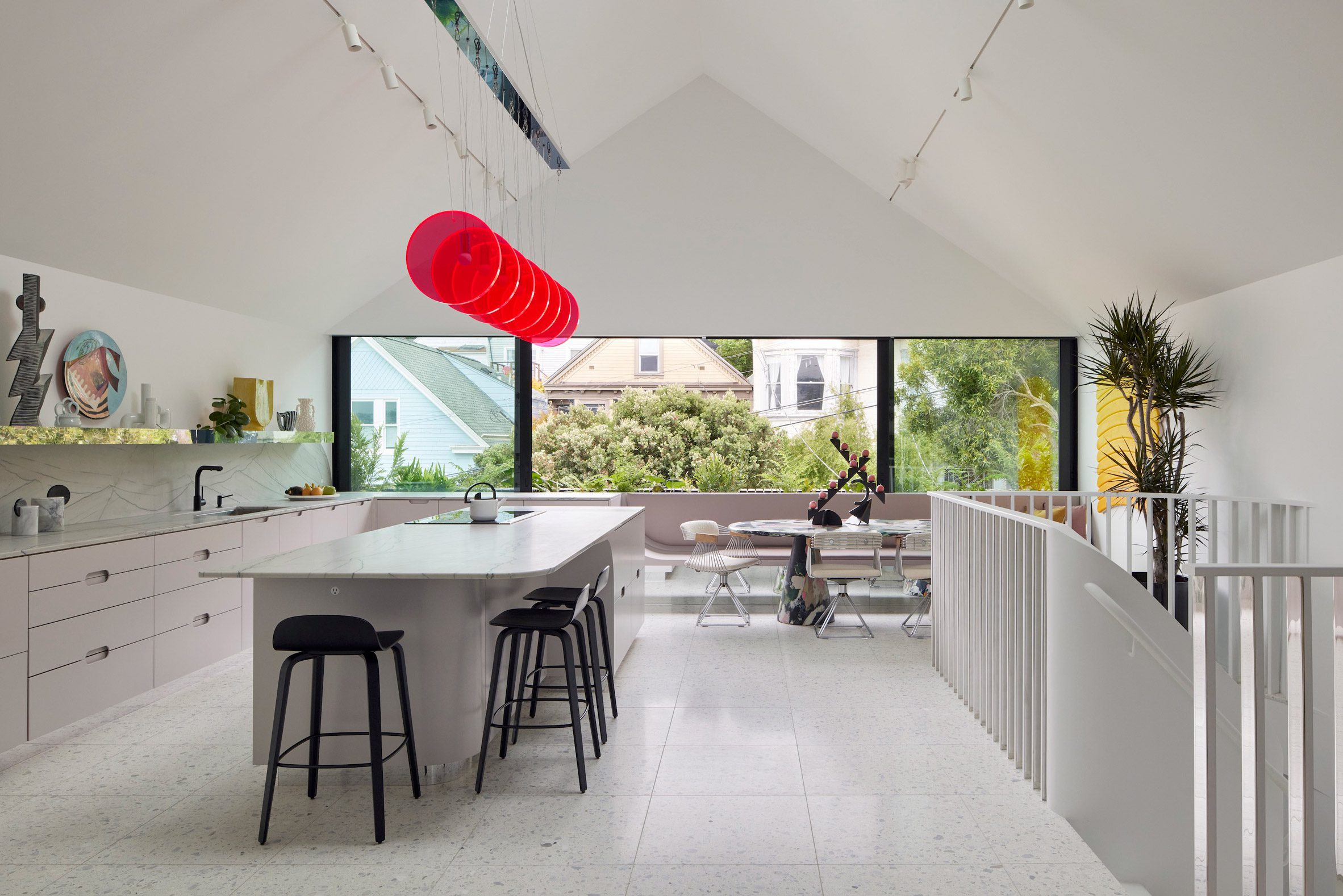



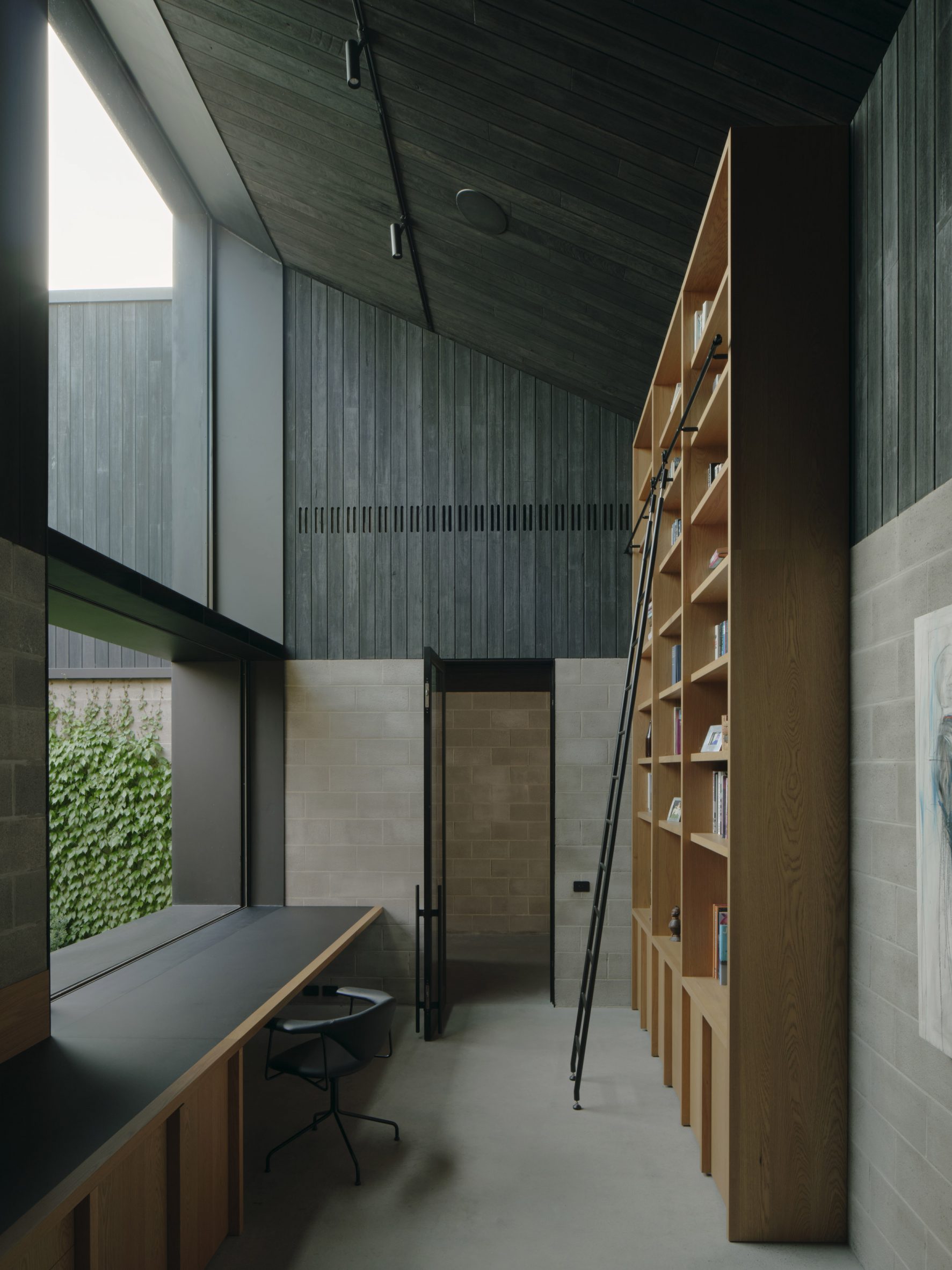
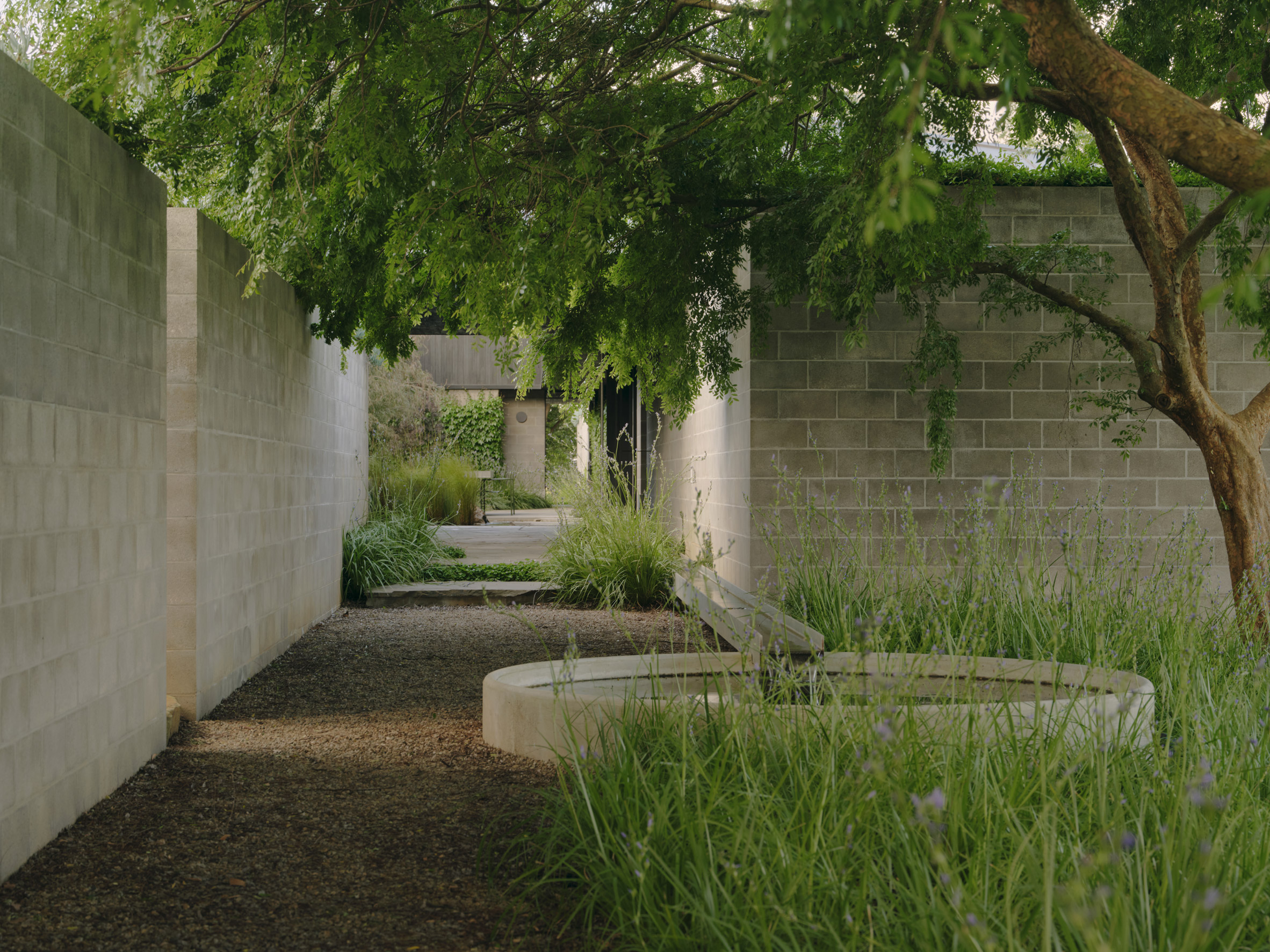
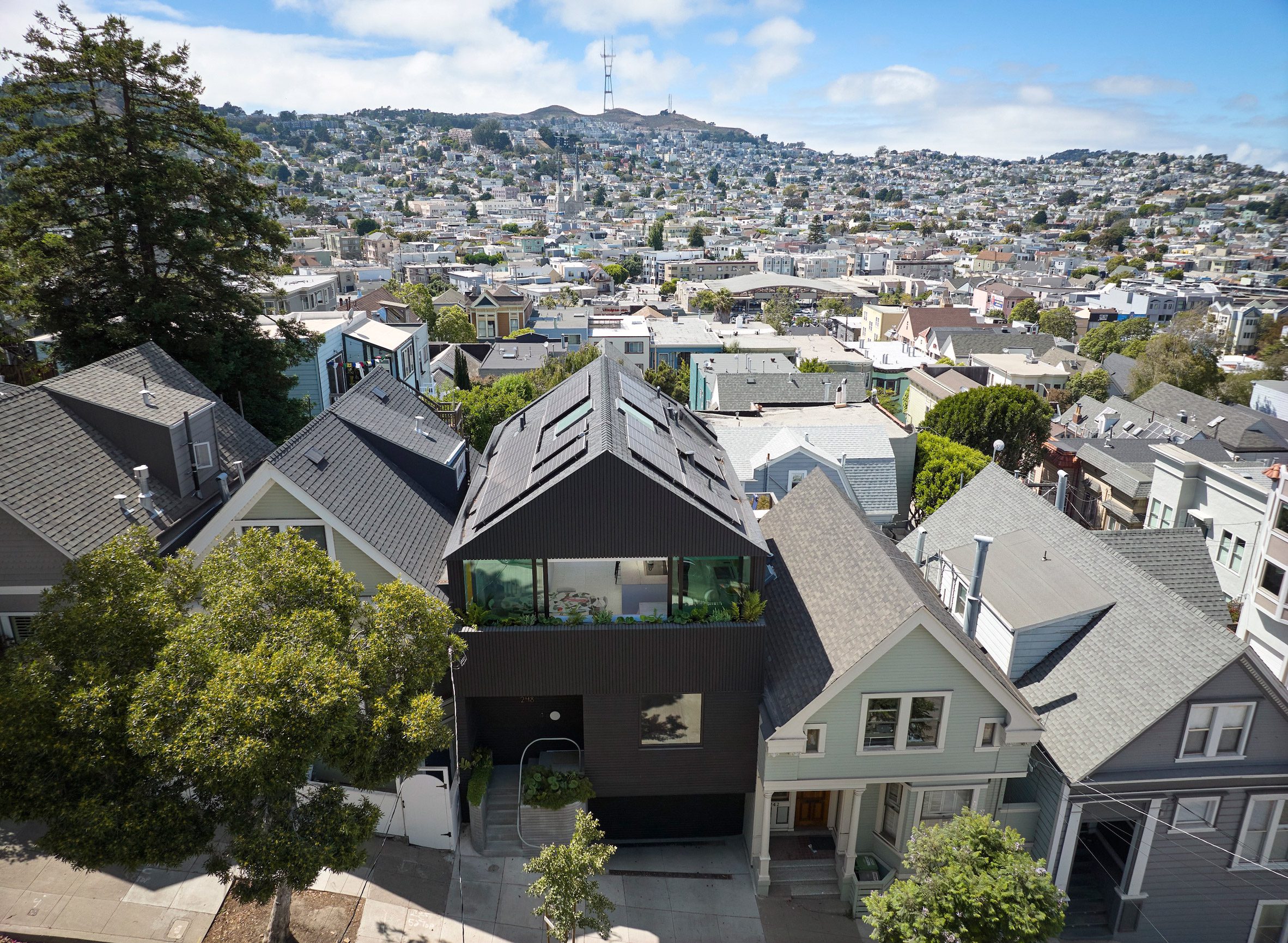
Mork-Ulnes Architects has completed the Silver Lining House, a crisp, gabled home clad in black-stained cedar that was designed for an architectural photographer and interior designer. Located on a sloped site in San Francisco's Bernal Heights neighbourhood, the house sits among Victorian and Edwardian homes that line the area's hilly streets.
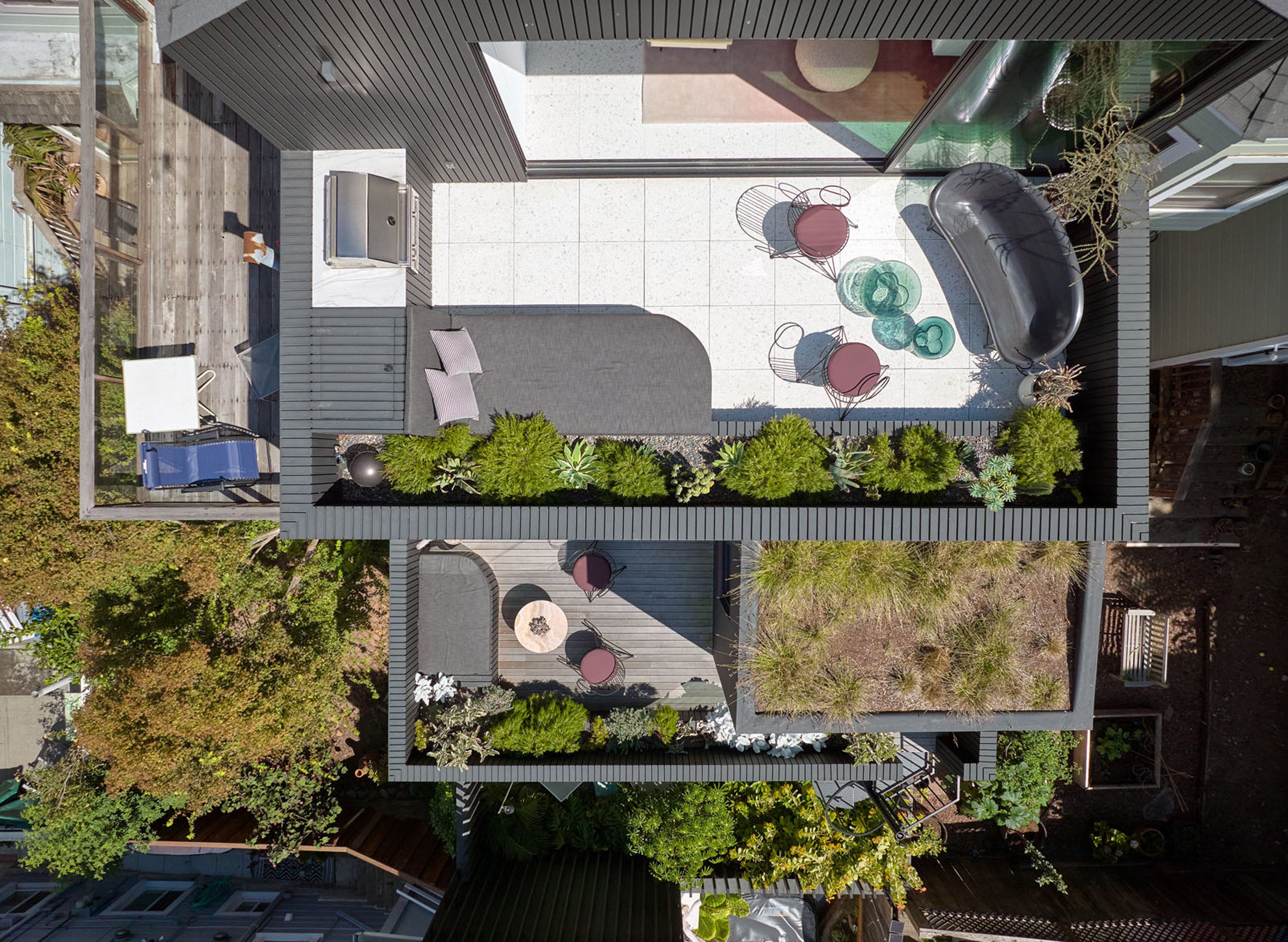


The project was designed for architectural photographer Bruce Damonte and interior designer Alison Damonte, who have long been friends with architect Casper Mork-Ulnes, founder of Mork-Ulnes Architects. The couple, who are avid collectors, desired a home that showcased their treasured belongings and supported their creative work.
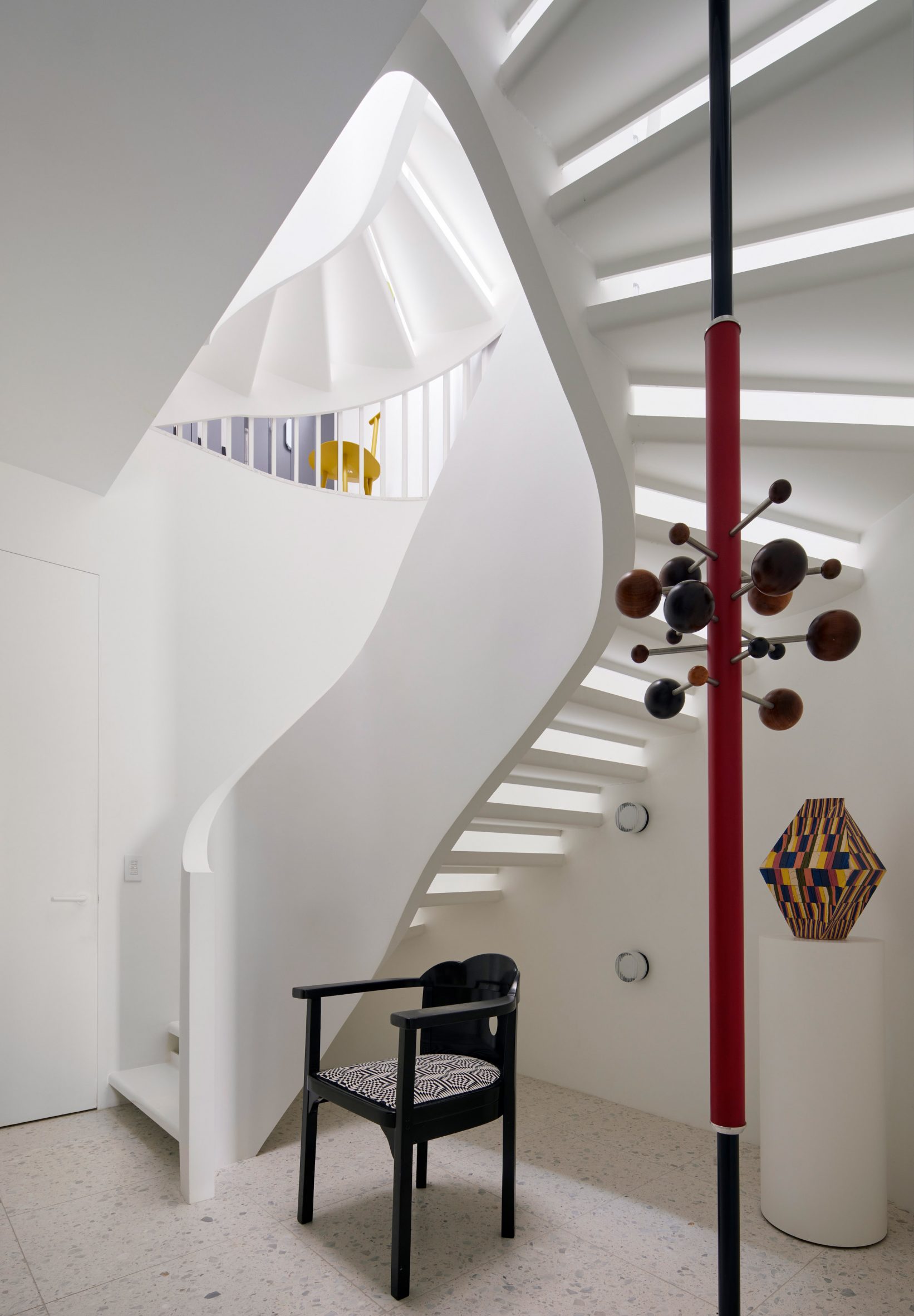



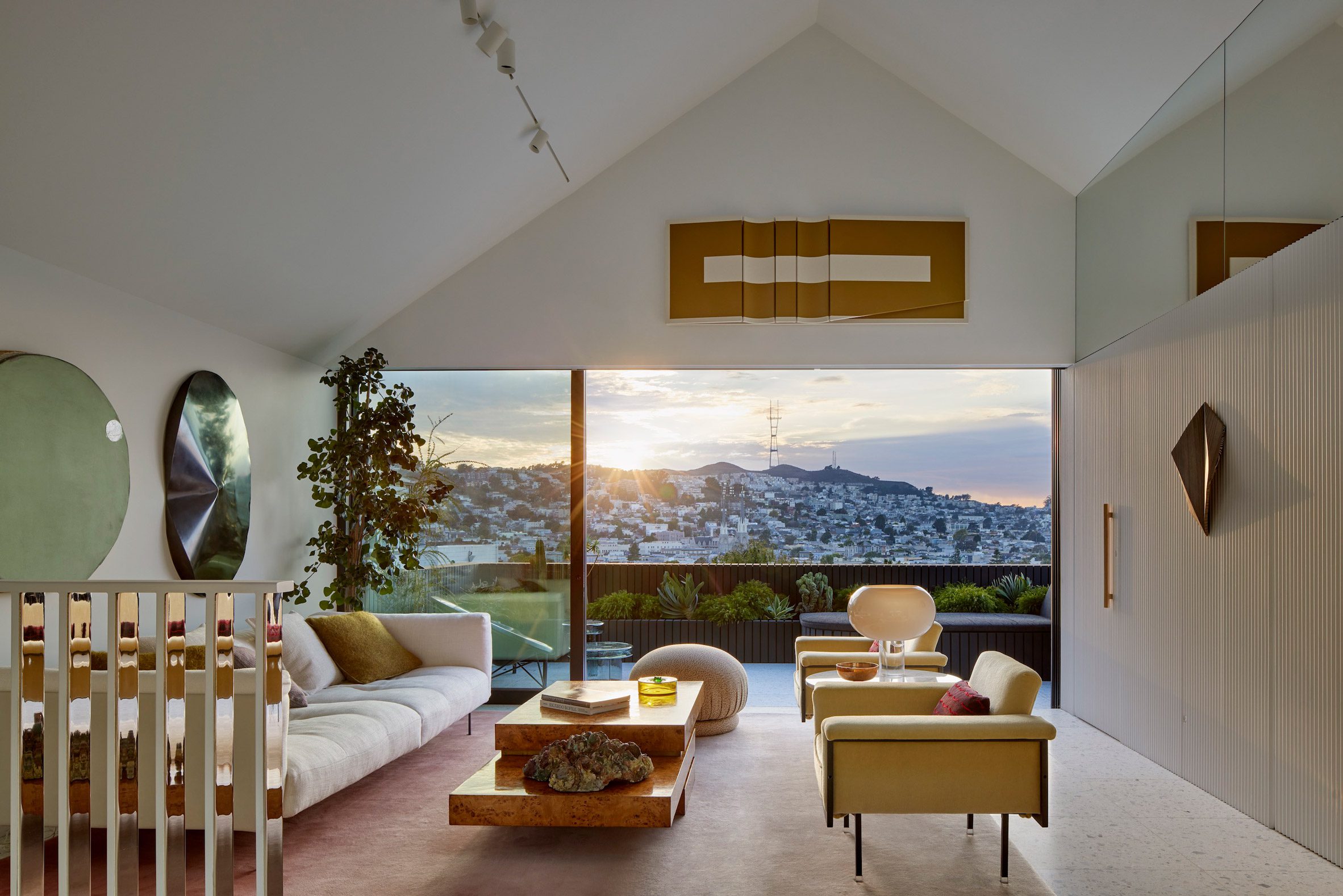
"We knew from the outset that this project would be an interesting collaboration, balancing our reductive tendencies with the more exuberant and maximalist impulses of our client/friends, whose style we had always admired and wanted to celebrate," said Casper Mork-Ulnes. The architect and his team at Mork-Ulnes Architects – which has offices in San Francisco and Oslo – conceived a home for the Damontes that "conceptually functions as a container for their furniture and art collections and a laboratory for their work".
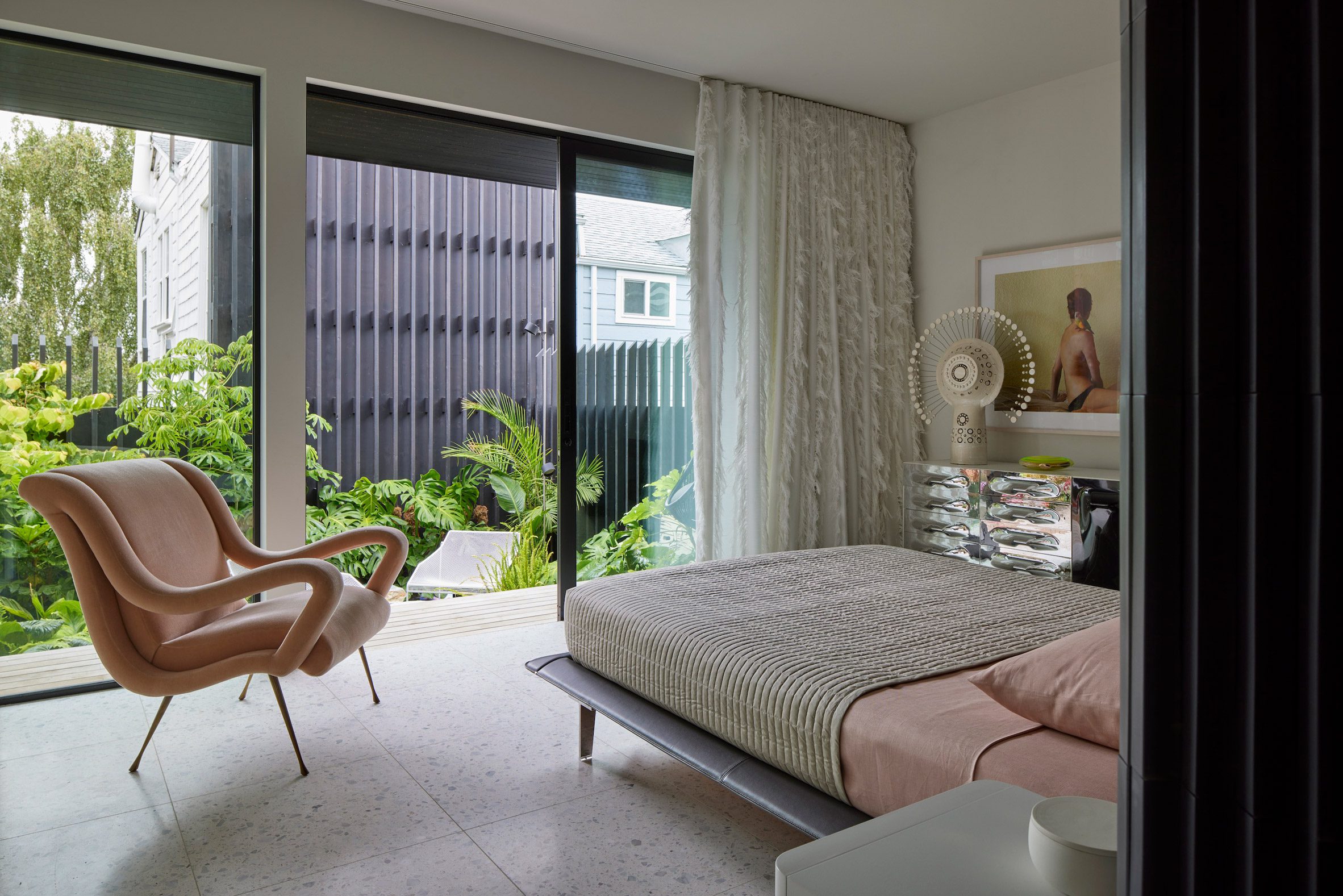
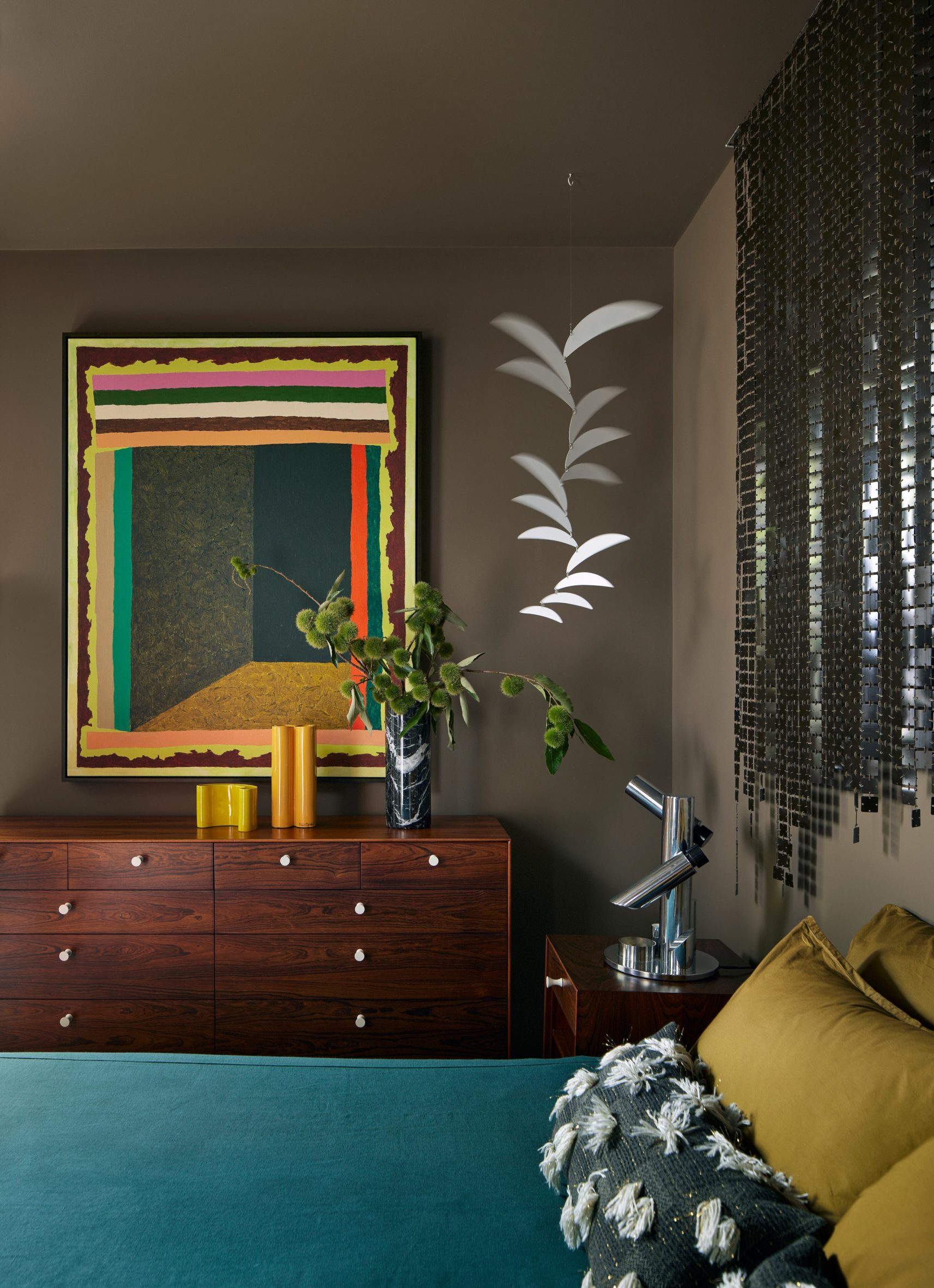




Rectangular in plan, the home rises three levels and features a crisp, gabled form. Facades are clad in strips of black-stained cedar and are punctured with openings of varying sizes. The architects took cues from the surrounding context when deciding on key design elements such as scale, massing and cladding – but they also strayed from the norm.
snip
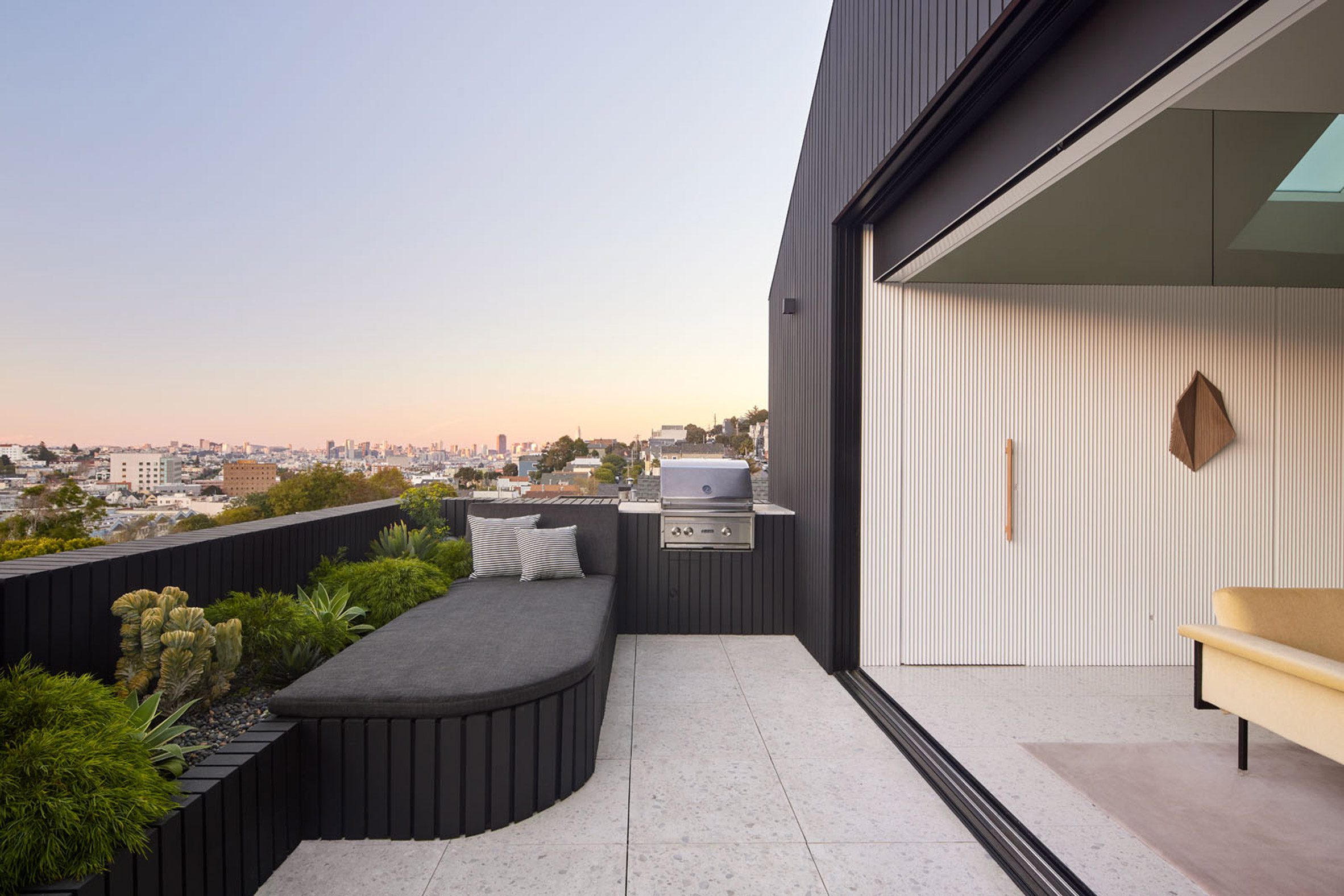
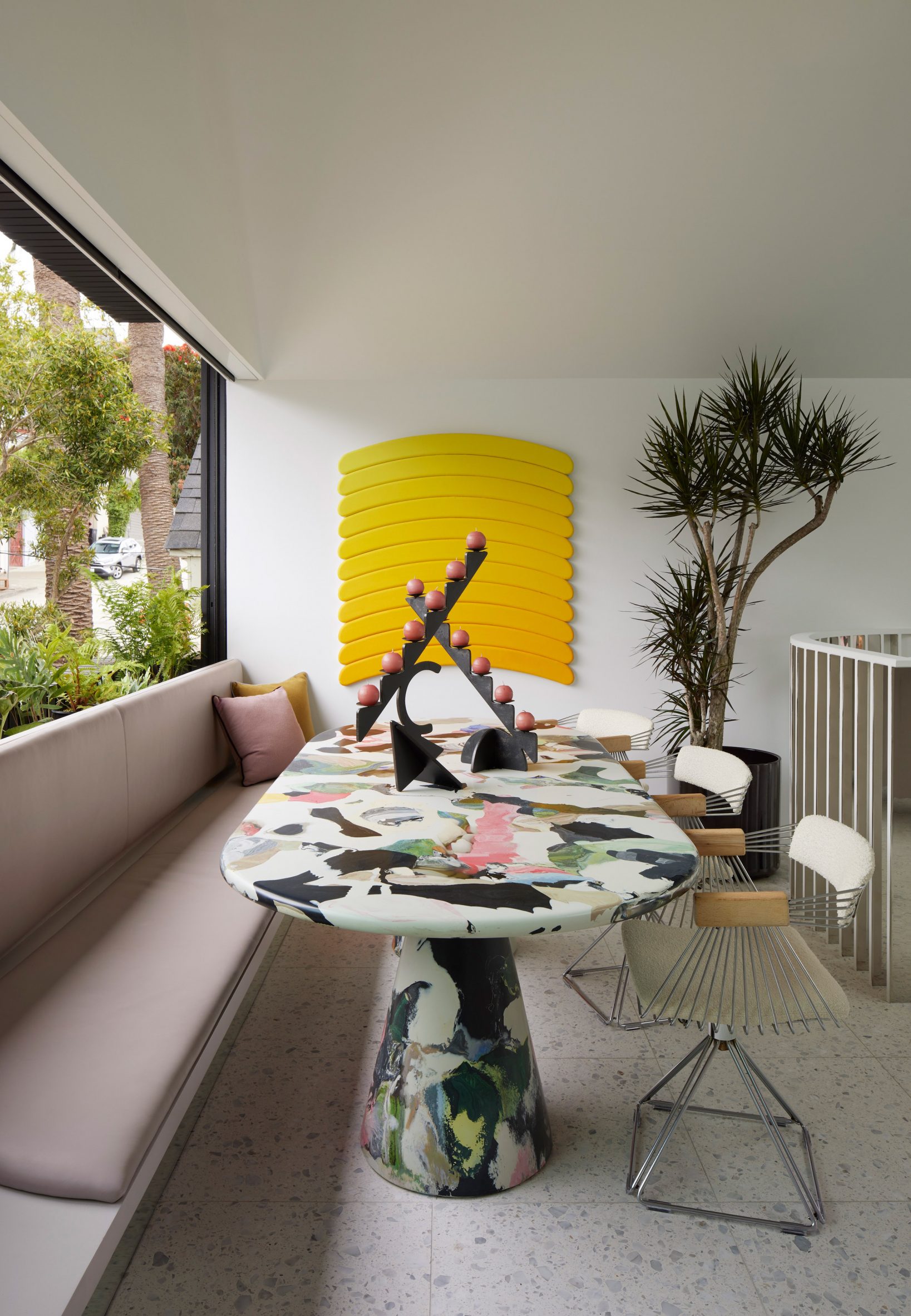







Mork-Ulnes creates black San Francisco house to be "laboratory" for creative work
https://www.dezeen.com/2023/09/19/mork-ulnes-black-house-san-francisco/


Mork-Ulnes Architects has completed the Silver Lining House, a crisp, gabled home clad in black-stained cedar that was designed for an architectural photographer and interior designer. Located on a sloped site in San Francisco's Bernal Heights neighbourhood, the house sits among Victorian and Edwardian homes that line the area's hilly streets.


The project was designed for architectural photographer Bruce Damonte and interior designer Alison Damonte, who have long been friends with architect Casper Mork-Ulnes, founder of Mork-Ulnes Architects. The couple, who are avid collectors, desired a home that showcased their treasured belongings and supported their creative work.



"We knew from the outset that this project would be an interesting collaboration, balancing our reductive tendencies with the more exuberant and maximalist impulses of our client/friends, whose style we had always admired and wanted to celebrate," said Casper Mork-Ulnes. The architect and his team at Mork-Ulnes Architects – which has offices in San Francisco and Oslo – conceived a home for the Damontes that "conceptually functions as a container for their furniture and art collections and a laboratory for their work".




Rectangular in plan, the home rises three levels and features a crisp, gabled form. Facades are clad in strips of black-stained cedar and are punctured with openings of varying sizes. The architects took cues from the surrounding context when deciding on key design elements such as scale, massing and cladding – but they also strayed from the norm.
snip







September 20, 2023
Label: Wichita – WEBB151T
Format: Vinyl, 12", 45 RPM, Single, Reissue
Country: UK
Released: 17 Sept 2007
Genre: Electronic, Rock
Style: Alternative Rock, Breakbeat, Lo-Fi, Electro


Label: Wichita – WEBB107T, Cooperative Music – WEBB107T
Format: Vinyl, 12"
Country: UK
Released: Aug 2006
Genre: Electronic, Rock
Style: Electro, Tech House, Indie Rock, Disco


Peter Bjorn and John - Young Folks 12-inch remixes (2006 and 2007)
Young Folks (Phones Problem Child Mix)
https://soundcloud.com/peterbjornjohn/young-folks-phones-problem
https://soundcloud.com/peterbjornjohn/young-folks-phones-problem
Label: Wichita – WEBB151T
Format: Vinyl, 12", 45 RPM, Single, Reissue
Country: UK
Released: 17 Sept 2007
Genre: Electronic, Rock
Style: Alternative Rock, Breakbeat, Lo-Fi, Electro


Label: Wichita – WEBB107T, Cooperative Music – WEBB107T
Format: Vinyl, 12"
Country: UK
Released: Aug 2006
Genre: Electronic, Rock
Style: Electro, Tech House, Indie Rock, Disco


September 20, 2023

Pandemic unemployment programs are significantly underreported, giving a misimpression about their effectiveness.
https://prospect.org/economy/2023-09-20-what-census-poverty-estimates-may-miss/

Last week, the Census Bureau released new data showing that poverty spiked in 2022 following the expiration of prominent pandemic programs. The supplemental poverty rate—a measure that integrates taxes paid, cash and in-kind benefits received, and basic costs like medical expenses—rose from a record low of 7.8 percent in the prior year up to 12.4 percent. All the progress made in reducing poverty over the previous several years was officially confirmed undone.
In particular, the increase in child poverty due to the expired 2021 Child Tax Credit expansion drove media reports, leading to strong responses from lawmakers. Members of Congress and the Biden administration correctly identified the need to make the CTC fully refundable again (i.e., guarantee the full credit amount to children regardless of their household income level). But missing from the conversation, notably, was just how effective the pandemic unemployment benefit programs were at preventing poverty.
For much of 2021, unemployment insurance (UI) benefit eligibility was expanded to more adequately cover gig workers, self-employed individuals, and those refusing hazardous work conditions. Claimants also saw their weekly benefit sizes topped up by an additional $300, down from a $600 boost in 2020 at the height of the pandemic but still significant (and much more than the expanded CTC). Well over ten million claimants received these benefits in 2021. One might expect the expanded UI in 2021 to have a greater impact on poverty than the expanded CTC, given that several hundred billion dollars in UI benefits were distributed to workers who would have otherwise seen dramatic drops in their income.

But the Census numbers show that the pandemic unemployment insurance benefits produced a smaller reduction in poverty. The Census Bureau found that stimulus payments and the expanded CTC prevented 8.9 million and 5.3 million people, respectively, from falling into poverty in 2021. Unemployment insurance, in contrast, kept only 2.3 million people out of poverty, under half of the CTC’s determined impact. These Census estimates may understate the full effect of unemployment insurance. The reason is technical: The Census Bureau may be undercounting the pandemic benefits sent to Americans.
snip
What Census Poverty Estimates May Miss

Pandemic unemployment programs are significantly underreported, giving a misimpression about their effectiveness.
https://prospect.org/economy/2023-09-20-what-census-poverty-estimates-may-miss/

Last week, the Census Bureau released new data showing that poverty spiked in 2022 following the expiration of prominent pandemic programs. The supplemental poverty rate—a measure that integrates taxes paid, cash and in-kind benefits received, and basic costs like medical expenses—rose from a record low of 7.8 percent in the prior year up to 12.4 percent. All the progress made in reducing poverty over the previous several years was officially confirmed undone.
In particular, the increase in child poverty due to the expired 2021 Child Tax Credit expansion drove media reports, leading to strong responses from lawmakers. Members of Congress and the Biden administration correctly identified the need to make the CTC fully refundable again (i.e., guarantee the full credit amount to children regardless of their household income level). But missing from the conversation, notably, was just how effective the pandemic unemployment benefit programs were at preventing poverty.
For much of 2021, unemployment insurance (UI) benefit eligibility was expanded to more adequately cover gig workers, self-employed individuals, and those refusing hazardous work conditions. Claimants also saw their weekly benefit sizes topped up by an additional $300, down from a $600 boost in 2020 at the height of the pandemic but still significant (and much more than the expanded CTC). Well over ten million claimants received these benefits in 2021. One might expect the expanded UI in 2021 to have a greater impact on poverty than the expanded CTC, given that several hundred billion dollars in UI benefits were distributed to workers who would have otherwise seen dramatic drops in their income.

But the Census numbers show that the pandemic unemployment insurance benefits produced a smaller reduction in poverty. The Census Bureau found that stimulus payments and the expanded CTC prevented 8.9 million and 5.3 million people, respectively, from falling into poverty in 2021. Unemployment insurance, in contrast, kept only 2.3 million people out of poverty, under half of the CTC’s determined impact. These Census estimates may understate the full effect of unemployment insurance. The reason is technical: The Census Bureau may be undercounting the pandemic benefits sent to Americans.
snip
September 20, 2023

The only way the UAW’s strategy of rejecting voluntary overtime can work is if Ford, GM, and Stellantis lack enough workers to make cars.
https://prospect.org/labor/2023-09-20-big-threes-labor-shortages-uaw/

We’re five days into the United Auto Workers strike of Ford, GM, and Stellantis, and two days from a second round. UAW president Shawn Fain has announced that workers at more plants will “stand up” and walk out if substantial progress is not made in negotiations by noon on Friday. But workers who are still on the job have found their own way to put pressure on the Big Three, by exploiting their long-standing worker shortages. Labor Notes reports on autoworkers’ strategy of “Eight and Skate,” which means working their shifts and then refusing voluntary overtime, which is routinely offered by the Big Three. Working your shift and then leaving work (in other words, doing exactly what it is you were hired to do) shouldn’t really be debilitating to the employer. In this case, it is.
The reason is understaffing: There are simply not enough workers at many auto plants to meet production goals. As a result, the companies turn to existing workers, paying them time and a half, or even double and triple time, to stay on the job. Management at some facilities consistently asks workers to work through their breaks or even lunch. By only working eight hours a day, then, autoworkers can reduce output at the plants. It comes at a cost to these employees, but it’s their way to contribute to the labor effort. And it’s been successful in shutting down some plants over the past weekend, when they would normally be open.
The auto companies could counter by making overtime mandatory, though workers would have to be notified well in advance. But the other thing the companies could do—what they could have done for years, more precisely—is simply hire more autoworkers. If your company is relying on overtime work, the problem is a lack of staff. This is not a new issue bound up with the labor shortages post-pandemic; it’s been this way for many years. As UAW leadership has explained, these companies have enjoyed record profits in recent years and ramped up pay packages to top executives. For which reason, they should have no problem increasing staff levels, or increasing pay to their workers. The companies have cried poverty, but if they are paying double-time rates for extra hours because demand is so high, it’s hard to square that claim. It would be far cheaper to pay a new employee at the base hourly rate than to pay an established worker for an hour of overtime.

So why don’t the companies want to hire more staff? Simply put, the benefits workers get on health care and retirement and paid time off add costs to the business. This is partially a function of the United States being the only major industrialized nation to not provide health care for workers. When employers bear that burden, they want to minimize the expense. But at some point, so much overtime is being paid out that the company isn’t avoiding costs at all. The heavy use of overtime work also calls into question the idea that the switch to electric vehicles will wipe out the automotive labor market. Under this theory, because EVs have fewer parts, fewer workers will be needed to produce and assemble them—about 30 percent fewer by one account. And if having fewer car parts leads to less wearing out of those parts, auto mechanics could go out of business; and if people mostly charge at home, gas stations could gradually close up shop.
snip
The Big Three's Labor Shortages

The only way the UAW’s strategy of rejecting voluntary overtime can work is if Ford, GM, and Stellantis lack enough workers to make cars.
https://prospect.org/labor/2023-09-20-big-threes-labor-shortages-uaw/

We’re five days into the United Auto Workers strike of Ford, GM, and Stellantis, and two days from a second round. UAW president Shawn Fain has announced that workers at more plants will “stand up” and walk out if substantial progress is not made in negotiations by noon on Friday. But workers who are still on the job have found their own way to put pressure on the Big Three, by exploiting their long-standing worker shortages. Labor Notes reports on autoworkers’ strategy of “Eight and Skate,” which means working their shifts and then refusing voluntary overtime, which is routinely offered by the Big Three. Working your shift and then leaving work (in other words, doing exactly what it is you were hired to do) shouldn’t really be debilitating to the employer. In this case, it is.
The reason is understaffing: There are simply not enough workers at many auto plants to meet production goals. As a result, the companies turn to existing workers, paying them time and a half, or even double and triple time, to stay on the job. Management at some facilities consistently asks workers to work through their breaks or even lunch. By only working eight hours a day, then, autoworkers can reduce output at the plants. It comes at a cost to these employees, but it’s their way to contribute to the labor effort. And it’s been successful in shutting down some plants over the past weekend, when they would normally be open.
The auto companies could counter by making overtime mandatory, though workers would have to be notified well in advance. But the other thing the companies could do—what they could have done for years, more precisely—is simply hire more autoworkers. If your company is relying on overtime work, the problem is a lack of staff. This is not a new issue bound up with the labor shortages post-pandemic; it’s been this way for many years. As UAW leadership has explained, these companies have enjoyed record profits in recent years and ramped up pay packages to top executives. For which reason, they should have no problem increasing staff levels, or increasing pay to their workers. The companies have cried poverty, but if they are paying double-time rates for extra hours because demand is so high, it’s hard to square that claim. It would be far cheaper to pay a new employee at the base hourly rate than to pay an established worker for an hour of overtime.

So why don’t the companies want to hire more staff? Simply put, the benefits workers get on health care and retirement and paid time off add costs to the business. This is partially a function of the United States being the only major industrialized nation to not provide health care for workers. When employers bear that burden, they want to minimize the expense. But at some point, so much overtime is being paid out that the company isn’t avoiding costs at all. The heavy use of overtime work also calls into question the idea that the switch to electric vehicles will wipe out the automotive labor market. Under this theory, because EVs have fewer parts, fewer workers will be needed to produce and assemble them—about 30 percent fewer by one account. And if having fewer car parts leads to less wearing out of those parts, auto mechanics could go out of business; and if people mostly charge at home, gas stations could gradually close up shop.
snip
Profile Information
Gender: FemaleHometown: London
Home country: US/UK/Sweden
Current location: Stockholm, Sweden
Member since: Sun Jul 1, 2018, 07:25 PM
Number of posts: 43,349