n2doc
n2doc's JournalEngineers Solve a Biological Mystery and Boost Artificial Intelligence
Jan. 29, 2013 — By simulating 25,000 generations of evolution within computers, Cornell University engineering and robotics researchers have discovered why biological networks tend to be organized as modules -- a finding that will lead to a deeper understanding of the evolution of complexity.
The new insight also will help evolve artificial intelligence, so robot brains can acquire the grace and cunning of animals.
From brains to gene regulatory networks, many biological entities are organized into modules -- dense clusters of interconnected parts within a complex network. For decades biologists have wanted to know why humans, bacteria and other organisms evolved in a modular fashion. Like engineers, nature builds things modularly by building and combining distinct parts, but that does not explain how such modularity evolved in the first place. Renowned biologists Richard Dawkins, Günter P. Wagner, and the late Stephen Jay Gould identified the question of modularity as central to the debate over "the evolution of complexity."
For years, the prevailing assumption was simply that modules evolved because entities that were modular could respond to change more quickly, and therefore had an adaptive advantage over their non-modular competitors. But that may not be enough to explain the origin of the phenomena.
more
http://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2013/01/130130082300.htm

Revolutionary Cooling System Uses Lasers
Jan. 30, 2013 — With the latest discovery by scientists from Nanyang Technological University (NTU), current cooling systems which uses refrigerant harmful to the ozone layer could be replaced by a revolutionary cooling system using lasers.
This discovery, published and featured on the cover of the 24 January 2013 issue of Nature, could also potentially lead to a host of other innovations. This includes making huge Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) machines, unwieldy night vision goggles and satellite cameras -- all of which require extreme cooling systems -- even more compact and energy saving.
This breakthrough in laser cooling technology can even lead to the development of almost sci-fi like computer chips that cool on their own, minimising heat and thus prolonging battery life for portable devices like tablets and smart phones.
Assistant Professor Xiong Qihua from the School of Physical and Mathematical Sciences and the School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering had cooled down a semiconductor from 20 degrees Celsius down to minus 20 degrees Celsius. Before this, the cooling of semiconductors by laser has never been proven.
more
http://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2013/01/130130101932.htm
It's unclear where the heat goes, or how energy efficient this is, but if it can be put on a chip, then it could really change some tech areas.
New England fishermen face grim vote on cuts
PORTSMOUTH, N.H. (AP) — New England's fishing fleet faced grim news Wednesday as regulators meet to consider steep cuts in catch limits that fishermen warn will trigger industry collapse.
The New England Fishery Management Council was meeting in Portsmouth to decide 2013 limits on stocks including cod on Georges Bank and in the Gulf of Maine. Fishermen are facing a year-to-year 81 percent cut on the Gulf of Maine cod catch limit, to 1,249 metric tons, and 61 percent on Georges Bank cod, to 5,103 metric tons.
Fishermen who chase the region's bottom-dwelling groundfish, such as cod and flounder, say the cuts will hollow out what remains of a struggling fleet, leaving it with too few fish to make a living.
The low limit reduces the catch on a storied New England species to just a fraction of what it once was, and it also prevents fishermen from landing more plentiful species, such as haddock and pollock. That's because fishermen can't pull up the healthier groundfish without catching too much of the cod that swim among them.
Read more: http://www.seattlepi.com/news/us/article/New-England-fishermen-face-grim-vote-on-cuts-4234340.php
Scientists figure out what makes beer good for you
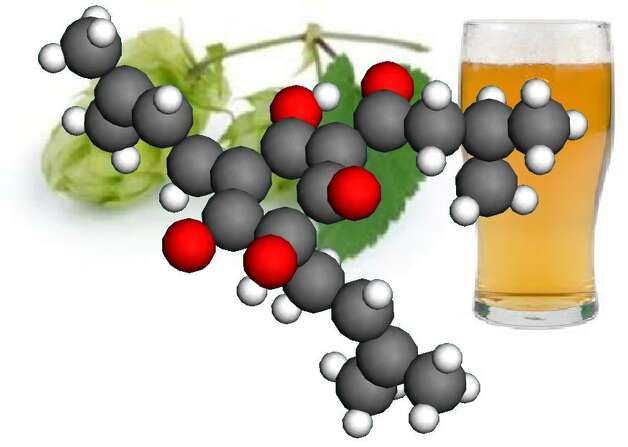
The configuration of a humulone molecule is superimposed on a hops vine and a glass of beer.
Our understanding of how hops becomes the molecules that give beer its flavor and the shape those molecules take has been wrong for 40 years, say scientists from the University of Washington.
Using a century-old technique, they've nailed down the precise structure of those molecules for the first time, overturning the long-standing assumptions. And, while beer brewers the world over are unlikely to change their recipes, the scientists hope to use the discovery to create new medicines.
"Now that we have the right results, what happens to the bitter hops in the beer-brewing process makes a lot more sense," Werner Kaminsky, a UW research associate professor of chemistry, said in a press release.
And, because beer and its bittering acids – in moderation (the school emphasizes) – have beneficial effects on diabetes, some forms of cancer, inflammation and perhaps even weight loss, knowing exactly what they become in beer means they can be used to make new pharmaceuticals.
Read more: http://www.seattlepi.com/national/article/Scientists-nail-down-what-makes-beer-good-for-you-4232757.php
The Real, and Simple, Equation That Killed Wall Street
“If it weren’t for those meddling kids!” That was the punch line for every Scooby Doo episode. It also is the overly simple narrative that many in the media have spun about the last financial crisis. Smart meddling kids armed with math hoodwinked us all.
One article, from the March 2009 Wired magazine, even pinpointed an equation and a mathematician. The article “Recipe for Disaster: The Formula That Killed Wall Street,” accused the Gaussian Copula Function.
...
The reality is much simpler and less sexy. Wall Street killed itself in a time-honored fashion: Cheap money, excessive borrowing, and greed. And yes, there is an equation one can point to and blame. This equation, however, requires nothing more than middle school algebra to understand and is taught to every new Wall Street employee. It is leveraged return.
What is leveraged return? It’s the return on assets using borrowed money.
The equation for the leveraged return, L, is:

Where Y is the return of the asset, R is the cost to borrow money, and N is the “haircut,” or the percentage of money the investor must put down to secure the loan (the down payment).
more
http://blogs.scientificamerican.com/guest-blog/2013/01/30/leveraged-yield/
Elon Musk: Boeing 787 battery fundamentally unsafe
By: ZACH ROSENBERG WASHINGTON DC
The lithium ion batteries installed on the Boeing 787 are inherently unsafe, says Elon Musk, founder of SpaceX and owner of electric car maker Tesla.
"Unfortunately, the pack architecture supplied to Boeing is inherently unsafe," writes Musk in an email to Flightglobal.
"Large cells without enough space between them to isolate against the cell-to-cell thermal domino effect means it is simply a matter of time before there are more incidents of this nature," he adds.
Both Boeing and Tesla use batteries fueled by lithium cobalt oxide, which is among the most energy-dense and flammable chemistries of lithium-ion batteries on the market. While Boeing elected to use a battery with a grouping of eight large cells, Tesla's batteries contain thousands of smaller cells that are independently separated to prevent fire in a single cell from harming the surrounding ones.
"Moreover, when thermal runaway occurs with a big cell, a proportionately larger amount of energy is released and it is very difficult to prevent that energy from then heating up the neighboring cells and causing a domino effect that results in the entire pack catching fire," says Musk.
more
http://www.flightglobal.com/news/articles/elon-musk-boeing-787-battery-fundamentally-unsafe-381627/
Profile Information
Gender: Do not displayMember since: Tue Feb 10, 2004, 01:08 PM
Number of posts: 47,953

























